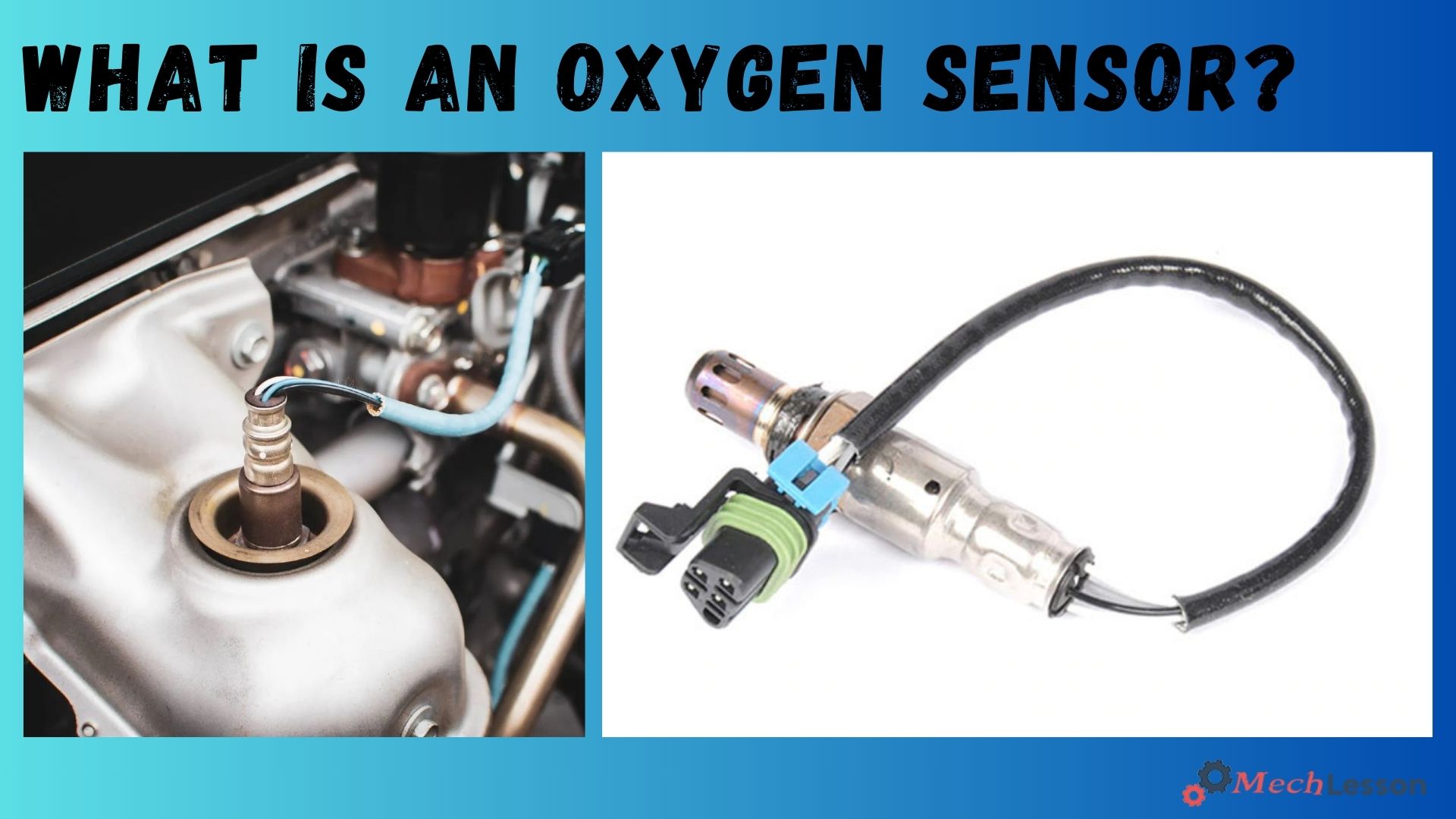
Oxygen sensors monitor the oxygen level in exhaust gases. It assists the engine control module in regulating the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion and efficient operation with minimal emissions.
You’ll experience various warning signs if your car’s oxygen sensor is bad, and you need to understand these noticeable symptoms. If this problem is ignored, fuel costs may grow, there may be engine damage, and pollution levels may rise.
To restore your vehicle’s optimal operation and lessen its environmental impact, it is wise to have your oxygen sensor examined and replaced by a qualified mechanic if you suspect it is defective.
Well, in this reading, we’ll be exploring what an oxygen sensor is, its functions, location, and how it works. We’ll also explore the symptoms of a bad oxygen sensor and how to bypass it.
What is an Oxygen Sensor?
An oxygen sensor is a device in a car engine also called an O2 sensor. It measures the quantity of oxygen in a liquid or gas using the sensor.
This oxygen sensor, created by the Robert Bosch firm in the late 1960s, gauges the concentration of oxygen in a liquid or gas.
This is how it works. In reality, the procedure is really straightforward. Platinum and zirconia covered in ceramic are used to make oxygen sensors. These days, they are present on all vehicles manufactured after 1980.
A computer within the engine receives data updates from the oxygen sensor, which is housed in the emissions control system. Your engine will continue to operate at peak efficiency, and emissions will be continuously under control when the O2 sensor is functioning properly.
Your check engine light will illuminate if your oxygen sensor malfunctions. Furthermore, an automobile with a malfunctioning oxygen sensor will fail an emissions test.
Location
The exhaust system of most cars contains at least two oxygen sensors: one downstream from the catalytic converter and one or more in front of it. The downstream sensor gauges the catalytic converter’s efficiency, while the “pre-cat sensor” controls the fuel delivery.
Related: What Are Car Sensors? Diagram and How They Work
Diagram
Symptoms of a Bad Oxygen Sensor
The symptoms of an oxygen sensor include low fuel economy, check engine light turning on, smells of sulfur or gas from the exhaust, low engine performance, engine stall, exhaust emitting black smoke, etc.
Low Fuel Economy
Have your gas expenses increased, or have you been filling up the tank more frequently than usual? Your O2 sensors may be to blame.
The mixture may become “rich” (fuel-heavy) if they are unable to keep track of the air-to-fuel ratio in your combustion cylinders, which would indicate that your engine is utilising more fuel than it should.
Check Engine Light Is On
Although a malfunctioning O2 sensor is one of the most frequent causes of a check engine light, it can also signify a variety of other issues.
Make an appointment for an engine diagnostic service at your neighbourhood Firestone Complete Auto Care as soon as the check engine light illuminates on your dashboard. If your car has high mileage, the oxygen sensor is probably to blame.
Smells of Sulfur or Gas from The Exhaust
When you turn on your automobile or stand outside of it while it is idling, take note of any odours you detect, such as sulphur, a rotten egg smell, or just plain gasoline.
This is the surplus fuel burning off in the engine, and it may be a sign that your oxygen sensors are not picking up on the shortage of air in the combustion cylinders.
Engine Performance Problems
Can rough idle and engine power loss be attributed to a malfunctioning O2 sensor? Of course. Additionally, you can experience stalling, sluggish acceleration, and engine misfires.
The engine’s vital functions, such as engine timing, combustion intervals, and air-fuel ratio, are disrupted by faulty oxygen sensors.
Engine Stall
Because it lacks the necessary gasoline and power to operate properly, the engine may misfire when the ignition is turned on or shut down entirely. This only occurs if you’ve been driving for a while with faulty oxygen sensors, and the engine has been harmed as a result.
Exhaust Emitting Black Smoke
Your engine burns fuel by using oxygen. When there is insufficient fuel, the combusting gasoline emits black smoke through the exhaust pipe.
When the O2 sensor isn’t working properly, the engine control module isn’t informed to change the air-to-gasoline ratio; therefore, the engine keeps consuming too much fuel.
Failure of the Catalytic Converter
Your catalytic converter transforms harmful exhaust emissions produced by engine combustion into less harmful ones.
If your oxygen sensors aren’t working, they might instantly malfunction and allow dangerous compounds to billow out of your exhaust pipes because they require a precise amount of air to function properly.
Your car could fail an emissions test due to a defective catalytic converter.
Unusual Pinging or Knocking Noise
The air-fuel ratio may run lean when your O2 sensors are unable to monitor it (more air than fuel). As a result, the combustion chamber accumulates carbon, which can sound pinging, knocking, or rattling (especially when the ignition is turned on).
Car Idles Rough
An idle engine’s RPM rate is typically less than 1,000. However, if there is too much gasoline in the engine as a result of defective oxygen sensors, the RPM may increase to 2,000 or even 3,000.
Though this isn’t a clear sign of a faulty O2 sensor, your engine may have a rough idling issue for a variety of reasons.
Emissions Levels are High
Your oxygen sensors are a crucial part of your emission control system; if you don’t have them, your exhaust will probably develop a significant imbalance of pollutants.
If you fail an emissions test that is required, ask your technician to do a diagnostic test. There are a number of potential causes for your emissions to be off, but one of the first things to check is your O2 sensors.
How to Bypass O2 Sensor
Before you consider bypassing your O2 sensor, you should make sure it’s legal to do so in the state you are in. Also, make sure that you’re capable of doing it.
Get The Car Ready
Let the car cool down before working on it, which may take a few hours for the exhaust to completely cool. Disconnect the negative battery cable by loosening the nut and sliding the clamp away from the terminal.
Jack Up The Car
Jack up the vehicle using the front jack point and place the jack stands under the frame towards the front of the vehicle. Lower the vehicle gently onto the stands.
Remove The O2 Sensor
Locate the O2 sensor in the exhaust system, which looks like a plug and may be found in the catalytic converter or before and after it. Disconnect the wiring by squeezing the tab and pulling it away from the housing. Use a special tool to turn it counterclockwise and remove it.
Insert a Dummy (fake) Oxygen Sensor
To install the new dummy sensor, also known as an O2 sensor simulator, turn it clockwise as you would with a new O2 sensor. After installation, connect the wiring and lower the vehicle to the ground. Once you start the car, check if the Check Engine Light has turned off.
You may need to drive the car for a short distance to turn off the light. It’s important to note that installing a dummy O2 sensor may be illegal, depending on where you live.
Why Would You Need to Bypass an O2 Sensor?
You might want to bypass your O2 sensor for a few reasons. Perhaps you want to improve your fuel efficiency, or perhaps you simply want a little more power. The best way to get around an O2 sensor if you want to increase your car’s performance is with a wide-band oxygen sensor.
Bypassing the oxygen sensor is not advised if you’re trying to pass an emissions test or keep the check engine light off. If you’re unsure whether to bypass your oxygen sensor or not, an illuminated check engine light may also be a sign that it has.
If you’re wondering whether or not to bypass your car’s oxygen sensor, we advise speaking with a qualified repair or automotive expert.
Related: What Is An Oil Pressure Sensor? Its Diagram, Location, And How It Works
Bottom Line
Oxygen sensors can fail due to age, contaminants, excessive fuel additives, and soot buildup. They do not need to be replaced all at once, and if one fails, the others should be considered due to age.
When an oxygen sensor fails, it can cause decreased fuel efficiency, increased emissions, poor performance, and damage to the catalytic converter.
FAQs
What happens when the oxygen sensor goes bad?
Poor fuel economy will occur as a faulty oxygen sensor will upset the air-to-fuel mixture, resulting in increased fuel usage. Rough engine idle or misfiring: since the oxygen sensor output helps control engine timing, combustion intervals, and air-to-fuel ratio, a faulty sensor can cause the vehicle to run rough.
What is an oxygen sensor used for?
Scientists use oxygen sensors to measure respiration or production of oxygen and use a different approach. Oxygen sensors are used in oxygen analysers, which find extensive use in medical applications such as anaesthesia monitors, respirators, and oxygen concentrators.
Does an oxygen sensor affect fuel consumption?
Yes, a faulty oxygen sensor can cause poor fuel economy.
Can I drive with a bad oxygen sensor?
It is not advisable to drive with a bad O2 sensor as the powertrain is not running on the correct fuel mixture. While it may perform fine in the beginning, if your engine is running rich and using too much fuel, it might begin to clog the catalytic converter.
Can you clean oxygen sensors?
While some sources suggest cleaning an oxygen sensor with carburettor cleaner or by soaking it in gasoline, we cannot recommend cleaning oxygen sensors. There are too many delicate electronic components that can be irreversibly damaged to make the effort worth the hassle.