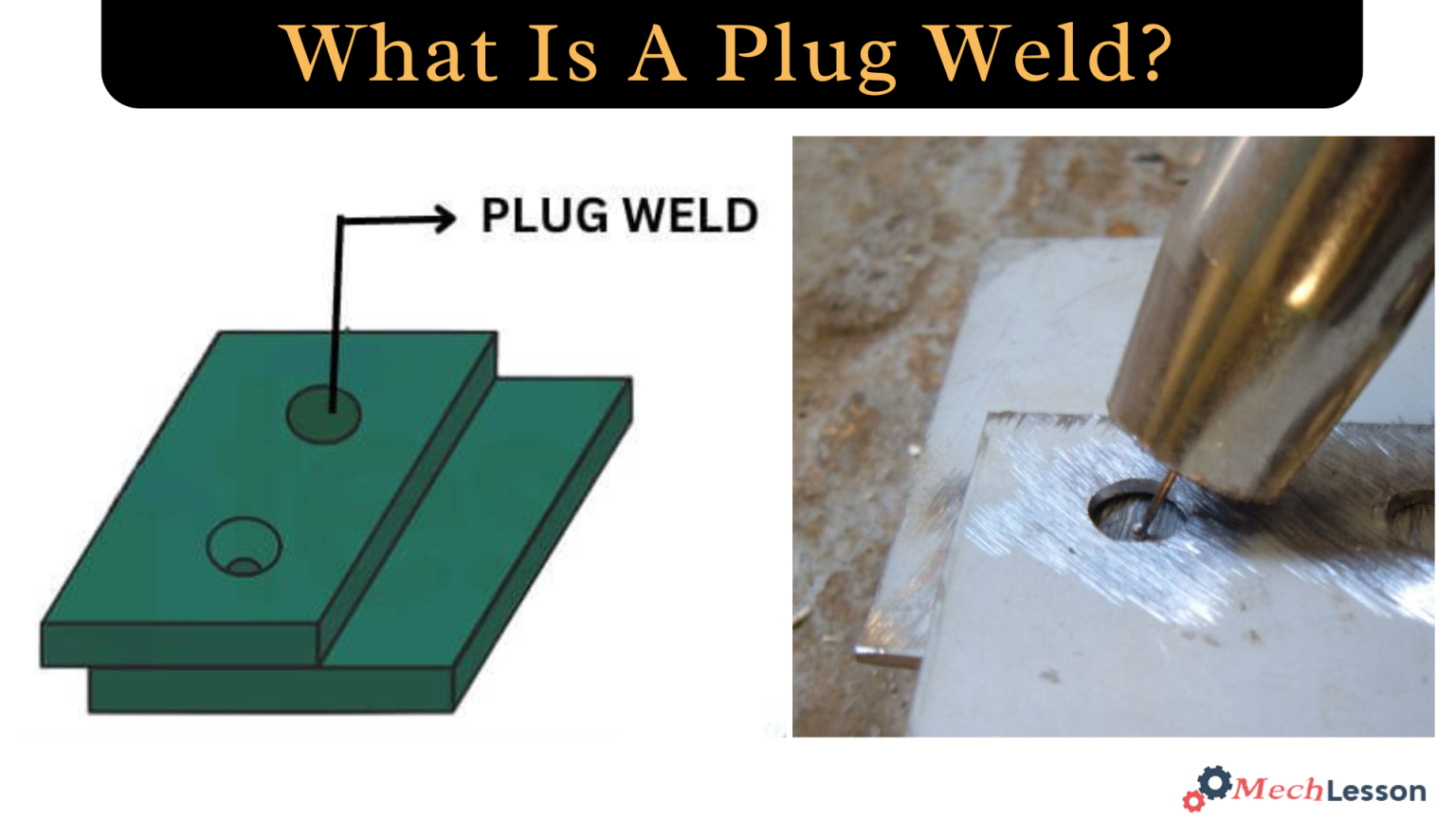
A plug weld is a welding technique where a weld is made inside a circular hole in one piece of metal, joining it to another piece; it is often used as an alternative to spot welding when access is limited or for stronger joints.
In this reading, we’ll explore what a plug weld is, its process, symbol, diagram, mistakes, benefits, and how it works.
Let’s get started!
Read about Fricton Stir Welding with this detailed guide!
What Is Plug Weld?
Plug weld is used to join two metals together by creating a weld inside small circular holes. Usually, this involves two metal sheets or sections that overlap, with the holes in the top one. The weld connects the two workpieces by filling the hole in the topmost material. It is sometimes called a rosette weld.
Plug welding creates a circular weld like spot welding, but it can be used when spot welding is difficult due to angles or space. In places where spot welds are unusable, plug welds can be stronger and a good substitute.
Plug Weld Application
There are several applications for plug welding. This weld joins metal sheets, welds a rod inside a pipe, and fastens exhaust pipes to cars. The automotive industry uses plug welding to install new floor pans in older vehicles. This process involves drilling small holes around the perimeter of the new pan.
Plug welding was frequently used to repair spot welds. In the 1960s, hot rod enthusiasts would remove the original spot welds from their wheel hubs, reverse the hubs, and then reattach them using plug welds.
This produced deep-dished wheels that were then chrome-plated or painted. Plug welding is often utilised in building projects to join metal support bars and beams. When spot welding is not feasible due to access issues, plug welds are utilised as an alternative method.
Process Of A Plug Weld
There are five steps in the plug welding process, which are as follows:
Preparing Workpiece:
It is essential to first clean the workpieces in order to prevent any faults that may occur during the welding process.
Marking:
Then, on the top workpiece (often the thicker one), mark where you want your plug welds placed. If you are using more than one, make sure they are uniformly spaced.
Drilling:
After marking the weld positions, the next step is to create the holes that the plug welds will fill. This is usually done by drilling the top piece. The size of the holes depends on the size of the pieces being joined. For example, 7.5mm holes should be big enough for 0.8 or 1mm sheets, while larger holes are needed for bigger sheets.
Clamping:
A plug weld clamp is essential for holding the metals together and preventing them from moving when welding.
Welding:
Read about Tack Welding with this detailed guide!
The plug weld is the final stage, which necessitates practice and experience to acquire. Most welders say to start by welding around the hole’s edge at an angle to make sure the metal joins together, just like with a fillet weld.
After securing the outer edge, you can finish the weld by working in circles toward the centre. This method increases the weld strength and lowers the possibility of a flaw by allowing the bottom and top metals to reach the same temperature.
More skilled welders, on the other hand, can start in the centre of the circle and watch how the weld pool flows to make sure the backplate is well penetrated.
Plug Weld Symbol
Plug weld symbols are used by welders to indicate the amount, diameter, locations, and spacing of the holes that need to be drilled. In addition to the amount of fill that is needed (in fractions of an inch), these symbols may also show the angle of the countersink for the plug weld holes.
Other information, including how the components are to be finished, which side they should be done on, and whether contouring is necessary, may also be included in the symbols. The purpose of these symbols is to help welders comprehend and adhere to standards.
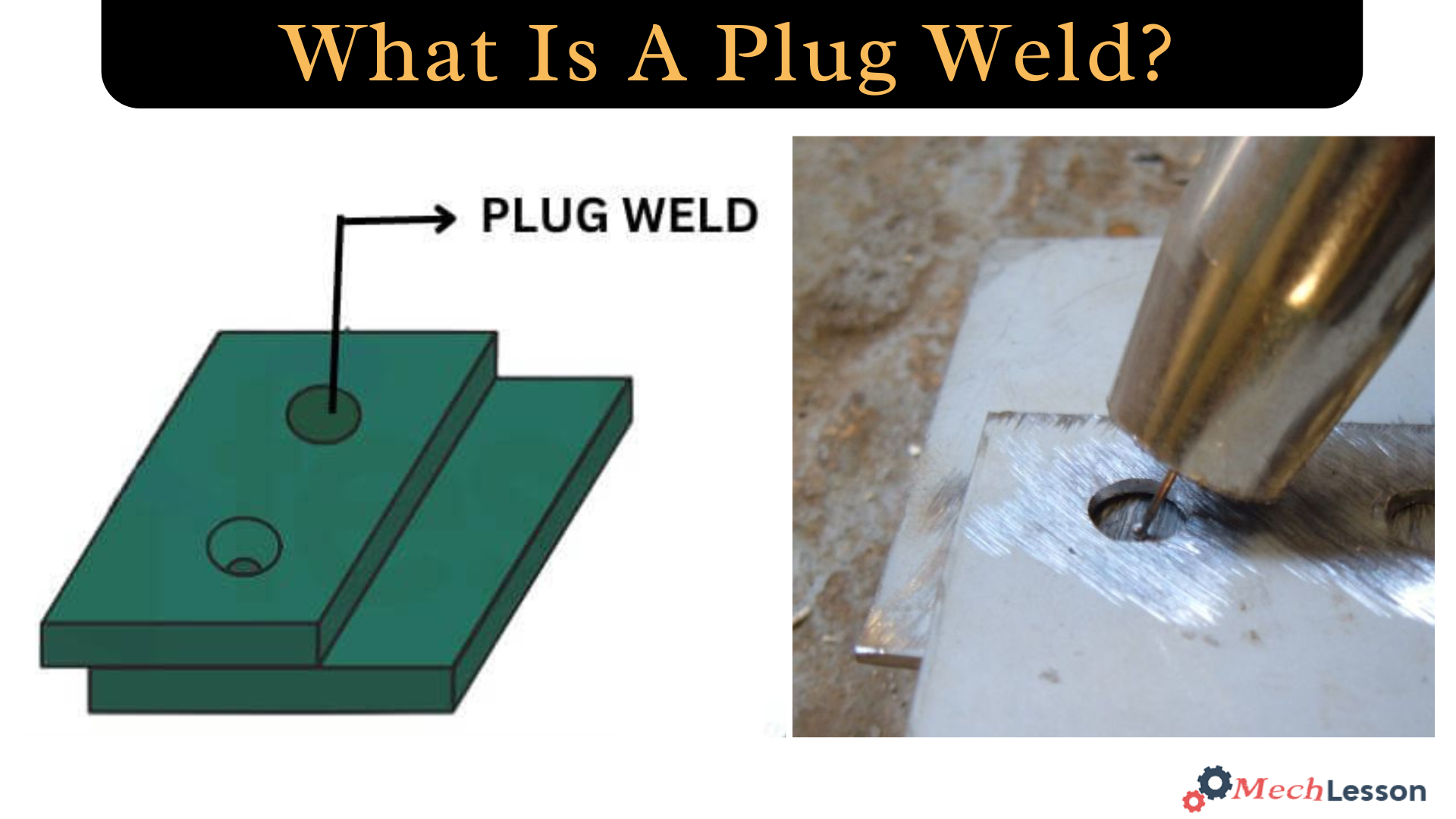
Diagram Of A Plug Weld
You should also read about Spot Welding with this detailed guide!
How Does A Plug Weld Work?
A plug weld joins two pieces of metal by welding a circular weld through a hole in the top piece, effectively “plugging” the hole and connecting it to the underlying piece. A hole is drilled or punched in the top piece of metal, which is then placed over the bottom piece. A weld is then made by running a bead inside of the drilled hole, thereby holding the two pieces together.
Common Mistakes In Plug Weld
When creating the plug weld, a common mistake is to make the welding holes in the metal piece too big. Mistakes like not cleaning the metals thoroughly enough or washing them too much can cause the hole to burn away when you begin to weld.
If you burn the metal sheets or pieces too much, the integrity of your final weld may be compromised. Also, you could over-penetrate or overfill the weld hole. Overfilling is easier to fix, though.
You need to make sure the hole is deep enough to make a strong bond but not so small that it will burn through when you start welding. If you are trying plug welding for the first time, it is most generally advised that you practice drilling the holes for the plug weld on a spare piece of metal.
Benefits Of Plug Weld
There are many benefits associated with plug welding, including the following:
Speed:
The plug welding method is a quick one, which might result in time savings during the manufacturing process.
Portable:
The portability of plug welding equipment makes it an excellent choice for operation in areas that are difficult to access.
Read about Welding Spatter with this detailed guide!
Versatile:
This process is versatile because it can be used on aluminium, steel, and stainless steel.
Strength:
Plug welds penetrate deep into the metal, creating strong joints for heavy-duty parts.
Straightforward:
Plug welding is a skill that new workers may pick up fast because of how simple it is to learn.
Clean And Safe:
The process of plug welding is comparatively clean and necessitates minimal cleanup after completion. Additionally, there is no requirement for preheating, which results in minimal fumes or smoke. Plug welding is a safer method of welding than other methods since it does not use open flames or sparks, and it also generates a very low amount of heat.
Cost Effective:
Plug welding is a process that is less expensive than other welding methods since it does not require a significant amount of material or electricity.
Drawbacks Of Plug Weld
Plug welding has several drawbacks, the most significant of which is that it might result in welds of low quality if their application is not done appropriately.
Some examples of this include joints that are not filled properly, spaces between the welded components that weaken the connection, seams that are not sealed properly because the rod was too small, joints that are weak because the rod was too big, using too much filler material, or not applying enough pressure.
Read about Orbital Welding with this detailed guide!
FAQs
What are plug welds?
Plug welds are a type of weld where a round weld is made inside a hole in one piece of metal, joining it to another piece.
When are plug welds used?
They are used when there is insufficient space for spot welding equipment or when a stronger joint is needed than spot welds can provide.
Are plug welds stronger than spot welds?
Generally, properly executed plug welds are stronger than spot welds because they provide a larger area of the weld, and the weld is placed within the metals themselves.
What materials can be plug-welded?
Plug welding is possible on steel and aluminium, but aluminium requires special preparation to remove the oxide layer.
What is the plug weld symbol?
The plug weld symbol is a rectangle with a diameter symbol placed to the left of the symbol, along with the number associated with that diameter.