An automobile engine might malfunction for a million different reasons. In the past, it was exclusively the owner’s and/or technician’s responsibility to slog through potential problems until they identified the broken or malfunctioning component. But because modern cars have advanced in intelligence (part of this intelligence is the knock sensor), they are now capable of seeing issues as they arise.
The functionality and health of a car are constantly monitored by dozens of sensors located all over it. Some measure the amounts of oxygen, air, or temperature, while others, like knock sensors, monitor vibration and sound levels to prevent the development of a piston-sized hole in the engine. Well, in this reading, we’ll explore what a knock sensor is, its functions, location, diagram, and symptoms of bad ones.
Let’s begin!
Learn about Engine Knocking with this detailed guide!
What is a Knock Sensor?
An engine knock, which is sometimes referred to as an engine ping or a detonation, is a sound and reaction that happens when there is a second spontaneous ignition or explosion inside a cylinder, independent of the normally regulated ignition from a spark plug. In other words, engine knock is terrible news. This can only happen if a few things go into place.
In essence, the flame front produced by the spark plug activation passes through the remaining cylinder space. The remaining air and fuel mixture is pressed by the movement of that flame front.
It gets hotter as a result of the increased pressure, and occasionally this might lead to a second ignition. When two reactions clash, you get knocked since the second ignition produces a second flame front.
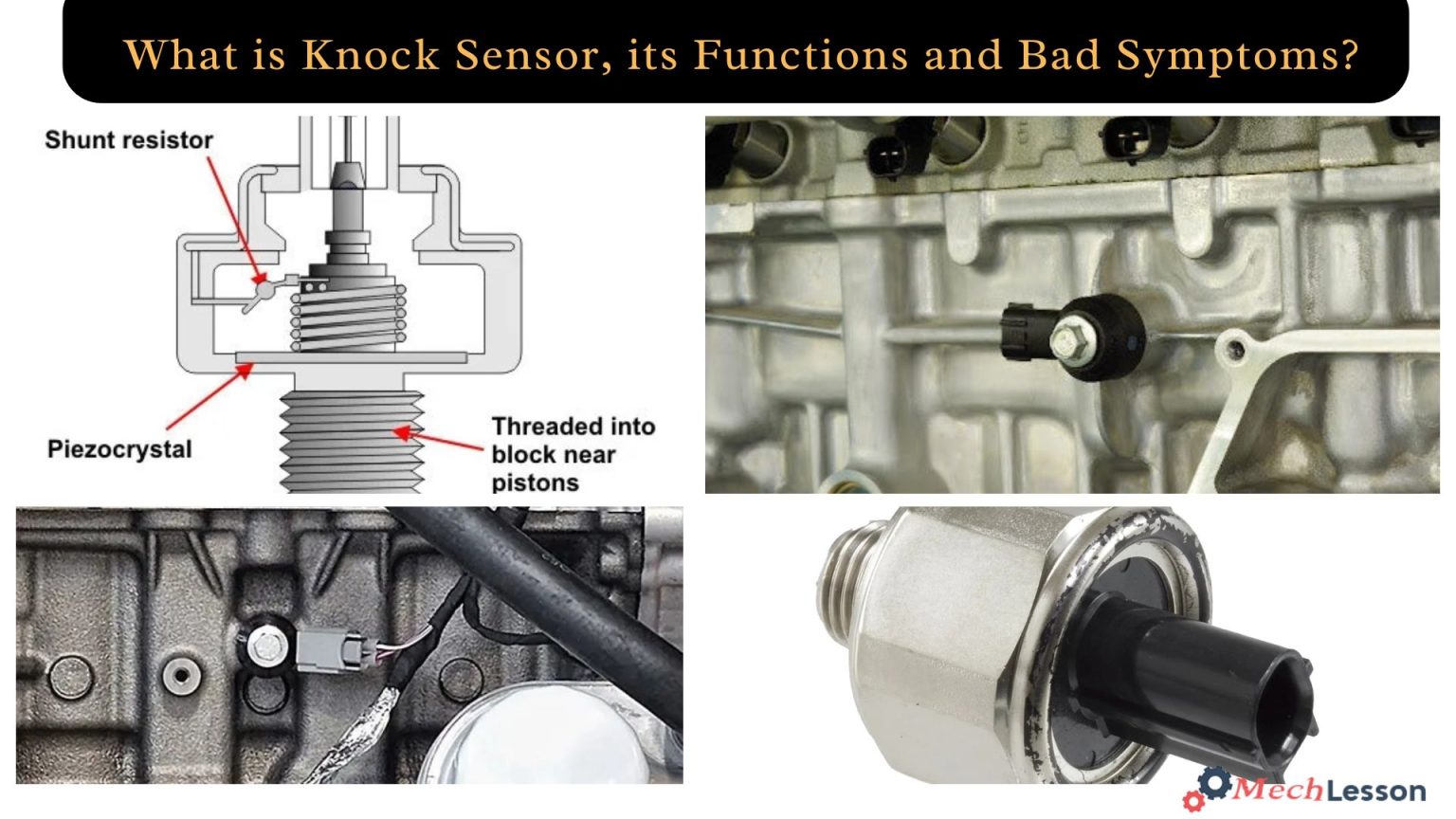
In essence, a knock sensor is a compact “listening” device inside or on top of the engine that listens for these strange vibrations and noises coming from the engine block. The combustion process in the engine is monitored by the knock sensor. Its signal aids engine control in shielding the motor/engine control from knocking combustion.
A knock sensor is usually located directly on the engine block’s exterior, but it can occasionally be found under the intake manifold.
Engine knock is a tapping sound that increases as the vehicle accelerates, depending on factors such as engine size, idling or acceleration. A knock sensor measures engine knock from vibrations and sends signals to the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) to adjust air/fuel composition if there are issues.
The knock sensor is crucial as it acts as an electronic ear against the engine, detecting potential issues and potentially damaging the engine. If there is one, it is typically bolted to the outside of the engine block, resembling the end of a stethoscope.
Most vehicles have one centrally located knock sensor, but some four-cylinder vehicles have four sensors for greater accuracy. This is to say, the knock sensor is an essential part of a vehicle’s electronic system.
Learn about Seized Engine with this detailed guide!
Function
The engine control unit (ECU) receives the signal from the knock sensor, which converts vibration and sound from the engine block into an electrical signal. After evaluating the data, the car’s computer decides whether or not to adjust the ignition timing. In an effort to protect itself from additional harm, it may also cause the check engine light (CEL) to come on or even shut down a portion of the motor.
Diagram
You should learn about LS3 and LS7 Engine with this detailed guide!
How Does a Knock Sensor Work?
Inside the knock sensor, there is a stack of paper-thin piezoelectric crystals within the knock sensor that produces electricity. Different voltage signals are sent to the ECU by the engine knock, which compresses the sensor’s crystals to various degrees. After that, the ECU may adjust the engine firing as needed to keep it going.
The knock sensor can detect nearly undetectable amounts of banging outside of an acceptable range, but human listeners may notice any significant knocking concerns.
The number of cylinders and engine technology determine how many knock sensors the engine has. A six-cylinder engine requires a knock sensor for each bank of three cylinders, but a four-cylinder engine may be measured with a single knock sensor. Although manufacturers are free to add more, this is often the bare minimum.
Modern knock sensors work on Albert Einstein’s Nobel Prize-winning discovery of the piezoelectric phenomena to detect engine knocks. Knock sensors feature crystals within that are compressed when they are struck by a shockwave from an engine knock. This works because crystals release tiny electric pulses when they are squeezed. An electrical pulse produced by that squeezing travels to the ECM through a wire. These pulses are interpreted by the ECM, which then performs the required corrections.
A particular frequency is tuned into the sensor to make it particularly sensitive. This indicates that the precise frequency at which knocks occur is when it releases the strongest pulses. This makes it easier to distinguish engine knocks from the typical noises and vibrations produced by an engine in operation.
Symptoms Of A Bad Knock Sensor
The common signs of a bad knock sensor include a check engine light, engine noise, power loss, and a decline in engine performance.
Check engine light: The engine light will come on, and an associated diagnostic problem code (DTC) will be set off when the Power train Control Module (PCM) discovers a bad knock sensor or voltage circuit.
Engine-making noise: The PCM might not be able to detect or adjust the spark knock frequency if the knock sensor fails. The engine may make a metallic pinging noise if the sensor fails. Additionally, you’ll observe that the noise is most noticeable while the engine is working under a heavy load.
Power Loss: Your car may experience power loss when the engine control unit detects a malfunctioning knock sensor. The amount of power lost depends on the engine’s maximum octane rating and its reliance on knock sensor input. High-compression and flex-fuel engines are most affected by power loss. This loss affects engine timing and prevents the transmission from engaging until the knock sensor is repaired.
Decline in Engine Performance: Engine performance may suffer as a result of the PCM incorrectly changing the ignition timing brought on by a damaged engine knock sensor. When traveling at high speed or when the car is pulling a heavy load, the engine might not feel right. Even if the check engine light is not on, you should have it checked by a certified mechanic.
You should also learn about The Symptoms of a Bad Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor with this detailed guide!
Why Do Knock Sensors Go Bad?
An engine knock can occur for a variety of reasons. Here are some possible reasons:
- Defective spark plugs
- Incorrect spark timing for ignition
- Deposits inside the cylinder (which may be caused by impurities like dirt and grime)
- Abnormally high operating temperatures for the engine
- Faulty spark plugs gaps
- Low-octane gasoline
- Incorrect knock sensor installation
- Insufficient fuel-to-air ratio
- Spark plugs of the incorrect type with deposits
- Inside the combustion chamber or chambers, a buildup of carbon
- Mechanical damage
How To Test and Diagnose a Knock Sensor?
Here is a basic troubleshooting process:
• Read the trouble code that was saved
• Verify the sensor’s proper fit and torque requirements.
• Check for proper connection, breakage, and corrosion in the electrical connections of the sensor wiring, the plug, and the sensor.
• In older vehicles, check the ignition point.
Using the Multimeter for Testing the Knock Sensor
Examine the wiring to the control unit by testing each wire at the plug for continuity and short circuits to the frame.
- Connect the ohmmeter: Place the ohmmeter in series with the removed control unit connector and the knock sensor connector. Setpoint: 1 Ohm (circuit diagram necessary for the control unit pin assignment).
- Use an ohmmeter to test the pin’s resistance to the ground: While the control unit connection is unplugged, test the corresponding pin at the wiring harness connector’s resistance to the ground using an ohmmeter. Setpoint: 30 MOhm or more.
Be aware that a connecting pin has continuity to the ground and can function as a shield.
When the engine is warm, use the oscilloscope to inspect
- Connect the test probes of the oscilloscope: Connect the oscilloscope test probes in a way that they are placed between the control unit pin for the knock sensor and the ground.
- Briefly open the throttle valve: Open the throttle valve briefly so that the oscillogram shows a signal with a noticeably larger amplitude.
- Signal not clear: Tap lightly against the engine block close to the sensor if the signal is not clear.
- Knocking is not detected: If the knocking is not recognized, there may be a sensor or circuit problem.
You should learn about Camshaft Position Sensor with this detailed guide!
How Much Does a Knock Sensor Replacement Cost?
Depending on your car and the particular repair shop you take it to, the average knock sensor replacement costs between $250 and $350. But keep in mind that this applies only if the knock sensor is broken, not if the engine is knocking.
Make sure you have an accurate diagnosis before replacing any components. By doing this, you can avoid changing the incorrect parts and wasting money.
By handling the repairs yourself, you can reduce your expenses. Depending on the vehicle you drive, an aftermarket knock sensor can cost anywhere from $20 to $100. However, keep in mind that OEM components will cost more, and if your car is still under warranty, you must use OEM parts. However, regular labor expenses for a knock sensor replacement range from $150 to $250 if a mechanic will be performing the repairs.
That’s because, depending on what you drive, it can be difficult to get to the knock sensor without disassembling other parts. You might anticipate paying more the more parts your mechanic needs to remove or workaround.
Unfortunately, that also increases the likelihood that you will first require the services of a licensed mechanic. However, you can typically save a few hundred dollars if you can complete the task yourself.
Bottom Line
The knock sensor (or sensors) in the engine can identify two potentially harmful types of aberrant combustion: preignition and detonation. Although full-fledged knocking and pinging can be heard by the human ear, the knock sensor only picks up barely audible levels.
The engine’s computer can delay the timing of the spark plugs when knocking is detected to stop it. The driver may hear banging or pinging and/or notice diminished acceleration, which is occasionally accompanied by a drop in gas mileage, in the case that the knock sensor fails. The most likely outcome is a check engine light.
You should also learn about Crankshaft Position Sensor with this detailed guide!
FAQs
What happens when a knock sensor goes bad?
The PCM might not be able to detect or correct the spark knock frequency if the knock sensor fails. The engine may make a metallic pinging noise if the sensor fails. Additionally, you’ll observe that the noise is most audible while the engine is working under a heavy load.
What does a knock sensor do?
The engine control computer then corrects the timing to eliminate the knock after receiving a signal from the knock sensor, which detects vibrations caused by a knock or an irregularity in combustion.
Can a car run without a knock sensor?
Your automobile would still be able to start even if the knock sensor was completely removed. Even while you can drive with a damaged knock sensor, it won’t pass the majority of state inspections until it is corrected and may have long-term negative impacts on your engine if there is a lot of pre-ignition.
Does a knock sensor affect fuel economy?
A defective knock sensor may prevent the engine from accelerating smoothly while traveling on the highway, resulting in decreased fuel economy.
Can a knock sensor affect gear?
Yes. A malfunctioning knock sensor will make the engine fire the spark plugs at a less-than-optimal timing, resulting in power loss. If the knock sensor were functioning properly, the transmission might utilize a different, more expensive gearing to make up for the power loss.
Can the knock sensor cause a misfire?
An engine misfire is another indicator of a malfunctioning knock sensor. This indicates a problem with the engine’s efficiency and smoothness, which could cause it to lose power, hesitate, or stall when accelerating.
What causes a knock sensor code?
Wiring in the knock sensor circuit that is harmed, frayed, or poorly connected. A bad coolant system in the engine. Fuel and air mixture that is not balanced in the engine cylinder. Faulty spark plug (while uncommon, it is nonetheless a potential cause)
What is another name for a knock sensor?
The knock sensor is known as a detonation sensor.
Can a knock sensor cause a car to stall?
A Knock sensor cannot cause a car to stall.
How many knock sensors does a car have?
If you have a v6 or v8 engine, you probably have two knock sensors instead of the typical one found in small engine vehicles. Some straight six-cylinder engines will also use a two-knock sensor setup.