Hey, gearheads, let’s talk about a very interesting topic in the automobile industry today: power steering. As a technician, auto student, or just a DIY learner, today i’ll be explaining what power steering is in a car, its functions, types, diagram and how it works. I will also be listing their advantages and disadvantages along with their FAQs
As a professional in this auto field, I have get my hands dirty with more 28 power steering in my autoshop and they all have almost different issues. With this experience am sure i can extensively discuss this topic in this platform. So, stick with me!
Let’s begin!
You should learn about Car Suspension System with this detailed guide!
What is Power Steering?
Power steering is a system in vehicles that uses engine power to assist the driver in steering, making it easier to turn the steering wheel, especially at low speeds or when parking. It works through hydraulic or electric power steering systems.
Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS) uses a pump to pressurize fluid, which acts on a piston to turn the wheels, while Electric Power Steering (EPS) uses an electric motor to provide assistance instead of hydraulic pressure.
The power steering system has progressed since it was first introduced. Electric power-assisted steering devices are available nowadays. It still includes a hydraulic pump to move fluid, but unlike earlier models, it no longer absorbs engine energy. Instead, the fluid is pressurized using an electric pump, which makes steering simpler.
There is hydraulic fluid in the reservoir. The fluid transfers and generates a force that acts to turn the wheels when you turn the steering wheel. Older systems extract energy from the engine through a belt connection. Instead, modern vehicles—especially hybrid ones—have an electric pump that is powered by the battery.
Power steering is essential since it powers several modern-day safety systems. The EPAS system could be involved in operation if your car has advanced technologies like lane assist, parallel parking assist, or others.
Functions
The primary function of power steering in a car is to reduce the effort required to turn the steering wheel, making it easier for the vehicle to maneuver at low speeds.
Power steering ensures the wheels are pointing in the desired direction due to a series of linkages, rods, pivots and gears. The system also gives stability to the vehicle, avoids vibration while steering, and reduces tire wear, as well as keeping the car’s front wheels straight.
You should learn about Transmission System with this detailed guide!
Diagram and Parts
The major part of a power steering system varies depending on its type. For hydraulic systems, its parts include a steering wheel, steering column, hydraulic pump or electric motor, steering rack, and fluid (in hydraulic systems).
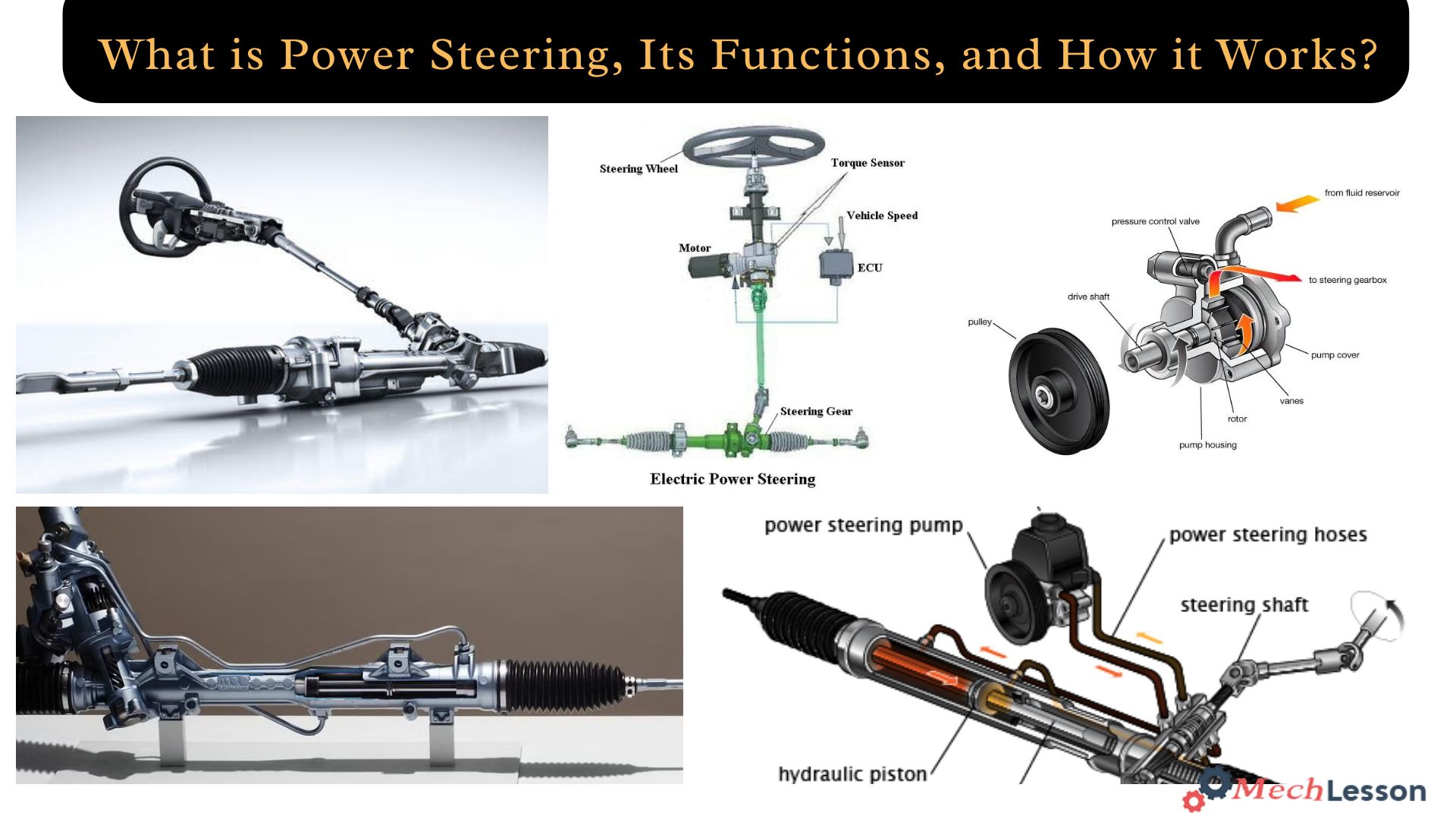
How Does Power Steering Work?
The system operates in a manner similar to other hydraulic systems. However, how does it create pressure, and how precise is it? A number of small and large components work together to preserve precision.
When the steering is pushed in a particular direction, the fluid that is stored in the reservoir is pumped. The force applied to the steering wheel is multiplied and transferred by the hydraulic fluid until it reaches the wheels of the vehicle.
Previously, the engine provided power to the pump. It had a belt connection to the engine and used the engine’s power to drive the pump. Today, the energy needed for the pump is produced by an electric pump.
A lot of energy was known to be consumed by the additional belt that was attached to the engine. The belt will be fastened even if you are not steering. As a result, the system as a whole is ineffective. This problem is fixed by using an electric pump.
When necessary, the electric pump draws power from the battery, increasing the effectiveness of the entire system. In essence, a power-assisted steering system is your power steering. In the past, we had a system that was entirely driven by hydraulic fluid and engine power. A hybrid system that uses an electric pump is more typical today.
The EPAS is another feature of power steering. It is independent of any hydraulic system. This is a rising technical characteristic right now. Many new automotive features, including lane assist, parallel parking assistance, and cornering features, were created using the new EPAS steering system.
You should watch the video below to learn more about power steering:
You should also learn about Air Suspension System with this detailed guide!
Types of Power Steering System
Hydraulic Power Steering System
Hydraulic power steering systems use a hydraulic system to multiply force applied to the steering wheel inputs to the vehicle’s front road wheels. The hydraulic pressure comes from a gerotor or rotary vane pump driven by the vehicle’s engine.
A double-acting hydraulic cylinder applies a force to the steering gear, which in turn steers the wheels. The steering wheel operates valves to control flow to the cylinder, and the more torque the driver applies, the more fluid the valves allow through to the cylinder, resulting in more force being applied to steer the wheels.
A torque sensor measures torque applied to the steering wheel using a torsion bar at the lower end of the steering column. The flow rate of hydraulic pumps is directly proportional to the engine speed, so at high engine speeds, the steering would naturally operate faster.
A restricting orifice and flow-control valve direct some of the pump’s output back to the hydraulic reservoir. The steering booster ensures that the steering will continue to work even if the booster fails.
Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering Systems (EHPS)
Electro-hydraulic power steering systems (EHPS) use hydraulic assist technology, but with a pump driven by an electric motor instead of a drive belt at the engine. Ford introduced “wrist-twist instant steering” in 1965, replacing the conventional steering wheel with two 5-inch rings and a fast 15:1 gear ratio.
The Subaru XT6 in 1988 had a Cybrid adaptive electro-hydraulic steering system, while Toyota introduced the second-generation MR2 in 1990. Volkswagen’s Golf Mk3 Ecomatic in 1994 had an electric pump, allowing power steering to operate while the engine is stopped to save fuel.
You should learn about Manual Transmission System with this detailed guide!
Electric power steering (EPS)
Electric power steering (EPS) uses an electric motor instead of a hydraulic system to assist the driver of a vehicle. Sensors detect the position and torque exerted inside the steering column, and a computer module applies assistive torque via the motor, connecting to the steering gear or steering column. This allows for varied amounts of assistance depending on driving conditions, optimizing ride, handling, and steering for each vehicle.
Engineers can add new driver assistance features, such as lane assist and wind drift correction. On Fiat group cars, the amount of assistance can be regulated using a button called “CITY.”
EPS systems also retain a mechanical linkage between the steering wheel and steering gear, serving as a backup in case of component or power failure.
Electric systems have advantages in fuel efficiency, eliminating belt-driven hydraulic pumps and high-pressure hydraulic hoses, simplifying manufacturing and maintenance. They can instantly vary torque assist levels to aid the driver in corrective maneuvers.
Difference Between Power Steering and Manual Steering
Power steering uses electric assistance to reduce wheel resistance, resulting in quicker steering responses and easier maneuvering at speeds or parking. Manual steering, on the other hand, requires physical effort from the driver to turn the wheel and offers a more direct connection to the road.
Power steering is suitable for drivers who prefer a less physically demanding driving experience, while manual steering has longer response times and requires more effort.
You should also learn about Differential with this detailed guide!
Power steering also reduces wheel movement resistance, making steering easier, while manual steering requires more effort. Additionally, power steering helps absorb shocks, enhancing comfort by minimizing the impact of bumps and road irregularities, while manual steering has limited capabilities. well, below are the differences in tabular form:
| Feature | Power Steering | Manual Steering |
|---|---|---|
| Steering Effort | Requires less effort, especially at low speeds or while parking. | Requires more physical effort to steer, especially at low speeds. |
| Mechanism Type | Uses hydraulic or electric assistance to help turn the wheels. | Purely mechanical, with no assistance; relies on driver’s force. |
| Comfort | Provides a smoother, easier, and more comfortable driving experience. | Feels heavier and can be tiring, especially in city driving or long trips. |
| Maintenance | More complex; may require maintenance of fluids, pumps, or electric motors. | Simpler and easier to maintain with fewer components. |
| Cost | More expensive to install and repair. | Cheaper to produce, install, and repair. |
| Steering Feedback | Can reduce road feel (though modern systems have improved). | Provides better road feel and direct connection to the wheels. |
| Vehicle Type | Common in almost all modern vehicles. | Mostly found in older cars or budget/utility vehicles. |
| Reliability | Can fail if components like pumps or motors malfunction. |
Learn about Automatic Lubrication System with this detailed guide!
Advantages of Power Steering
- Easier to Steer: Reduces the amount of physical effort needed to turn the steering wheel, especially at low speeds or while parking.
- Better Maneuverability: Enhances control and handling, especially in tight spaces or during complex driving situations.
- Improved Safety: Allows quicker and more precise steering adjustments, which can help avoid accidents.
- Less Driver Fatigue: Reduces strain on the driver, especially during long drives or in urban traffic.
- Supports Heavier Vehicles: Makes it practical to drive heavier vehicles like SUVs and trucks without excessive effort.
- Enhanced Driving Comfort: Smoother and more responsive steering makes for a more comfortable driving experience.
- Quick Return to Center: The steering wheel returns to the center more easily after a turn, improving stability and control.
Disadvantages of Power Steering
- Higher Cost: More expensive to install and maintain compared to manual steering systems.
- Complex Maintenance: Components such as pumps, hoses, and fluids require regular maintenance and can fail over time.
- Fuel Consumption (for Hydraulic Systems): Traditional hydraulic power steering systems slightly reduce fuel efficiency because they draw power from the engine.
- Potential for Leaks: Hydraulic systems can develop fluid leaks, leading to reduced performance or total system failure.
- Less Road Feel: Some drivers feel less connected to the road due to the assistive nature of power steering, particularly in older systems.
- Heavier and Bulkier: The system adds weight and complexity to the vehicle, which may affect performance and space under the hood.
- Failure Can Be Dangerous: Sudden power steering failure can make steering extremely difficult, posing a safety risk.
Conclusion
Power steering has transformed modern driving by reducing the effort needed to steer and improving overall control and safety. Whether it’s a hydraulic, electric, or electro-hydraulic system, power steering ensures a smoother and more comfortable ride, especially during low-speed maneuvers or long trips.
While it comes with some drawbacks—such as higher maintenance and cost—the benefits often outweigh the disadvantages for most drivers. Understanding how your power steering system works and maintaining it properly will keep your vehicle running safely and efficiently.
You should learn about Flywheel with this detailed guide!
FAQs about Power Steering
1. What is the main purpose of power steering?
The main purpose is to reduce the physical effort needed to turn the steering wheel, making it easier to control the vehicle, especially at low speeds.
2. How do I know if my power steering is failing?
Common signs include difficulty turning the wheel, whining or squealing noises while steering, fluid leaks, or a stiff steering wheel.
3. What are the types of power steering systems?
The three main types are Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS), Electric Power Steering (EPS), and Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering (EHPS).
4. Does power steering affect fuel economy?
Yes, traditional hydraulic systems can slightly reduce fuel efficiency because they use engine power. Electric systems are more fuel-efficient.
5. Can I drive without power steering?
Technically, yes—but it’s not recommended. Steering will be much harder, especially at low speeds, which can be dangerous in emergency situations.
6. How often should I check power steering fluid?
Check it during routine maintenance—about every 5,000 to 10,000 miles or as recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
7. Can I upgrade my car to power steering if it doesn’t have it?
Yes, but it’s a complex and potentially expensive modification that involves replacing or adding various components.