Hey technician, auto students, and curious drivers who have always wanted to learn about the fuel injection system. The truth is, manufacturers have replaced carburetors with a system due to its effectiveness and precision, so if you are driving a newer car model, your vehicle might be delivering fuel into the combustion chamber using the fuel injector.
As an auto technician with over a decade of experience, I have serviced and replaced more than 400 clogged fuel injectors, so i know in and out of the part.
So, in this reading, we’ll explore what a fuel injection system is, its functions, parts, types, and how it works. We’ll also learn its advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s begin!
Related: Difference Between Fuel Injection And Carburetor
What Is A Fuel Injection System?
The fuel injection system detects the amount of air that enters the engine and gives the necessary fuel for combustion. An ECU controls the amount of fuel injected and the duration for which the fuel injection valves (injectors) remain open. The ECU calculates the fuel injection amount based on signals from a sensor that measures the air intake.
Before the existence of fuel injectors, carburetors were highly used on engines, and to date, this engine still exists. In fact, many other machines, like lawnmowers and chainsaws, still use carburetors. But because the component got complicated trying to control all requirements on automobiles, a better alternative is released.
Furthermore, throttle body fuel injection systems were the first to replace carburetors. This system is also known as a single-point or central fuel injection system. It has electrically controlled fuel injection valves in the throttle body.
This alternative was nearly optimal, enabling auto manufacturers to avoid drastic modifications to engine designs. Gradually, as new engines were designed, multi-port fuel injection replaced the throttle body fuel injection. This multi-port fuel injection is also known as port, multi-point, or sequential fuel injection.
In addition, the system contains a fuel injector for each cylinder, which sprays right to the intake valve. It provides more accurate fuel metering and quicker response. Watch the video below to learn more about the working fuel injection system in a car:
Functions Of Fuel Injection System
The fuel injection system performs a notable function in a car. Below are the system’s common functions:
- The main purpose of fuel injection systems in diesel engines is that the components have a significant impact on their design.
- Fuel injectors help deliver fuel to cylinders.
- It enhances the engine in terms of performance, emission, and noise characteristics.
- Fuel is delivered under extremely high injection pressures.
- Its materials are designed to withstand higher stresses for durability that matches the engine working.
- The injection system also aims to inject fuel at the appropriate time. In other words, the system controls the injection timing.
- The correct amount of fuel must be delivered to meet the engine’s power requirements. This is why the injection metering is controlled.
- We manufacture injectors with greater precision and tolerance to ensure their working efficiency. It also avoids leakage.
- The fuel injector atomizes fuel into a tiny fuel particle, ensuring every small droplet of fuel vaporizes and undergoes the combustion process.
- There is enough oxygen to mix with the atomized fuel, which ensures complete combustion.
Related: What is Fuel Induction Service And Its Cost?
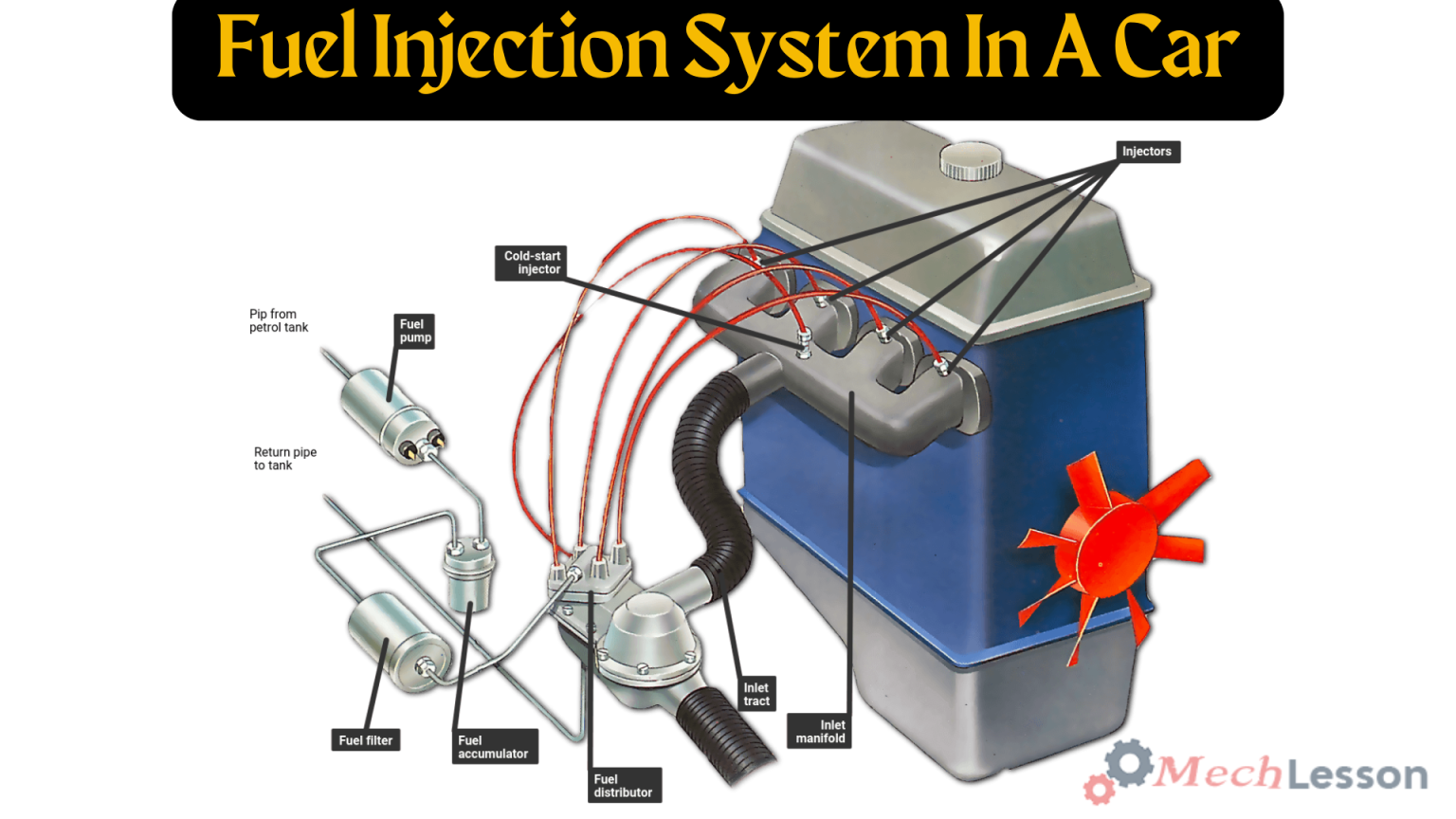
Diagram Of A Fuel Injection System

Parts Of Fuel Injection System
The fuel injection system consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in delivering the right amount of fuel to the engine. Here are the main parts:
Fuel Tank
Fuel goes into your fuel tank when you pump it. The tank holds fuel before it’s injected into the combustion chamber.
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump is a component that is located inside the fuel tank. Modern cars often feature the pump in their fuel tanks. The fuel pump is responsible for pumping fuel into the engine.
And the car’s battery is most likely what powers an electric pump mounted on the fuel tank. However, when the pump is outside, the motor’s movement powers it.
Fuel Filter
A working fuel delivery system depends on the fuel filter. This requirement applies more to fuel injection than carbureted cars. Dirt can damage fuel injectors due to their close tolerances, but fuel-injected cars use electronic fuel pumps.
The electric fuel pump burns itself trying to push past a clogged filter. Cars usually have two filters. There is one filter located in the gas tank and another at the fuel injectors or carburetor.
Unless a severe and unique issue causes a lot of dirt to enter the gas tank, only the line filter needs replacement.
Fuel Lines
Steel lines and flexible hoses transport fuel from the tank to the engine. Copper or aluminum cannot be used to service or replace steel lines. Replace steel lines with steel. Use the right hose when replacing flexible rubber hoses.
Ordinary rubber, such as that used in vacuum or water hoses, softens and deteriorates. Keep all hoses away from the exhaust.
Fuel Injectors/Carburetors
The fuel injector is the final point for fuel delivery in your engine before it ignites within the combustion chamber. An electrically driven gate opens just long enough to give the engine the right amount of fuel. Most cars used carburetors until the late 1980s.
Manual, non-electric carburetors mix vaporized fuel with air to create a combustible or explosive mixture for internal combustion engines. Electronic fuel injection has replaced carburetors.
Related: What is Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor? Its Functions And Location
Intake Valve
The valve opens to draw air/fuel into the combustion chamber. Deposits on the intake valves can limit or alter the flow of air/fuel into the combustion chamber. Deposits on the intake valve might prevent fuel from entering the combustion chamber. The appropriate fuel additive can help restore performance.
Throttle Body
This part regulates the air entering the engine, controlling engine power and speed.
Combustion Chamber
The air/fuel mixture burns here. Combustion chamber deposits may have an impact on air/fuel compression and heat transmission. Excess heat might lead to early ignition and knocking. Some vehicles have knock sensors to detect engine knocks or pre- or post-detonations.
These sensors allow the computer to detune the engine to eliminate this performance-degrading condition. It’s crucial to clean your fuel system since deposits cause knocking.
Piston
The pressure from combustion is converted into motion via the piston’s up-and-down motion. Effective detergent additives can decrease or eliminate deposit-related drivability and performance loss.
Engine Control Unit (ECU)
The ECU manages the fuel injection process by adjusting the timing and amount of fuel injected in response to engine conditions.
Related: What Is A Carburetor? Its Function and How It Works
Types of Fuel Injection Systems
Fuel injection systems can be classified into several types based on their design and operation. Here are the main types:
Single-Point or Throttle Body Injection
The single-point type of injection system is the earliest and simplest fuel injection that replaces carburetors. It contains one or two injector nozzles in the throttle body, which is the throat of the engine’s air intake manifold. This injector system is not as precise as the system that followed, but when compared with carburetors, it has better control, is less expensive, and is easier to service.
Port or Multiport Fuel Injection
Each cylinder in a multiport fuel injector houses separate injector nozzles at its intake port. This is why the system is sometimes called a port injector, shooting the fuel vapor close to the intake spot, ensuring it’s completely drawn into the cylinder.
This injector’s meter is more precise than the single point’s. It is also perfect for achieving the required fuel-air ratio, and it virtually eliminates the possibility that fuel will condense or collect in the intake manifold.
Sequential Fuel Injection
This type of fuel injector is also known as a sequential port fuel injection or a timed injection. It is a type of multiport injection, even as basic multiport uses multiple injectors.
The injectors spray fuel either simultaneously or in sequence, causing the fuel to linger for up to 150 milliseconds when the engine is idling.
The benefits of sequential fuel injection are that the system responds more quickly if the driver makes a sudden change. The valve only has to wait for the next intake valve to open, not the engine’s full revolution.
Direct Injection
Direct injection is common in diesel engines, although it is starting to be prevalent in gasoline engine designs. We sometimes refer to it as DIG, which stands for direct injection gasoline.
The process injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber, bypassing the valves. Fuel metering is more precise than other fuel injection types. Direct fuel injection gives engineers another variable to influence precisely how combustion occurs in the cylinders.
The science of engine design examines how air-fuel mixture swirls around in the cylinders. Additionally, it studies the path of the explosion from the ignition point. Direct injection in a gasoline engine can handle things such as the shape of cylinders and pistons.
Also, port and spark plug locations, timing, duration, and intensity of the spark. Number of spark plugs per cylinder. All these affect how completely and evenly fuel combusts in a gasoline engine.
Related: What is Fuel Pump? its Functions, Types and How it Works
How A Fuel Injection System Works
The working of a fuel injector system is fascinating and easier to understand. The main work is from the fuel injector to the combustion chamber after fuel is pumped to it from the fuel tank.
As earlier said, the fuel injector is an electronically controlled mechanical device that is responsible for fuel spraying. The injector gets energized and an electromagnet moves a plunger that opens the valve.
This valve allows the pressurized fuel to squirt out through a tiny nozzle. The nozzle’s design atomizes the fuel, facilitating its easy combustion. The amount of time the fuel injector stays open will determine the fuel supplied to the engine.
Additionally, an ECU device is in charge of controlling this, which is known as “pulse width.” Fuel injector systems are mounted directly to the intake manifold so that fuel can be sprayed directly into the intake valve.
There is a spring inside the conventional injector that holds the needle valve in a closed position. It holds this needle valve until the high-pressure line meets a specific value.
There is a pipe called a “fuel rail” that supplies pressurized fuel to the injectors. The right amount of fuel is supplied to the required parts.
Sensors installed in various engine parts inform the ECU about the fuel level and allow for necessary adjustments. The various sensors have been listed and explained in the above part of this article.
Advantages
Below are the benefits of the fuel injection system:
- A precise fuel mixture of fuel and air ensures maximum possible fuel efficiency and power production.
- The combustion process is significantly more efficient in fuel-injected engines.
- Fuel injection engines are more economical, and they maximize and minimize the emission level.
- Cold starting is eliminated in fuel-injected engines, making manual choking unnecessary.
- It’s also used on modern performance motorcycles.
- The fuel injection system automatically balances the air-fuel mixture considering the environmental situation.
- Engine vibration is reduced, and the issue of spark plug fouling is minimized.
Related: Symptoms of Leaking and Clogged Fuel Injector
Disadvantages
Despite all the benefits of the injection system, some limitations still occur. Below are the disadvantages of the system:
- It is a complex, electronically controlled device that works with few electronic sensors.
- Maintenance and repair of the system are very limited. That is, not all workshops can do their work.
- The fuel injection system is costly.
- Good-quality material and fuel are highly recommended.
- There is no solution for low cost and low capacity.
Conclusion
The fuel injection system is the heart of modern engine performance, delivering the right amount of fuel at the right time for efficient combustion. Unlike older carburetors, fuel injectors offer better fuel economy, reduced emissions, smoother acceleration, and improved reliability. Whether it’s multi-port, direct, or throttle body injection, each type is designed to maximize power while minimizing waste.
Understanding how your fuel injection system works helps you spot early signs of trouble and ensures you keep your engine running at its best. With proper maintenance, like using clean fuel, replacing filters, and servicing injectors when needed, your car will reward you with reliable performance and long-term efficiency.
If you found this explanation helpful, don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe for more simple breakdowns of how your car works!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Fuel Injection System
What is the main function of a fuel injection system?
It delivers the correct amount of fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber at the right time for efficient burning.
How is fuel injection better than a carburetor?
Fuel injection provides more precise fuel delivery, improving fuel economy, reducing emissions, and enhancing engine performance compared to carburetors.
What are the common types of fuel injection systems?
The main types are single-point (throttle body injection), multi-point injection, direct injection, and sequential injection.
What are symptoms of a bad fuel injector?
Poor fuel economy, engine misfires, rough idling, difficulty starting, reduced power, and the smell of unburned fuel are common signs.
How often should fuel injectors be cleaned?
Generally, every 25,000 to 30,000 miles, but this can vary depending on fuel quality and driving conditions.
Can I drive with a faulty fuel injector?
Yes, but it’s not recommended. A bad injector can cause poor performance, damage the catalytic converter, and increase fuel consumption.
How much does it cost to replace a fuel injector?
Replacement costs typically range from $150 to $400 per injector, depending on the car make, model, and labor costs.