Automobiles are designed with an air conditioning system to keep users comfortable by cooling the car interior in hot weather. Modern vehicles also control cold weather by using heat from the engine.
The Packard Motor Company first introduced the AC system in the United States in 1939, and it is now a standard feature in all vehicles for the convenience of people. A vehicle’s air conditioning system works by using a refrigerant gas and compressor to cool the air in the cabin. This compressor is connected to an evaporator that cools the air as it passes through.
The cooled air is then distributed through the vents in the car cabin. Well, in this reading, we’ll learn what a car air conditioning system is, its diagram, parts, types and how it works. We’ll also learn its symptoms of failure.
Let’s get started!
Learn about car cooling system with this detailed guide!
What Is A Car Air Conditioning System?
A car air conditioning system is a set of components that work together to cool the vehicle’s interior. It functions similarly to the AC systems used in homes and offices.
A car AC system works by compressing and cooling a refrigerant, then blowing that cool air into the passenger compartment. This system consists of several key components that work together to regulate temperature and humidity inside the vehicle.
The system does not actually create cold air but rather cools the surroundings to provide comfort, using components such as a compressor, condenser, and evaporator. Cars use two types of air conditioning systems, one of which includes an expansion valve system that lowers the refrigerant pressure, and the other uses an orifice tube.
The automotive air conditioning (AC) has been around since 1939, with Packard being the first car company to offer factory-installed systems in 1940. By 1969, over half of the new cars had AC built in. However, the refrigerant used in AC, R-12, was found to be damaging the ozone layer, leading to its ban in the US and the introduction of an alternative, R-134a or HFC-134a, for cars manufactured after 1996.
In 2012, the Environmental Protection Agency began phasing in a newer, better-for-the-environment refrigerant, R-1234yf or HFO-1234yf, with a GWP of 4, compared to R-134a’s 1,430. By 2022, 97% of new vehicles in the U.S. used the new refrigerant.
You should learn about Force-placed Auto Insurance, and its Drawbacks with this detailed guide!
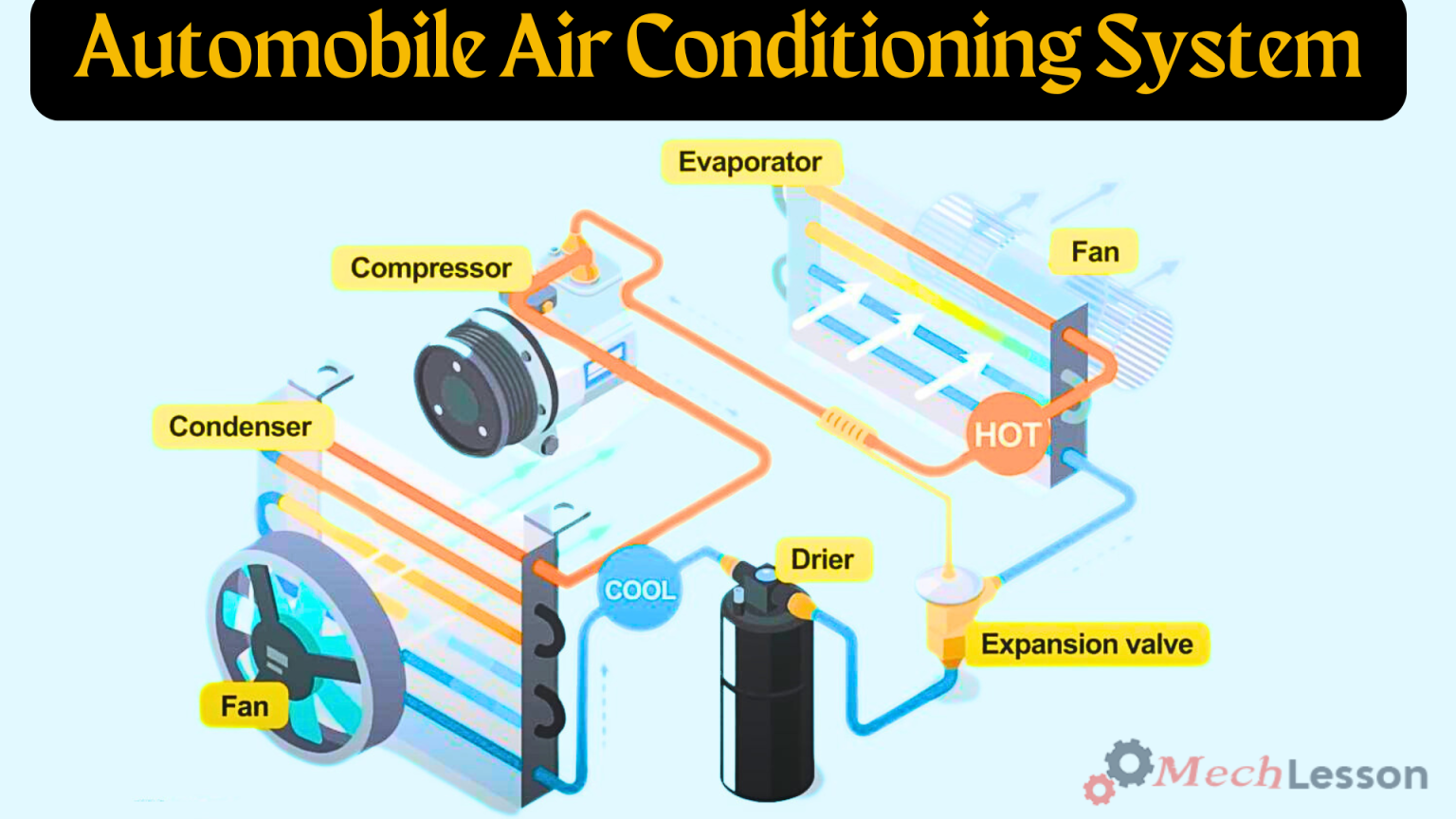
Parts Of A Car AC System
A car’s air conditioning (AC) system consists of several key components that work together to cool the interior of the vehicle. Here are the main parts:
Compressor
The compressor is one of the major components in the air conditioning system. Its functions include pressurizing the refrigerant to cool the air, sensing temperature changes inside and outside the car, monitoring and controlling temperature output, and finally moving air to the condenser.
Condenser
The condenser in the car’s air conditioning system is located at the front of the radiator. It has been named a mini-radiator because it looks like a radiator. As the compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, it cools and compresses the hot gases that escape from the system.
Another function of a condenser is to transfer cooled liquid refrigerant to the receiver, dryer, or accumulator.
Receiver, Dryer, or Accumulator
Vehicles use either a receiver or an accumulator based on their model. The receiver is used in vehicles with a thermal expansion valve, while an accumulator is used in vehicles with an orifice tube.
The receiver separates gas from liquid to prevent liquid from entering the compressor. Compressors are designed to handle gas, as liquid can cause contaminants, but filters help protect the system. Compressors also remove moisture using desiccant.
Thermal Expansion Valve or Orifice Tube
The thermal expansion valve, or orifice tube, is located between the condenser and the evaporator. The thermal expansion valve uses a receiver or dryer, while vehicles with orifice tubes utilize an accumulator. The purpose of the car cooling system is to monitor the amount of pressure and temperature in the system.
You should also learn about car electrical systems with this detailed guide!
Evaporator
The evaporator, located behind the dashboard, cools the air with refrigerant before it is blown into the vehicle’s cabin. The system works by circulating refrigerant through a closed-loop system, changing it from gas to liquid and back to gas.
The car engine powers the compressor, which converts low-pressure gas into high-pressure before sending it to the condenser to release heat and cool the gas.
Diagram Of A Car AC System
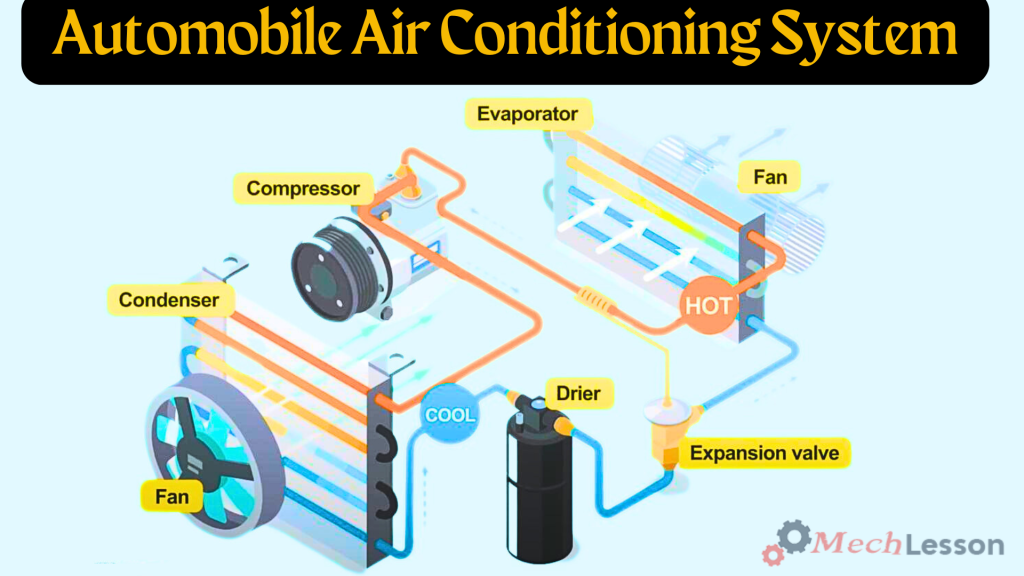
Learn about car batteries with this guide!
Types Of Car Air Conditioning System
Today’s automotive industry uses two main types of AC systems in a car. What makes each system unique is the kind of device that lowers the refrigerant pressure. The following are its two main types:
Expansion Valve System
Among automotive air conditioning systems, the expansion valve system is the most often used. It controls the refrigerant flow to the evaporator with an expansion valve. The expansion valve keeps the refrigerant flowing at a steady pace, which helps to keep the car’s interior temperature stable.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
Fixed Orifice Tube System
A less complicated type of car AC system is the fixed orifice tube system. It controls the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator using a fixed orificetube. By limiting the refrigerant flow, the fixed orifice tube helps to keep the car’s interior temperature stable.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
How A Car Air Conditioning System Works
In order to transfer refrigerant from a liquid to a gaseous form, an automobile’s air conditioner controls temperature and pressure. The car’s heat turns the refrigerant from a liquid when it enters the evaporator into a gas. Heat may be absorbed by refrigerant when it is a gas.
The process restarts by pushing the refrigerant out of the car, which removes heated air from the vehicle and returns it to the compressor, where it is compressed again into a liquid. In addition, cold air is blown into the passenger cabin by a fan located outside the evaporator chamber.
It then goes through the receiver/dryer to eliminate moisture and impurities. It then proceeds to the expansion valve. As it flows into the evaporator, the refrigerant undergoes a process of cooling as it loses pressure and heat. The dashboard’s evaporator functions similarly to a little radiator.
Air is forced through the chilled evaporator, which cools and eliminates moisture from the air. That cool, dry air enters the passenger compartment via vents. For you to enjoy that cool, refreshing air, your air conditioning system has to work hard.
You should also learn about a car transmission system with this detailed guide!
Symptoms Of A Bad AC System In A Car
If your car’s air conditioning system is not functioning properly, you may notice several symptoms. Here are some common signs of a bad AC system:
Weak Airflow
There are numerous causes of the weak airflow that drivers experience over time in their vehicles. This symptom could damage or cause fatal damage to the A/C system. Below are the causes of weak airflow:
- A fried ventilation fan is a cause of weak airflow. This is when the fan in the system is not blowing, causing air to not flow effectively.
- There could be mold accumulating in the evaporator core from residual moisture.
- Hose loss is the root cause of poor airflow in automobile air conditioning systems.
- The core case that houses the blower has seals that can open up. This will also diminish the airflow in the system.
Reduced A/C System Functionality
There could be a number of causes for your A/C to occasionally lack essential coolness. When the symptom occurs, it should be fixed as soon as possible, or else big damage will be caused to the system. Below are the causes of these symptoms.
- A failed blower motor or blower resistor.
- If there is a clog that expands the tube or refrigerant charging hose,
- When electrical parts like a fuse, switch, relay, solenoid, or control module fail, symptoms occur.
- A damaged or failing condenser or evaporator is also a major cause.
- Leak vacuum
- A failed compressor or compressor clutch can also cause a weak system.
- A failing o-ring seal or component is the root cause of a freon leak.
Learn about a turbocharger with this guide!
A/C Cools First But Warms Shortly
Numerous problems are to blame, but you should look into and address them to keep the system functioning normally. A DIYer won’t be able to fix the issue; otherwise, the whole system will be scattered. Below are the common causes of such a problem:
- A clogged expansion valve is a major cause of this problem.
- A faulty compressor clutch is also a major cause of such an issue.
- The fuse that powers the A/C system can shoot out and cause the system to stop working.
A/C Vents Smelling Like Gym Lockers
Instead of experiencing cool air from the vent, the odor from the gym locker takes charge, which is not cool. Below are the common causes of the issue:
- A moldy evaporator case is a common cause.
- Old and dirty cabin filters are another potential cause.
Conclusion
The car air conditioning (AC) system is essential for providing comfort by cooling and dehumidifying the air inside the vehicle cabin. It operates by circulating refrigerant through components like the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator, effectively transferring heat from the interior to the outside.
Modern AC systems also improve air quality through cabin filters and climate control features. Regular maintenance—such as checking refrigerant levels, cleaning filters, and inspecting components—ensures optimal performance and longevity of the system.
You should also learn about superchargers with this detailed guide!
FAQs on Car Air Conditioning System
How does a car AC system work?
It works by compressing and circulating refrigerant through a closed loop, absorbing heat from inside the car and releasing it outside via the condenser.
What are the main parts of a car AC system?
The key components include the compressor, condenser, receiver/drier, expansion valve, and evaporator.
Why is my car AC not cooling properly?
Common causes include low refrigerant levels, a faulty compressor, clogged filters, or a leaking AC system.
How often should I service my car AC?
It’s recommended to inspect it at least once a year, especially before summer. Refrigerant top-up might be needed every 1–2 years.
You should also learn about Friction (Conventional Braking) vs. Regenerative Braking with this detailed guide!
Can I run the car AC without refrigerant?
No, the system requires refrigerant to cool the air. Running it without refrigerant can damage the compressor.
What type of refrigerant is used in car AC systems?
Most modern cars use R134a or R1234yf refrigerant, depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
Does using the AC affect fuel efficiency?
Yes, running the AC increases engine load slightly, which can reduce fuel economy by 5–10%.