Surprisingly, the oil pump circulates oil in an internal combustion engine. The oil pump is a part of an engine lubrication system that pumps oil under pressure. It pumps oil from the sump through the galleries to the rotating bearing, the sliding pistons, and the engine’s camshaft.
The system’s primary purpose is to pressurize lubricating oil to circulate within the engine’s moving parts. The pumped oil also maintained the temperature of the engine. In this reading, we’ll explore what an oil pump is, its functions, diagram, types, and how it works.
Let’s begin!
Related: What is Fuel Filter? Its Functions and How it Works
What Is an Oil Pump?
The oil pump is a mechanical device that is used in an engine to circulate oil to moving parts like bearings, camshafts, and pistons to avoid wear and tear on the parts. It is one of the essential parts of an engine lubrication system that must not go wrong or be faulty; otherwise, a breakdown will occur.
An internal combustion engine component called the oil pump distributes engine oil under pressure to the engine’s camshaft, sliding pistons, and rotating bearings. This helps cool the engine, lubricates the bearings, and permits the use of fluid bearings with a larger capacity.
Pressurized oil is increasingly being used as a hydraulic fluid to power tiny actuators in addition to its basic usage for lubricating. The use of hydraulic tappets in camshaft and valve actuation was among the earliest noteworthy applications in this manner.
Variators for variable valve timing systems or the tensioner for a timing belt are two newer applications that have become more widespread.
Function Of An Oil Pump
The functions of an oil pump in an automobile include
- Transferring oil to the essential parts of the engine under pressure.
- Ease movement of the engine lubricant around the engine.
- Offers direction to the movement of the oil through the galleries to various parts.
- It helps return the hot oil to the coolant oil in the reservoir.
- Keeps the oil circulation within the engine constant.
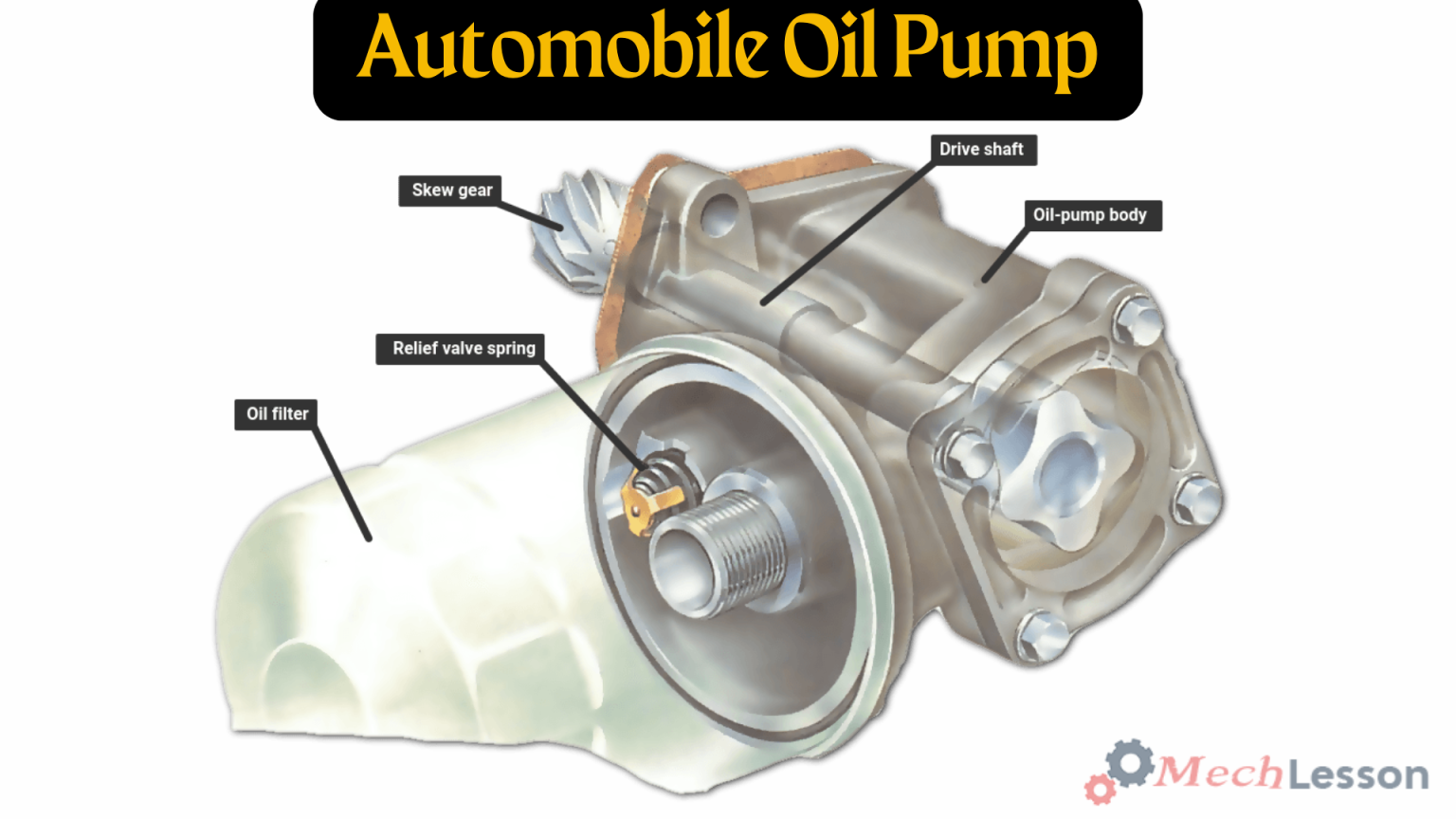
Diagram Of An Oil Pump

Related: What is Coolant Temperature Sensor? Its Location & How It Work
Types of Oil Pump
Below are the three types of oil pumps used in engines and how they work:
Rotor oil pump
A rotor type of oil pump is also called a gerotor pump. It contains an inner gear that turns inside the outer rotor. The inner rotor features one less lobe than the outer one, and it’s mounted slightly off-center of the outer rotor. This forces the outer rotor to spin at about 80% of the speed of the inner gear.
Twin Gear Pump
The twin-gear pump is also known as an external pump. The engine mounts the twin-gear pump inside its oil pan. It pumps oil using two intermeshing gears. The first gear drives a shaft, and the first gear drives the second gear. The shaft that drives the first gear is usually connected to the crankshaft, camshaft, or distributor shaft.
Front-cover oil pump
The front-cover oil pump is also known as an internal or external pump. It’s often mounted in front of the engine cover. It operates similarly to a rotor pump, which uses an inner drive gear and outer rotor. In this case, the inner drive is mounted directly on the crankshaft.
How An Oil Pump Works
From a strainer, oil passes into the oil pump and then flows through the heat exchanger, where it’s cooled. The cooled oil then flows through the galleries to the moving parts of the engine before returning to the sump. If an engine is designed with an injector, a small portion of oil is diverted to it.
The oil that is injected into the cylinder seals the space between the cylinder wall and the piston rings. This seal prevents the compressed air from escaping through the pistons, which increases the overall efficiency of the engine. An engine’s oil pressure generates up to 10 psi per 1000 revolutions per minute (rpm), which is about 55–65 psi.
The relief valve on the relative pump sets a pressure limit of 50 or 60 psi, but the crankshaft journal and bearing are subject to much higher pressures that can reach hundreds of psi.
The relative speeds of the crankshaft journal in feet per second, not rpm, are what generate this high pressure. The bearing, bearing width, oil viscosity, and temperature are considered in balance with the bearing clearance (the leakage rate).
Related: What Is An Engine Lubrication System? Its Functions And Parts
Common Failures on Oil Pump
The failure of an oil pump could cause serious damage to a vehicle, especially if the driver did not know its failure symptoms. Drivers are notified of an engine problem by the oil light indicator on the car’s dashboard, which turns on to alert them. Below are the symptoms of an oil pump failure:
Low Oil Pressure
A faulty or worn oil pump won’t be able to properly pump oil through the system. The failure will result in low oil pressure and could cause damage to the engine. Although there are several symptoms of low oil pressure, as stated earlier in this post,
Increased Engine Working Temperature
oil acts as a cooling agent in a vehicle’s engine as it reduces friction. The engine will be at normal temperature when the pump is in excellent condition and the flow of oil is constant. However, hot oil that cannot flow continues to lubricate the parts when the engine oil flow is slow or stopped.
Noise
A hydraulic lifter in a vehicle begins to make noise if it is not properly lubricated. When the oil pump is in good condition and the oil circulates properly, these lifters tend to be silent. The lifters are costly to replace, which is why it’s important that engines never lack oil.
Conclusion
The oil pump is a critical component of an engine’s lubrication system, responsible for circulating oil under pressure to all moving parts. This ensures that components stay lubricated, reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing engine wear.
A properly functioning oil pump is essential for maintaining engine health and performance. Regular maintenance and attention to oil levels can help detect potential oil pump issues early and prevent major engine damage.
Related: What Is Wet and Dry Oil Sump System? How They Work
FAQs on Oil Pump
What is the main function of the oil pump?
The oil pump circulates engine oil under pressure to the bearings, pistons, and camshaft, ensuring all moving parts are properly lubricated.
What are the signs of a failing oil pump?
Common signs include low oil pressure warning lights, engine overheating, unusual noise from the valve train, or a drop in overall engine performance.
Can you drive with a bad oil pump?
No, driving with a bad oil pump can cause severe engine damage within minutes due to lack of lubrication.
What causes an oil pump to fail?
Causes include wear and tear over time, oil contamination, clogged oil passages, or lack of proper oil maintenance.
How much does it cost to replace an oil pump?
Oil pump replacement can cost anywhere from $400 to $1,200, depending on the vehicle make and labor involved.
How often does an oil pump need to be replaced?
Oil pumps typically last the lifetime of the engine if regular maintenance is performed, but they may need replacement if they show signs of failure.