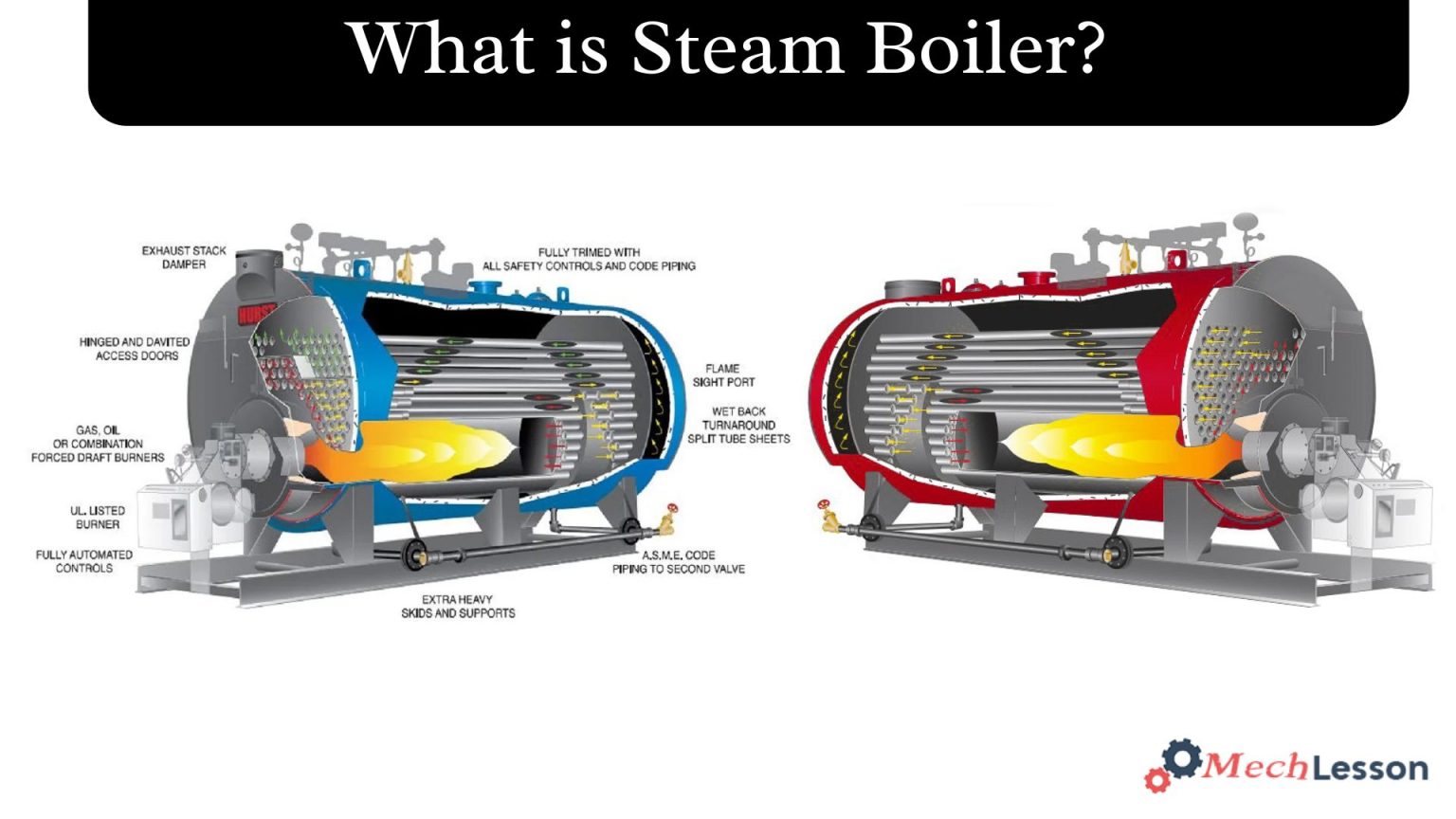
Steam boilers are employed in many different sectors and are essential to modern manufacturing. They supply steam at high temperatures and high pressures for heating, power generation, and mechanical operation.
In general, a steam boiler is a kind of closed container made of steel that heats water to produce steam using an energy source, such as fuel combustion, over time.
Well, in this reading, we’ll explore what a steam boiler is, its functions, types, diagram, and how it works. we’ll also explain its advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s begin!
Learn about Best High Mileage Motor Oil for Engines with this detailed guide!
What Is a Steam Boiler?
A steam boiler is a power-generating machine that uses thermal energy to create steam from water. This boiler is widely employed anytime a steam source is required, and its size and kind mostly rely on the use, such as road vehicles, steam locomotives, and mobile steam engines, which include handy engines.
Older boilers have a pressure range of 7 kPa to 2000 kPa/1 psi to 290 psi, which is low to medium pressure. Because modern boilers operate at higher pressures than their predecessors, they are more practical.
The produced vapour may be supplied at low pressure for industrial development tasks in cotton mills and sugar factories, as well as for producing steaming water that can be used for heat-fixing at very low force.
Ten litres of water should fit in the boiler, and its operating pressure should be 3.4 kgf/cm³ (kilogramme force). The definition of a steam boiler and the varieties used in power plants to produce steam are covered in this article.
Some cars have a small boiler that runs on steam. Power plants and stationary steam engines often have their own huge steam-generating capacity.
Functions
A steam boiler’s primary purpose is to create, store, and distribute vapour. The liquid-contained burner is only a shell, and the heat energy produced during fuel combustion is transferred to water, which subsequently turns into steam at the proper temperature and pressure.
One of the boiler’s primary requirements is that the water container be securely locked. The ideal conditions—quality, pace, pressure, and temperature—should be met while supplying the water vapour.
Components Of Steam Boiler
When regarded as a primary mover, the steam boiler or generator is an essential part of a steam engine. To a certain degree, different generator types can be coupled with different engine units; therefore, it must be handled independently. To burn the fuel and produce heat, a boiler has a firebox or furnace. Boiling occurs when the heat produced is transferred to water to create steam.
The pace at which saturated steam is produced might change based on the pressure above the boiling water. The output of steam increases with boiler temperature. The resulting saturated steam may either be superheated to a greater temperature or utilised right away to create electricity using a turbine and alternator.
This lowers the amount of suspended water, increasing the temperature gradient and enabling a given volume of steam to do more work. This lessens the possibility that condensation may occur.
In order to warm the feed water before it enters the boiler, any heat that remains in the combustion gases can either be removed or forced to flow via an economizer.
Learn about Steam Engine with this detailed guide!
Diagram
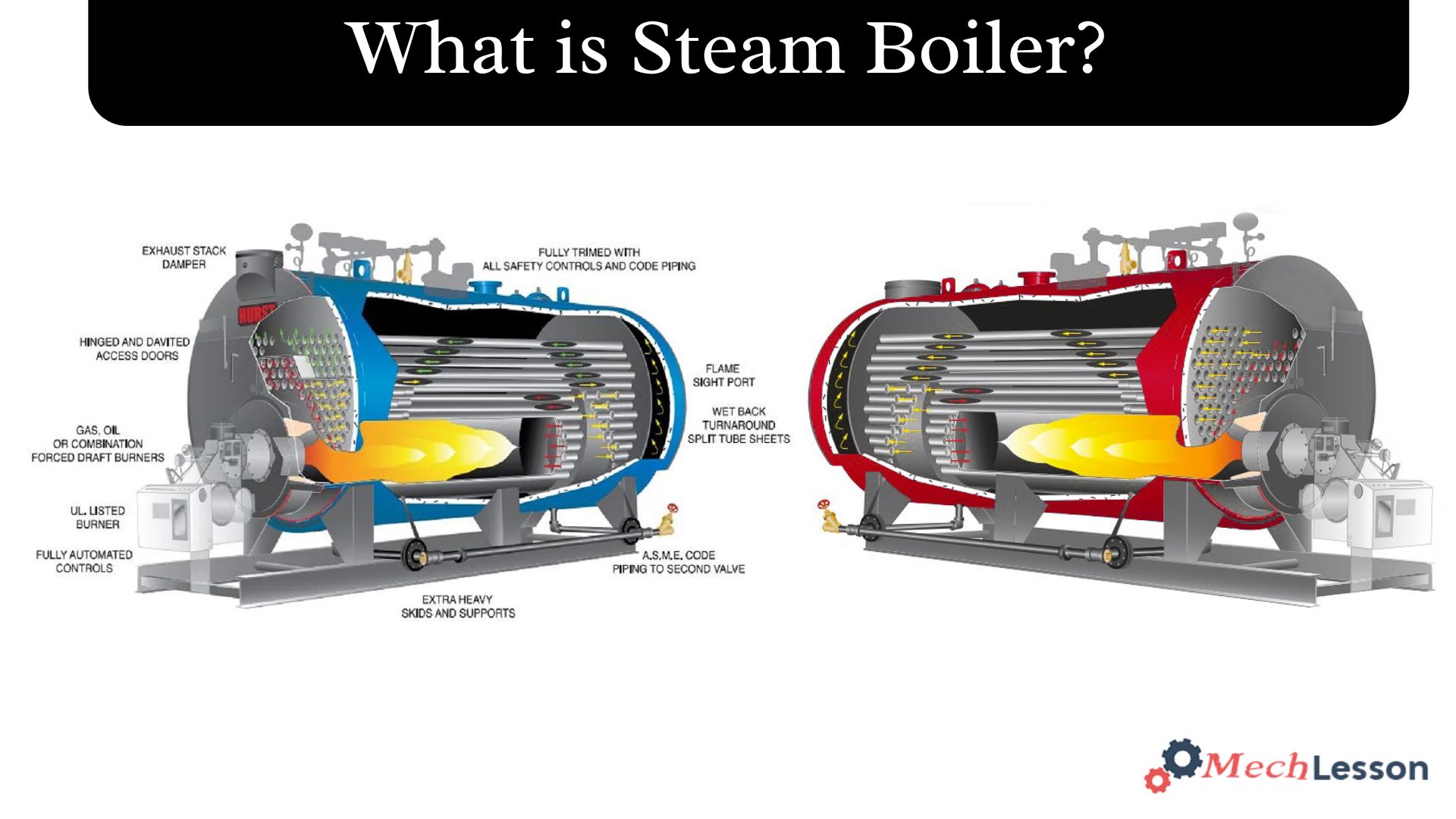
Types of Steam Boiler
The following are the various types of steam boiler:
- Shell Boilers.
- Fire Tube Boilers.
- La Mont boilers, Benson boilers, and Loeffler boilers.
- Water Tube Boilers.
- Oil Boilers.
- High Pressure Boilers.
- Low Pressure Boilers.
- Gas Boilers.
- Electric Boilers.
- Hot Water Boilers.
Learn about Engine with this detailed guide!
Shell Boilers:
Shell boilers are heat transmission surfaces encased in a steel shell. Different tube configurations are used, which have an impact on how many times heat moves through the system before being released.
Shell boilers, also called flue boilers, use fire tubes and feature a long, cylindrical water tank. These fire tubes heat the water by transferring heat from the boiler or combustion chamber.
The Cornish boiler, which had a long cylinder with a single huge flue or pipe holding the heat or fire, was the first of this style of boiler. The Lancashire steam boiler, which had two fire flues, eventually took its place.
One of the most basic boiler types, shell steam boilers—also known as shell and tube boilers—are renowned for producing steam effectively and affordably.
Fire Tube Boilers:
Water flows around the tubes in a steam boiler with fire tubes, heating them. Gases from burning coal or oil provide the heat inside the tubes, transferring thermal energy to the water and creating steam.
Low-pressure steam is usually produced in fire tube steam boilers. Cochran, locomotive, and Lancashire are the three primary varieties of steam boilers with fire tubes. An economizer can be added to a steam boiler with fire tubes to improve its heat recovery and efficiency.
La Mont Boilers, Benson Boilers, and Loeffler Boilers:
La Mont, Benson, and Loeffler steam boilers use draft fans and forced circulation to produce huge amounts of steam efficiently. A centrifugal pump moves water via tubes with tiny diameters that are tightly spaced.
An economizer, which uses pipe or flue gases from the combustion chamber to warm the water, increases their efficiency.
Related: Step-by-Step Guide on How to Bleed A Radiator
Water Tube Boilers:
The water tube boiler circulates water through tubes within the boiler. The fire from the combustion chamber burns around the exterior of these tubes, heating them and, in turn, heating the water within.
This design creates high-pressure steam by applying tangential pressure, or hoop stress, applied to the perimeter of the tubes. This tension is similar to the strain imposed on the bands of a wooden barrel as it fills.
Various types of water tube boilers have been used since the introduction of the first boiler, changing and improving throughout the years.
Oil Boilers:
Although they use oil in the combustion chamber rather than gas, oil steam boilers function similarly to gas boilers. The water is heated by the exchanger, which is heated by the burning oil. Boilers that use oil steam can reach over 90% efficiency.
They are more costly than gas steam boilers, but they usually last twice as long. One issue with oil boilers is the need for an oil tank, either indoors or out, that must be regularly filled to ensure a steady fuel supply.
High Pressure Boilers:
Excessive pressure is produced by high-pressure steam boilers to power machinery and equipment. A pump that pushes the steam into the circulation system at high pressure generates the force and power of a high-pressure steam boiler.
A boiler must be able to generate pressure between 15 and 800 psi at temperatures higher than 250°F (ca. 121 °C) in order to be classified as a high-pressure steam boiler.
High-pressure steam boilers are routinely checked for temperature and pressure for efficiency and safety. Their high-pressure loads fall into one of two categories: continuous or batch.
Continuous loads are appropriate for long-term demands, whilst batch loads are employed for short-term ones.
Low Pressure Boilers:
Heat is transferred using low-pressure steam boilers at temperatures of 300°F (149°C) and pressures ranging from 10 to 15 psi. Applications needing constant temperatures with no need for abrupt fluctuations are best suited for this kind of boiler.
Low-pressure steam boilers are widely used because they produce steam much faster than high-pressure steam boilers.
Gas Boilers:
Gas steam boilers: this boiler is powered by propane or natural gas. From an outside source, the fuel is piped straight into the boiler. The way a gas steam boiler distributes heat is determined by its particular arrangement.
Gas steam boilers can be used for low-pressure applications as well as industrial settings.
You should also Learn about Construction Technology with this detailed guide!
Electric Boilers:
Electric boilers provide a quicker and more effective heating method; they do not require fuel combustion, making them a cleaner and more environmentally friendly system.
They are more durable, require less cleaning, and require almost no maintenance; however, it is crucial to control the accumulation of scaling in the water reservoir.
Hot Water Boilers:
Hot water boilers are tanks made up that transmit hot water, which is subsequently circulated for heating. These boilers can tolerate high temperatures and pressures because they are made of materials like steel, cast iron, aluminium, and stainless steel.
Water tube and fire tube are the two types of tube systems used to categorise hot water boilers. Heat is transferred through tubes submerged in water in fire tube boilers, heating the water around them. Water is heated outside and circulated within the tubes of water tube boilers.
How Steam Boiler Works
The main working principle of a steam boiler is easy. This boiler is an example of closed equipment with a cylindrical form. The boiler has enough capacity to hold both water and steam.
Depending on the vessel’s size and other requirements, the liquids are often kept in the boiler to produce steam by burning fuels or applying heat energy at various pressure levels. Lastly, the boiler’s steam is sent via a pipe to various enterprises, including plants.
A shell, furnace, grate, mountings, water space, accessories, refectory, water level, scale, foaming, lagging, and blowing off are the boiler’s primary parts.
Advantages Of Steam Boiler
- The boilers are low-construction-cost
- It uses any chimney.
- It occupies less floor area.
- The boilers are also portable.
- It has a self-enclosed boiler.
Disadvantages Of Steam Boiler
- The Steam Boiler Design Challenges
- Its vertical design limits steam-raising capacity.
- The boiler has limited pressure and capacity.
- Its also difficult in cleaning and examination.
- Finally, it requires high headspace.
FAQs
What is a steam boiler used for?
The function of a boiler is to either produce hot water or steam. Hot water boilers heat water for the purpose of domestic or commercial heating and hot water supply. Steam boilers generate steam in order to power turbines for power generation and various other industrial heating applications.
Where are steam boilers used?
The main sectors in which industrial steam boilers are used are: Food, in industrial bakeries or baby food (as an example) Textile, in rotary dryers. Chemical, for reactors or storage.
What are the different types of steam boilers?
There are two basic boiler styles for steam boilers in this range, Firetube and Watertube boilers. As their names imply, the Firetube boiler has the fire (combustion gases) inside the tube and the Watertube boiler has the water inside the tube.
What are the three main functions of a steam boiler?
- Generating electricity.
- Powering industrial machinery.
- Sterilizing medical equipment.