A bevel protractor is a precision measuring instrument used to accurately measure and set angles. Its base is located at the bottom side of the angle, while the blade moves to match the opposing side. This is a common tool in woodworking and metalworking.
Well, in this reading, we’ll explore what a bevel protractor is, its applications, parts, diagrams, types, ranges, and how it works. We’ll also explore its advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s begin!
Learn about the vernier caliper with this detailed guide!
What is a Bevel Protractor?
Just as mentioned earlier, a bevel protractor is a precision measuring tool used in engineering and machining, especially in metalworking and woodworking. It is used for precision engineering and layout work, especially for beveled and angular workpieces.
The instrument features a pivoting blade and graduated dial that give space for precise angle measurement. The device is a circular scale marked with gradations and an arm, typically pigmented, which is why it can take precise measurements and construct angles.
The least count of a bevel protractor is around 5 minutes (1/12th of a degree) or 0.0833 degrees. Its standard unit of measurement in geometry is degrees. Although its modern version incorporates one or two swinging arms for angle measurement with a minimum increment of 5 minutes.
A bevel protractor is essential for tasks that require precise angle measurements, like layout and machining of parts, alignments of machine tools, and creating intricate geometric shapes.
Applications of Bevel Protractor
Bevel protractor is a powerful tool used in engineering, construction, and quality control. Its applications include:
- Bevel protractor is used for precise angle measurement in components, geometric shapes, and workpiece fabrication.
- It is particularly useful for checking V Blocks and measuring acute angles.
- Graduated circular protractor with one pivoted arm, used for marking off angles.
- Bevel protractors are widely used in architectural and mechanical drawing, but usage is decreasing with modern software or CAD.
- The Universal bevel protractors measure angles by mechanical contact.
- It is often used with jigs and other objects for accurate measurements.
- Its standard unit of measurement in geometry is degrees.
- Sophisticated versions incorporate one or two swinging arms for angle measurement.
You should also learn the 5 Types of Precision Measuring Instruments and Their Uses with this detailed guide!
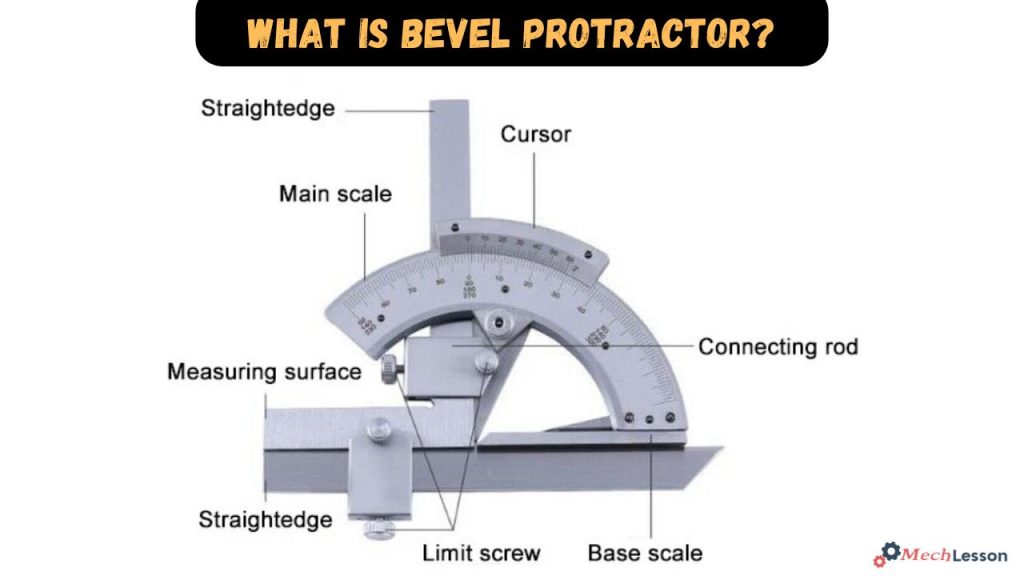
Parts of a Bevel Protractor
Below are the various parts of a bevel protractor:
- Pivotal swivel plate and vernier scale for precise angle measurements.
- Vernier scale, marked at every tenth degree, is crucial for minute angle measurements.
- Dial, the foundational base, hosts the primary scale with a graduated angle measurement range from 0 to 360 degrees.
- Blade, crafted from high-carbon steel, aligns parallel to the stock.
- Blade-lock screw secures the blade at a specific position, especially for determining blade length.
- Stock moves in relation to the blade, causing changes in the angle value displayed on the dial scale.
- Workpiece and blade align during angle measurement for accurate determination.
Diagram

How Does A Bevel Protractor Work?
The Vernier Bevel Protractor is a tool used for measuring the angle between two points on a circular plate. The Base Plate acts as one of the working edges, while the other working edge is the blade held on the circular plate.
The adjustment blade can be rotated along with the circular plate on the main body, allowing the vernier scale to be rotated on the graduated main scale. The Vernier scale has 12 divisions on each side of the center zero, representing 24 divisions. One division equals 60 minutes, while the same portion is represented as 23° on the main scale.
The zero line on the vernier scale moves on the main scale, indicating the reading on the main scale. The Vernier scale reading coincides with the divisions on the main scale, and using these values and the least count of the Vernier bevel protractor, the reading can be calculated.
How to Use it
To use the Bevel Protractor, unscrew the large clamp on the front part of the protractor, allowing the blade to swivel. Align the base on one side of an angle and swivel the blade for the other side. Tighten the clamp and spot the zero on the vernier scale, which is smaller on the inner side of the protractor. Read the number of degrees on the main scale, directly above the zero on the vernier scale.
Learn about micrometer screw gauge with this detailed guide!
Range of Bevel Protractor
The bevel protractor is a versatile tool designed for precise measurement of angles, with a range of 0 degrees to 360 degrees. It features a beam, graduated dial, and a blade connected to a swivel plate. The swivel plate’s edge marks coincide with the 0 lines on the graduated dial when parallel.
The reading for angles between the beam and blade is based on the graduation number on the dial, while for angles over 90 degrees, the dial’s number must be subtracted from 180 degrees. The bevel protractor is particularly useful for precise testing and establishing close tolerances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bevel Protractor
Benefits:
- High accuracy in angle measurement.
- Easy to use and read.
- Durable and suitable for a wide range of angles.
- Essential for quality control, inspection, layout and machining tasks.
Limitations:
- Limited measurement range
- Operator skill limitations
- Potential parallax error.
- Modern models incorporate anti-parallax features.
- Not suitable for hard-to-reach or confined spaces due to size.
Conclusion
A bevel protractor is a precision measuring instrument used to measure and lay out angles accurately, especially in metalworking, machining, and drafting. Its ability to measure angles with fine resolution—often to the nearest 5 minutes or 1/12 of a degree—makes it invaluable for tasks requiring high angular accuracy.
With components like a vernier scale, adjustable blade, and dial, the bevel protractor offers both versatility and precision, making it essential for quality control and inspection in engineering applications.
You should also learn about 30 Types of Measuring and Marking-out Tools and Their Uses with this detailed guide!
FAQs on Bevel Protractor
What is a bevel protractor used for?
It’s used to measure and mark precise angles, typically in machining, metalworking, and engineering drawings.
How accurate is a bevel protractor?
Vernier bevel protractors can measure angles up to ±5 minutes (1/12°), offering high precision.
What are the main parts of a bevel protractor?
Key parts include the base, adjustable blade, protractor dial, vernier scale, and locking devices.
What’s the difference between a regular protractor and a bevel protractor?
A regular protractor is simpler and less precise, while a bevel protractor includes a vernier scale for greater accuracy and is used in technical work.
Can a bevel protractor be used to check existing angles?
Yes, it can measure internal and external angles on existing parts for inspection or replication.
Is it suitable for both internal and external angles?
Yes, the adjustable blade allows measurement of both internal and external angles with ease.