The throttle is referred to as a regulator in steam-powered engines, an accelerator pedal in automobiles, and a thrust lever in aeroplanes. The drive-by-wire system is used in modern cars.
Many of the mechanical systems in cars have been replaced with sensors in this system. The engine control unit, a computerised device, keeps track of the information obtained from various sensors and manages the vehicle.
Well, in this reading, we’ll explore what a throttle position sensor is, its application, part, diagram, types, symptoms, and how it works.
Let’s begin!
Learn about Camshaft Position Sensor with this detailed guide!
What Is Throttle Position Sensor?
A throttle position sensor (TPS) is an engine’s ECU used to monitor the position of the throttle body valve. In order to immediately monitor the throttle position, the sensor is typically mounted on the butterfly spindle or shaft.
Additionally, more sophisticated sensor types are employed. To show that the throttle is fully closed, for instance, an additional “closed throttle position sensor” (CTPS) can be used.
If electronic throttle control (ETC) or “drive by wire” technologies are utilised by some engine control units (oecus) to regulate the throttle position, the position sensor is employed in a feedback loop to make such control possible.
Automobiles have throttle systems that monitor and regulate the engine’s fluid flow. By altering the engine’s air-fuel ratio, which is accomplished by restricting the throttle, the vehicle’s engine output may be managed.
Application
The engine control unit receives information from this sensor on the butterfly valve’s position. It is employed to determine the valve’s wide open throttle and idle position. The sensor’s output voltage is less than 0.7V while the valve is in the idle condition. The sensor’s output voltage is around 4.5V when the full load status is recognised.
When the throttle position sensor is damaged, the check engine signal flashes. When this sensor malfunctions, the computer is unable to accurately calculate the valve’s position, which causes the vehicle to surge or stall.
Parts & Diagram
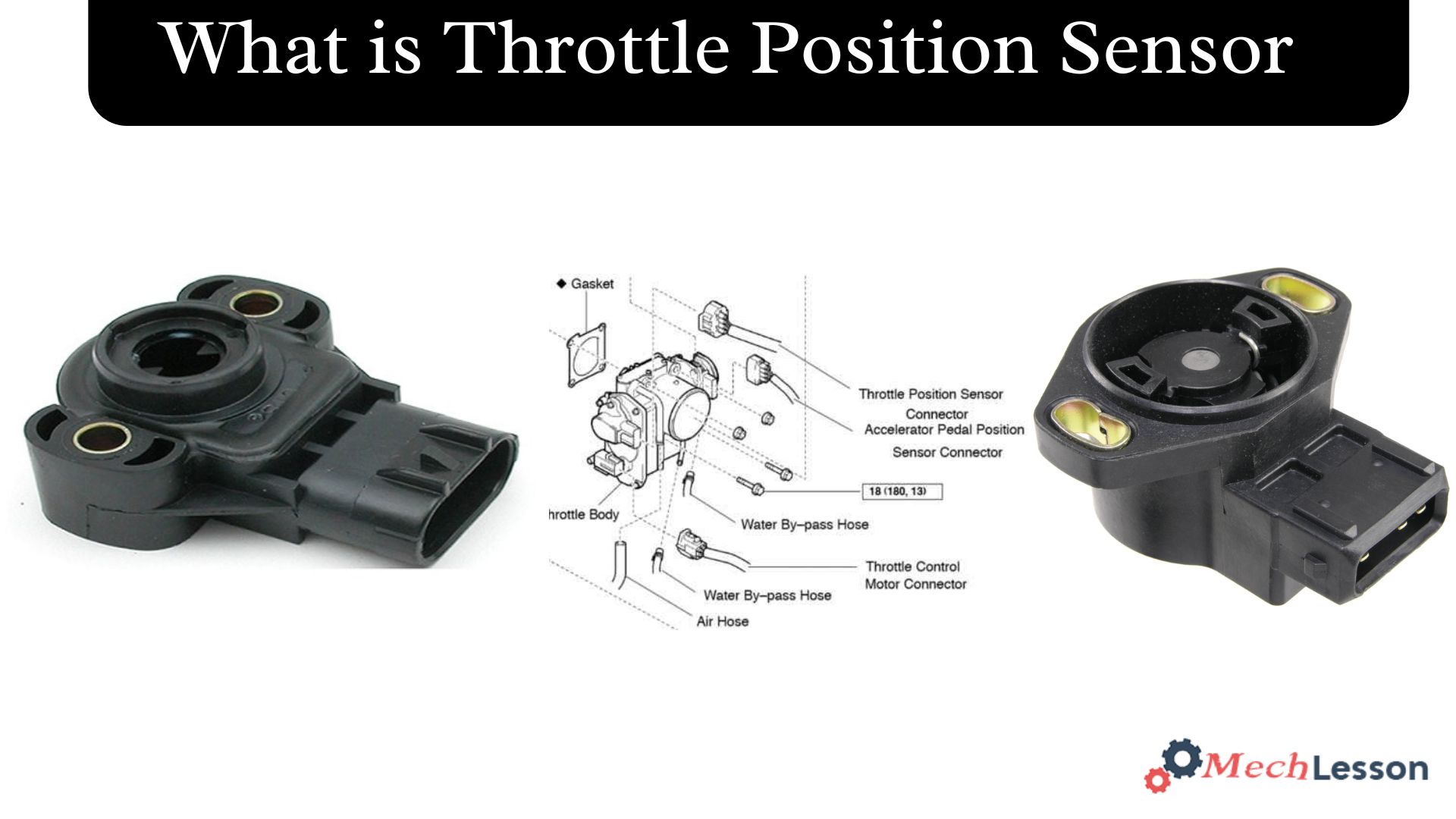
Importance Of Throttle Position Sensor
The throttle position sensor plays a significant part in the power control and emission management of the automobile. It lets the ECU detect the driver’s acceleration intention to correctly manage the fuel injection and ignition timing.
Learn about Coolant Temperature Sensor with this detailed guide!
This procedure not only influences the acceleration performance of the automobile but is also directly tied to the fuel economy and the achievement of pollution criteria.
In the event that the throttle position sensor malfunctions, the engine may lose power, respond slowly, or even illuminate the engine failure light. To guarantee the car’s regular running, routine TPS inspection and maintenance are therefore essential. Visit our DRex Electronics page to find out more about electronic components and their uses.
Types of Throttle Position Sensor
These are the mainly following types of throttle position sensors:
1. Digital Throttle Position Sensor: It employs digital signal output and is typically compatible with the computer control system of newer automobiles, which may offer more precise throttle position data.
2. Single Throttle Position Sensor: This kind is appropriate for basic engine control systems and just contains one sensor.
3. Dual Throttle Position Sensor: It as two sensors are used to increase safety and redundancy. The system can continue to function normally even if one of the sensors fails.
4. Analog Throttle Position Sensor: This system is suitable for early automobile models; it outputs a continually changing voltage signal to show when the throttle is opened.
Symptoms
There are many symptoms of a failed throttle position sensor. While some of these symptoms could also be signs of other engine issues, watch out for these symptoms of a bad TPS, or throttle position sensor.
- It’s hesitations during acceleration.
- Its difficulty or delay in gear shifting.
- Its surges unusually during acceleration.
- Its work is unexplainable bucking and jerking.
- It as sudden idle surges.
- Its works: unseen engine stalling.
- It works in sudden speed surges on highways.
- Its intermittent check engine light is flashing.
- Its drop in fuel economy.
- It has poor power.
How To Reset Your Throttle Position Sensor
A throttle position sensor cannot be reset using a “one size fits all” approach. In the past, resetting a TPS required rotating the sensor slightly on its mounting pad, loosening the sensor, and using a multimeter to read the sensor output in order to obtain a certain output value.
Resetting your throttle position sensor is as simple as removing the engine control module fuse or unplugging the negative line from your battery for a maximum of five minutes. If you’re not comfortable with electricity, don’t try this since it might be harmful to remove the incorrect fuse or cable from your battery.
Sometimes all you need to do to get your sensor back is to reset it. Your throttle position sensor may operate improperly or irregularly due to code issues. Otherwise, reprogramming your sensor will need expert software. The ideal person to undertake this work is a professional mechanic.
The majority of contemporary techniques include pressing the gas pedal to the floor in a certain order while turning the ignition key on and off. Others need specialised diagnostic tools in order to communicate with the onboard computer.
Although several of these methods are actually throttle recalibrations, many users still call them throttle position sensor resets.
You should also learn about 7 Possible Symptoms Of Bad Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor with this detailed guide!
How Throttle Position Sensor Works
Typically, this sensor is installed on the throttle body. It communicates with the engine control unit by detecting the position of the butterfly or throttle valve. This sensor provides the output current that determines the location of the accelerator pedal and tracks how far down it is pushed. The engine’s airflow is controlled by the pedal’s position.
The engine receives a lot of air while the valve is wide open, and vice versa. The engine control unit receives the output from this sensor and other sensors and determines how much fuel should be pumped into the engine based on that information.
This sensor is a potentiometer with three wires. The resistive layer of the sensor receives a 5V power supply via the first wire. While the third wire connects to the potentiometer wiper and supplies input to the engine control system, the second wire serves as ground.
Generally speaking, the TPS is installed in the throttle body or near the accelerator pedal and works through potentiometer, Hall effect or magnetic induction principles.
- Magnetic induction principle: Magnetic induction sensors employ induction components to sense the throttle position, much like the Hall effect does. Although they are often more complicated, they also provide signals with greater accuracy.
- Hall effect principle: The Hall effect sensor senses the throttle position by detecting variations in the magnetic field. The built-in magnet’s location in relation to the sensor changes when the accelerator pedal is depressed, and the ECU also receives the electrical signal that is produced. Typically, this kind of sensor is more resilient and capable of preventing interference.
- Potentiometer principle: Potentiometers are the most often used form of throttle position sensor. It is made up of a fixed resistor and a sliding contact that may be moved. The sliding contact on the resistor moves as the accelerator pedal is displaced, altering the resistance value and producing a voltage signal proportionate to the throttle opening. The engine control unit (ECU) receives this signal and uses it to modify the ignition timing and throttle fuel injection quantity.
Learn about MAP Sensor withi this detailed guide!
FAQs
What happens when the throttle position sensor goes bad?
A bad TPS can cause unstable idle, no idle, staling, poor performance, poor fuel economy, no acceleration or a car accelerating on it’s own.
Will a car run without a TPS sensor?
Yes, a car can start without a throttle position sensor (TPS), but it might not run properly. The throttle position sensor is crucial for the engine control unit (ECU) to determine the position of the throttle valve, which affects fuel injection and ignition timing.
What will happen if I unplug my throttle position sensor?
Disconnected TPS results in improper idling and intermittent stalling. The absence of accurate throttle position data disrupts the air and fuel mixture, leading to ineffective engine combustion.
What is the work of the throttle position sensor?
The throttle position sensor plays a key role in the power control and emission management of the car. It helps the ECU monitor the driver’s acceleration intention to accurately control the fuel injection and ignition timing.