Similar to the indirect injection system, direct injection introduces fuel into internal combustion engines. It is common in gasoline (petrol) engines, but it is now also used in diesel engines to provide similar performance characteristics.
Gasoline engines use direct injection systems to boost efficiency, optimize power output, and minimize exhaust emissions.
In this reading, we will explore the concept of direct injection, including its functions, diagrams, operation, and components. We’ll also explore the advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s begin!
Learn about the fuel injection system with this guide!
What is a Direct Injection System?
A direct injection system is a fuel injection process that allows fuel to be injected directly into the top of the piston in the combustion chamber.
A gasoline direct injection (GDI), which is also known as petrol direct injection (PDI), is a mixture formation system for internal combustion engines that work with gasoline (petrol).
The combustion chamber receives a direct injection of fuel. In 1925, Mitsubishi introduced this direct gasoline engine as a low-compression truck engine.
The engine was quite popular in German cars during the 1950s, as it utilized a Bosch mechanical GDI system. It became more popular when introduced in an electronic GDI system in 1996 by Mitsubishi.
However, the automotive industry has widely adopted the system recently.
Diesel engines are the first to use the direct injection principle. It’s a basic type of fuel injection system used in diesel engines. A simple DI diesel engine directly injects fuel into the combustion chamber above the piston.
The compression of air inside the chamber raises the temperature above 400 degrees Celsius, which then ignites the diesel fuel immediately after it’s sprayed directly into the combustion chamber.
Also learn about the indirect injection system with this guide!
Functions of a Direct Injection System
Below are the functions of a direct injection system in automotive engines
- To burn fuel efficiently
- To produce more power
- Cleaner emissions, and
- Increased fuel economy.
Diagram
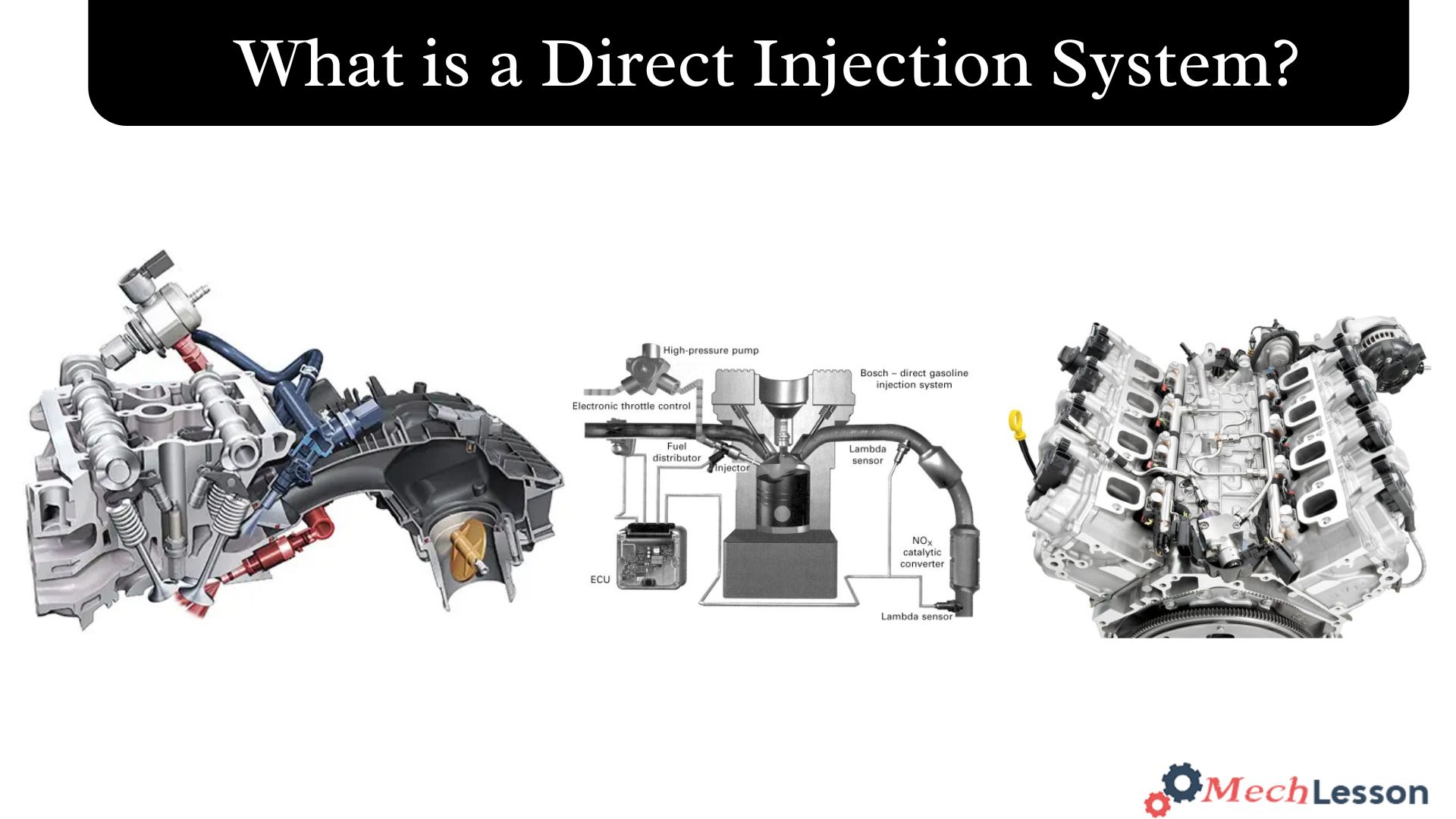
Components of a Direct Injection System
Below are the components of a direct injection fuel system:
- Injectors
- Fuel injection pump
- High-pressure lines
- Fuel feed pump
- Fuel filter
- Governor
Learn about the air injection system with this detailed guide!
Working Principle
The workings of a direct injection system are less complex and can be easily understood. Conventionally, gasoline engines work by sucking a mixture of gasoline and air into the cylinder.
A piston compresses this mixture, and a spark from a spark plug ignites it, causing an explosion. This resulting explosion moves the piston downwards, producing power.
Traditionally, in an indirect fuel injection system, gasoline and air are pre-mixed in a chamber outside the cylinder known as the intake manifold. Now, in a direct injection system, air and gasoline are not pre-mixed. Instead, the intake manifold allows the air to enter, and the cylinder receives the direct injection of gasoline.
The “charge mode” distributes fuel into the combustion chamber. This charge includes homogeneous charge mode and stratified charge mode. In the homogeneous charge mode, the manifold injection evenly mixes the fuel with the air throughout the combustion chamber.
Furthermore, in the stratified charge mode, a zone with a higher density of fuel surrounds the spark plug, while a leaner mixture, which has a lower density of fuel, is located farther away from the spark plug.
In a direct injection system, there are common techniques for creating a desired fuel distribution throughout the combustion chamber. These injection methods include spray-guided, air-guided, or wall-guided injection.
Also learn about the multi-point fuel injection system with this detailed guide!
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
Below are the benefits of direct injection in gasoline engines:
- Low maintenance
- High low-end torque
- Sturdiness
- Longer engine life
Disadvantages:
Despite the advantages of direct injection, some limitations still occur. Below are the disadvantages of direct injection in gasoline engines:
- Lower engine speeds and BHP
- Working is Sluggish
- Higher noise, vibration, and harshness levels
- Heavier engine components
- No valve cleaning action
- Producing peak power at high engine speed is limited
