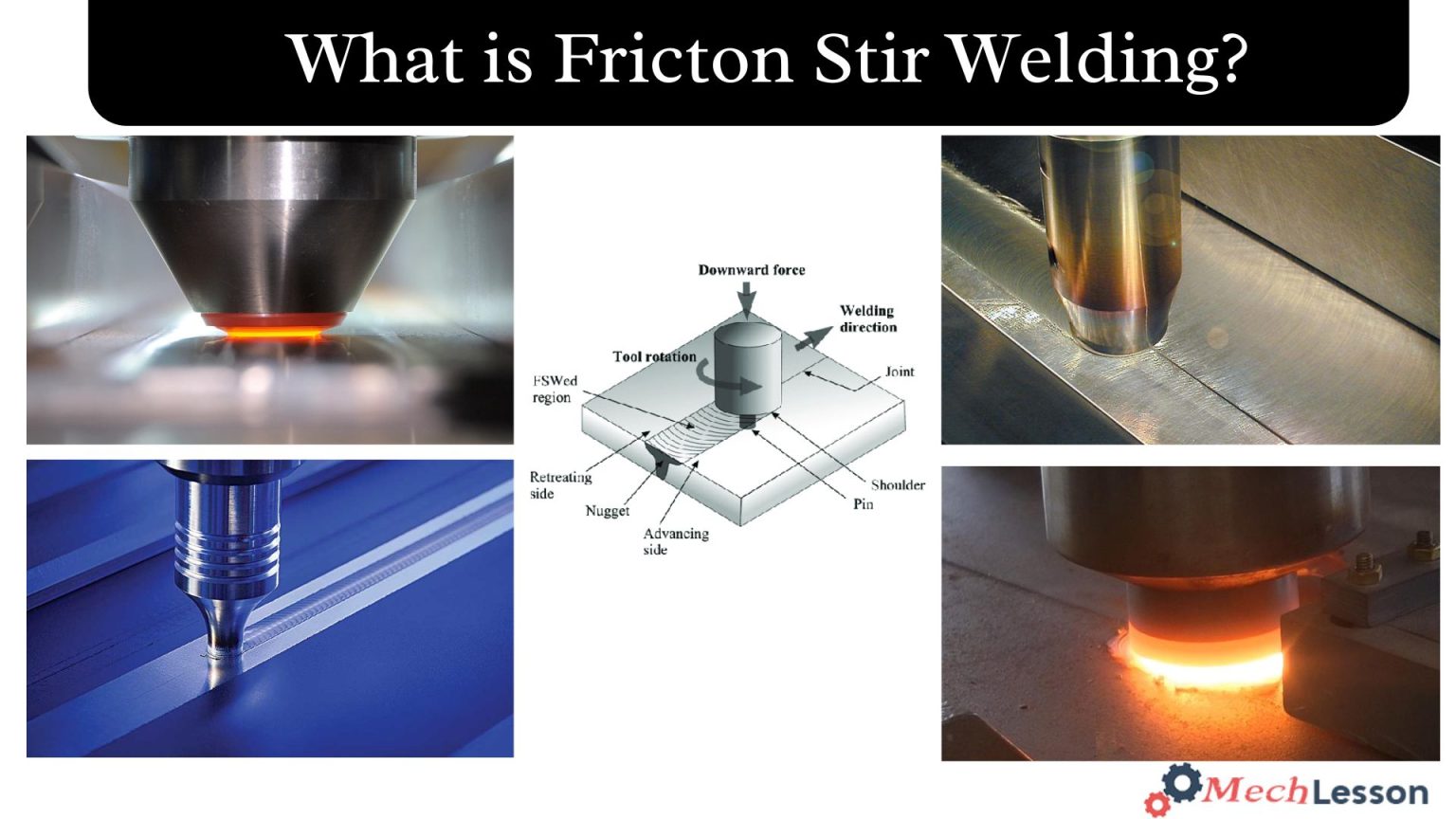
The first use of friction stir welding (FSW) occurred in 1991. It is a solid-state method of connecting two components. Parts of the metal do not melt during this procedure. Rather, the FSW tool generates heat by welding friction between the metal components, allowing the atoms of the two metal sections to fuse.
Well, in this reading, we’ll explore what fricton stir welding is, its application, diagram and how it works. We’ll also explore the advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s begin!
What is Fricton Stir Welding?
Friction stir welding is a cutting-edge method for continuously connecting materials. With FSW, two pieces of sheet or plate material are butted together, and a cylindrical, shouldered tool with a profiled probe is rotated and slowly inserted into the joint line.
In order to avoid forcing the faces of the abutting joints apart during the welding process, the components are secured. The materials to be connected and the wear-resistant welding equipment produce frictional heat.
This heat softens or melts later, allowing the instrument to move along the joint line. The plasticised material is moved from the tool probe’s leading edge to its trailing edge, where it is forged by the tool shoulder’s close contact to create a weld between the two components.
Application
Friction Stir Welding Applications in Different Industries:
Automotive Industry:
- Uses FSW for motors, battery pack boxes, engine frames, DC/DC converters, and airbag inflators.
- FSW welding allows easy welding of fully loaded airbag inflators due to its narrow heat-affected zone.
Network and Communication Industry:
- Requires FSW for joining telecommunication device parts and 5G communication components.
- FSW companies worldwide manufacture parts for this industry.
Aerospace Industry:
- Uses FSW for joining low compression rotors and cluster gear in aerospace.
Marine Industry:
- Speeds up construction on marine projects, saving time and increasing profits.
- Needed in flooring, decks, bridges, seawalls, panels, bulkheads, walkways, etc.
Agricultural Industry:
- Needed for water pumps, water pump gear, and diesel engines.
- FSW companies significantly reduce costs for agricultural components.
Diagram
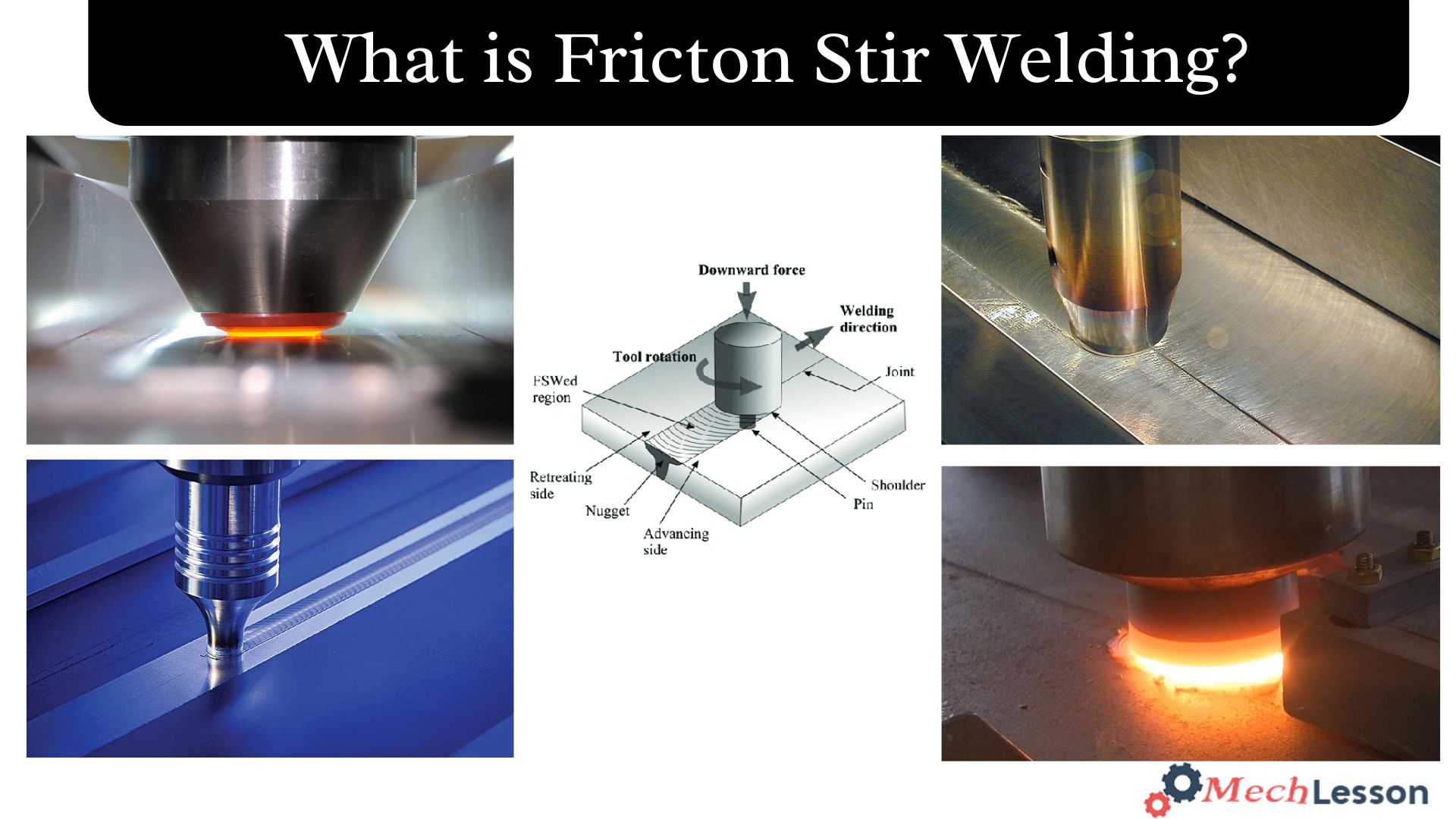
How Fricton Stir Welding Works
Friction stir welding is performed with a rotating cylindrical tool that has a profiled pin (also known as a probe) having a diameter smaller than the diameter of its shoulder. The tool is inserted into a butt joint between two clamped workpieces during the welding process until the probe pierces the workpiece and its shoulder makes contact with the workpiece’s surface.
The tool shoulder rides atop the work surface, and the probe is somewhat shorter than the necessary weld depth. The tool is pushed forward along the joint line at the predetermined welding speed following a brief dwell period.
The work components and the wear-resistant tool create frictional heat. Stirred materials soften without melting due to this heat, as well as heat produced by the mechanical mixing process and adiabatic heat within the substance.
A unique probe profile pushes plasticised material from the leading face to the back as the tool advances, where the strong pressures help create a forged consolidation of the weld. A severe solid-state deformation, including dynamic recrystallisation of the base material, is the consequence of the tool moving along the weld line in a plasticised tubular shaft of metal.
Advantages
These are the following advantages of fricton stir welding as follows:
- Its good mechanical properties in as-welded condition.
- Its improved safety is due to the absence of toxic fumes or molten material spatter.
- There are no consumables required; a threaded pin made of conventional tool steel can weld over 1 km of aluminium.
- It’s easily automated on simple milling machines – lower setup costs and less training.
- It’s an operation in all positions due to no welding pool.
- Its generally good weld appearance and minimal thickness under/overmatching.
- It can use thinner materials with the same joint strength.
- It has low environmental impact.
- Its general performance and cost benefits from switching from fusion to friction.
Disadvantages
- It left an exit hole when the tool was withdrawn.
- It requires large down forces for heavy-duty clamping.
- It’s less flexible than manual and arc processes.
- Its often slower traverse rate than some fusion welding techniques.
FAQs
What is meant by friction stir welding?
Friction stir welding (FSW) is a solid-state joining process that uses a non-consumable tool to join two facing workpieces without melting the workpiece material. Heat is generated by friction between the rotating tool and the workpiece material, which leads to a softened region near the FSW tool.
What are the benefits of friction stir welding?
Advantages of FSW
There is a shrinkage reduction because of the lower temperature. Decreasing the requirement of highly skilled workers (welders) and needed limited operator training. FSW does not suffer from gas porosity owing to the solid-state technique, and there is no requirement of post-machining for FSW parts.
What is friction stir welding analysis?
Friction stir welding is one of the most modern methods of joining metals and their alloys in the solid state [1]. However, ensuring the constancy of the performance of the joints requires the optimal choice of welding-process parameters, i.e., tool speed and feed rate [2].
Does SpaceX use friction stir welding?
Today SpaceX is actively developing the technologies to make this possible, with the ultimate goal of enabling human life on Mars. RESPONSIBILITIES: Set up and operate large, motion-controlled machines to create friction stir welds on launch vehicles.