A car cooling system is a closed circuit that helps keep your engine running at a safe temperature. A cooling system is needed because internal combustion engines create heat at extremely high temperatures.
The cooling system is a set of components that enables the flow of liquid coolant to the passages in the engine block and head to absorb combustion heat. In this reading, we’ll explore what a car cooling system is, its functions, diagram, components, types, and how it works. We’ll also learn about its maintenance.
Let’s get started!
Learn about an engine lubrication system with this detailed guide!
What Is A Cooling System?
The car cooling system is a set of components that enables the flow of liquid coolant to the passages in the engine block and head so as to absorb combustion heat. The heated fluid will then return to the radiator through a rubber hose for cooling. An air stream cools the heated fluid (hot water) as it flows into the radiator through the thin tubes.
Modern internal combustion engines are cooled with both water and air, but some engines use either air or liquid to remove the waste heat from the engine.
Special-purpose or small engines are cooled using air from the atmosphere, which makes the system lightweight and relatively less complex. In some engines, heat is transferred from a closed loop of water to the radiator, where cooling is achieved.
Functions of Engine Cooling System
The engine cooling system in automobiles ensures that the temperature of the burning gases (combustion gas) in the engine cylinder is between 1500 and 2000 degrees Celsius. This is above the melting point of the material of the cylinder head and body of the engine. Therefore, if the heat is not dissipated, serious problems and failures will occur with the cylinder material.
The engine cooling system also reduces the temperature of the lubricating oil that lubricates and cools the moving parts. Very high temperatures cause the film of the lubricating oil to get oxidized, which produces a carbon deposit on the surface. This often results in piston seizure.
Because too much heat removal lowers the thermal efficiency of the engine. The system is designed to remove at least 30% of the heat generated at the combustion chamber. A functional cooling system should be able to remove heat at a fast rate when the engine is hot.
Engines are cool during the start; much cooling is not needed so that the working parts can reach their working temperature in a short time.
You should also learn about automatic lubrication systems with this detailed guide!
Components of Engine Cooling System
Below are the components of an engine cooling system in automobiles and their functions:
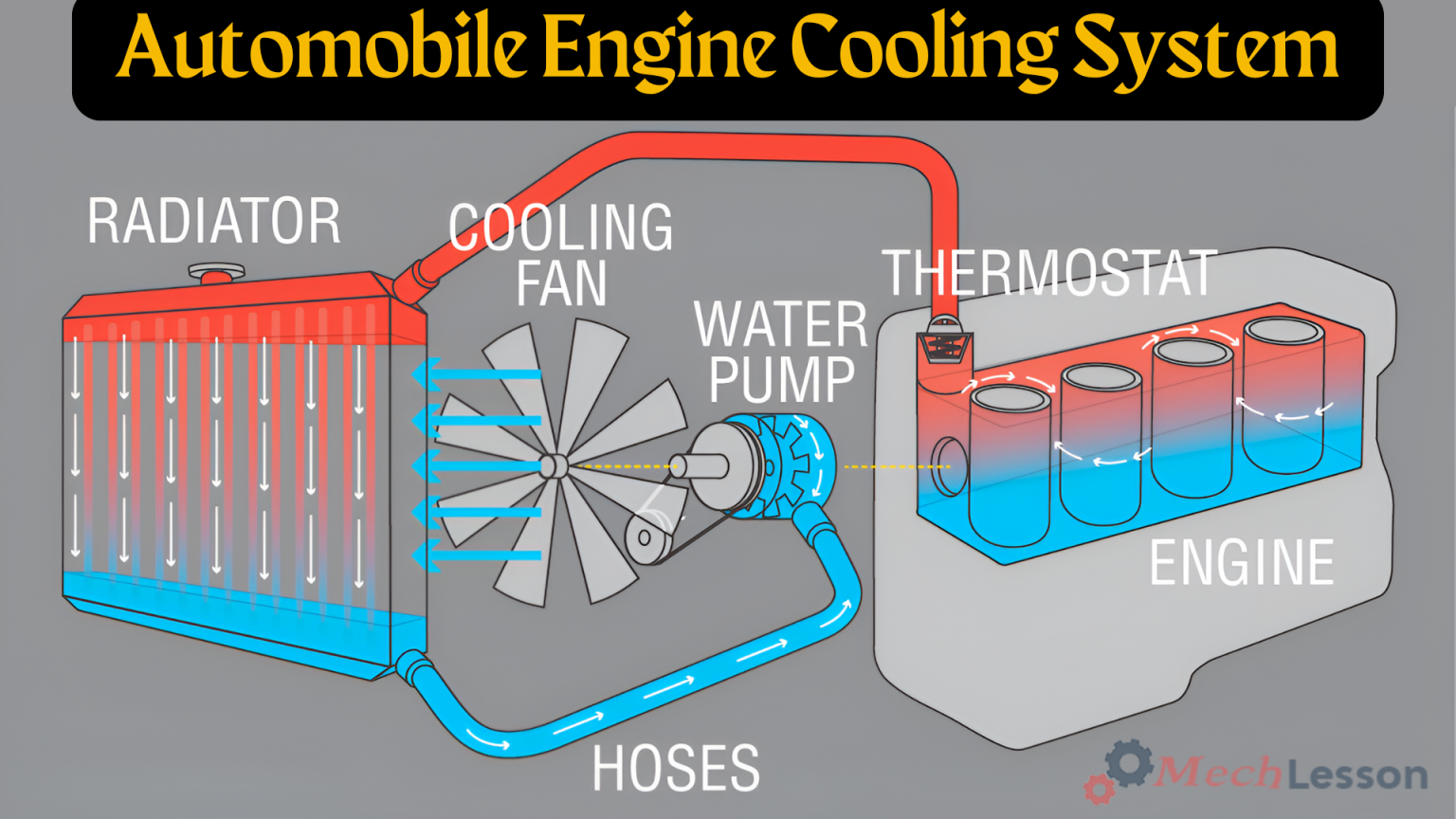
Radiator
This engine cooling part is made up of aluminum tubes and strips that zigzag between the tubes. High-temperature fluid flows inside the radiator through a hose. This heated fluid is then transferred from the tube to the air stream, which is then blown away into the atmosphere.
Cooling Fan
The cooling fan is located a bit after the radiator, which is closest to the engine. The part is designed to protect fingers and direct airflow. It blows air to the radiator to cool the hot fluid while the engine is running, so the fan helps to cool down the temperature of the radiator.
Pressure Cap and Reserve Tank
Radiators are now designed with pressure caps so that pressurized coolant flows out as it expands. Thus, the function of the pressurized cap is to maintain pressure in the cooling system up to a certain point. This cap featured a spring valve calibrated to the correct pounds per square inch (psi). If the pressure is higher than the set pressure points, it opens, and a small amount of coolant bleeds off.
Water Pump
The water pump is another important component of an engine cooling system. It’s mounted on the front of the engine, and it keeps circulating the coolant as long as the engine is working. The part is made of cast iron or cast aluminum and has an impeller blade that pumps the coolant.
Thermostat
A thermostat is simply a valve that senses or measures the temperature of the engine coolant. If the coolant is not hot enough, the thermostat remains closed, but as soon as the coolant temperature reaches some specific temperature, it opens and allows the coolant to flow through the radiator.
Heater Core
A lot of hot coolant serves better purposes for the car interior when required. To achieve this, the cooling system is designed with a heater core that has many lookalikes of the radiator. The component is connected using a pair of rubber hoses to collect and return the coolant from the water pump to the top of the engine.
Hoses
Hoses allow for the complete circulation of coolant from the radiator to an internal engine component and back to the radiator and some associated components. But the main hoses are known as the upper and lower radiator hoses. They are bigger and wider compared with others.
Bypass System
This component works when the coolant in the engine is hot enough to open the thermostat. Thus, it allows the coolant to bypass the radiator and return directly to the engine so the coolant temperature can be balanced. It’s often available as a rubber hose, but some manufacturers use a fixed steel tube.
Learn about oil coolers in this guide!
Cylinder Head Gaskets and Intake Manifold Gaskets
This component also helps the engine cooling system as it securely tightens the mating surfaces of the combustion chamber. It prevents coolant and oil leakage out of the engine or into the combustion chamber. Even though the mating surfaces are precisely machined and tight, coolant can still flow through them. This is why gaskets are employed.
Freeze Plugs
This is a part of the engine that is manufactured with special sand along with molten metal. It molded to the shape of the coolant passages in the engine block. Coolant flows through the part, which is why it must plug into the hole, or else the coolant will pour right out.
Diagram of a Car Engine Cooling System

Types of Engine Cooling Systems
There are two types of cooling systems in internal combustion engines:
Air Cooling System
In air cooling systems, the stream of air radiates and disperses the heat that the engine’s outer components reflect. The fins effectively direct this airstream, which comes from the atmosphere, to the engine parts. The fins are made of metallic ridges, and the size determines the amount of heat that will be blown during the process.
Below are the benefits of engines with air cooling systems:
- The system is cheaper to manufacture.
- It is lighter in weight because the design does not include water jackets, radiators, circulating pumps, or the water itself.
- Less requirement for maintenance.
- The risk of damage from frost, like cylinder jacket cracks or radiator water tubes, won’t occur.
- Air-cooled engines are less complex
You should also learn about wet and dry oil sump system with this guide!
Water Cooling System
So far, we’ve been discussing many types of cooling systems because they are common in automobile engines. Well, they serve two purposes in the working of an engine, which include eliminating excess heat and preventing it from overheating. It also keeps the engine at an efficient working temperature and is economical.
Water cooling systems are of four different types, which include:
- Direct or Non-return System
- Thermo-Syphon System
- Hopper System
- Pump/Forced Circulation System
How A Cooling System Works
The system is made of passages inside the engine block and heads and a water pump that circulates the coolant. It is also made of a thermostat that controls the temperature of the coolant and a radiator cap to control the pressure of the system. The coolant flows to all these spots with the aid of interconnected hoses.
The water cooling system works by transferring liquid coolant through passages in the engine block and heads. The coolant flows from the radiator to absorb excessive heat production during the combustion process. After the coolant receives the hotness, it’s transferred to the radiator through a rubber hose.
As soon as the hot coolant enters the radiator, cooling begins. The air stream entering the engine compartment from the front side of the car is what provides the cooling. After the coolant is cooled, it returns to the engine to carry out the same process. The water pump helps the circulation of coolant to enter the hidden passages. Learn more about car engine cooling systems here!
Learn about oil pump with this detailed guide!
Maintenance Of The Cooling System
An engine’s cooling system is extremely important, so it needs to be maintained to prolong both the engine’s and the cooling system’s lifespan. The most frequent maintenance that can be done is to periodically flush and refill the engine coolant.
As manufacturers will always indicate, using ordinary coolant will cause corrosion, which tends to increase when several types of metal interact with each other. This will cause a scale that eventually develops and begins to clog the thin, flat tubes in the heater core and radiator.
The antifreeze formulation can serve for five years, or 150,000 miles, before replacement. It’s usually reddish and greenish in color. As reverse-flush cooling systems require professional and special equipment, ensure the operation is carried out in the right mechanic workshop.
Conclusion
The engine cooling system plays a critical role in maintaining optimal operating temperature by dissipating excess heat generated during combustion. It includes components such as the radiator, water pump, thermostat, coolant, hoses, and cooling fans, all working together to prevent overheating and ensure efficient engine performance.
A well-maintained cooling system improves fuel efficiency, reduces wear on engine parts, and extends engine life. Regular checks, proper coolant levels, and timely maintenance are key to avoiding breakdowns and costly repairs due to overheating.
You should also learn about fuel pump in this detailed guide!
FAQs on Cooling System
What is the purpose of a vehicle’s cooling system?
It regulates engine temperature by transferring excess heat away from the engine to prevent overheating.
What are the main components of the cooling system?
Radiator, water pump, thermostat, coolant, radiator fan, hoses, and sometimes an expansion tank.
What causes engine overheating?
Common causes include low coolant level, faulty thermostat, broken water pump, radiator leaks, or fan failure.
How often should I check my coolant?
Coolant levels should be checked at least once a month or before long trips. Flush and replace coolant every 2–5 years depending on the manufacturer’s recommendation.
Can I drive with a cooling system leak?
It’s not advisable. Driving with a leak can lead to rapid coolant loss and serious engine damage due to overheating.
What’s the difference between air-cooled and liquid-cooled systems?
Air-cooled systems use airflow to reduce engine heat, while liquid-cooled systems circulate coolant to absorb and dissipate heat via a radiator.