The use of technology and systems to automate a production process with the ultimate goal of lowering costs and boosting productivity is known as factory automation. The level of automation can range from end-to-end automation, which eliminates human intervention, to single-operation automation.
The implementation of factory automation is possible at any stage of the manufacturing process, including material quantity control, production, assembly, and packaging and dispatch.
In this reading, we’ll explore what factory automation is, its types, diagram, benefits, and cost of implementation.
Let’s get started!
Learn about Laminated Object Manufacturing with this detailed guide!
What Is Factory Automation?
Factory automation is the process of automating a manufacturing process using systems and technology with the ultimate goal of lowering costs and boosting productivity. It is a compelling method to improve quality, efficiency, safety, sustainability, and security in today’s rapidly evolving industrial world.
Basically, factory automation opens the door to greater profitability and improved performance as competition increases and margins are squeezed. Also, the degree of automation can range from end-to-end automation, which eliminates human intervention, to single-operation automation.
Any stage of the manufacturing process, including material quantity management, production, assembly, packaging, and delivery, can benefit from the implementation of factory automation. Many sectors have started embracing industrial automation systems in an effort to boost workplace productivity and efficiency as a result of modernization and technological advancements.
The majority of industrial manufacturers are already aware of the increasing use of industrial automation systems throughout the world, but many are not well-versed on the various kinds of automation systems and how each might help a business.
Automated conveyor systems and warehouse automation are two examples of the many forms of automation that can be useful to many industries.
Types Of Factory Automation
Several things will affect the type of factory automation that is best for your business. These include the goods being made, the amount being made, and the budget. If you have the right customized factory software development for your firm, any type of manufacturing automation can improve productivity, quality, and cost.
Fixed Automation
The purpose of fixed automation systems, sometimes referred to as hard automation, is to repeatedly perform a single set of tasks. Usually, continuous flow systems or discrete mass production require fixed automation systems. An automated conveyor belt used in the automobile industry is an example of a fixed automation system; it increases efficiency by moving goods with little effort.
Programmable Automation
Commands from a computer program operate programmable automation systems. As a result, the automated procedures can change according to the commands that the designer’s code sends to the computer.
The utilization of programmable automation is prevalent in environments where identical items are manufactured using identical automated processes and instruments. Paper and steel rolling mills, for example, use similar operations to produce a wide range of products.
Learn about Modular Construction with this detailed guide!
Flexible Automation
When working with multiple goods in a batch, flexible automation—sometimes called soft automation—is the way to go. Each piece of equipment receives instructions from a computer operated by a human, allowing updated code to be sent for more flexible production.
Flexible automation’s main benefit is that it eliminates the need for additional time to set up the equipment between batches, allowing for quick and automatic product modifications. Additionally, it is commonly used in the food processing, paint, and textile manufacturing industries.
Integrated Automation
With integrated automation systems, production facilities are fully automated with little assistance from humans. You may use computers to do all three of these things: design the parts, test them, and then make them. Integrated automation works for batch and continuous manufacturing.
Robotic Process Automation
The use of software robots to automate processes that are normally handled by people is known as robotic process automation (RPA) in the manufacturing industry.
Items such as data entry, customer service, financial transactions, and even more intricate tasks like inventory management, quality control, and assembly line processes may be included. Despite being a relatively new technology, RPA is growing in popularity as companies search for methods to cut expenses and increase productivity.
Diagram Of Factory Automation
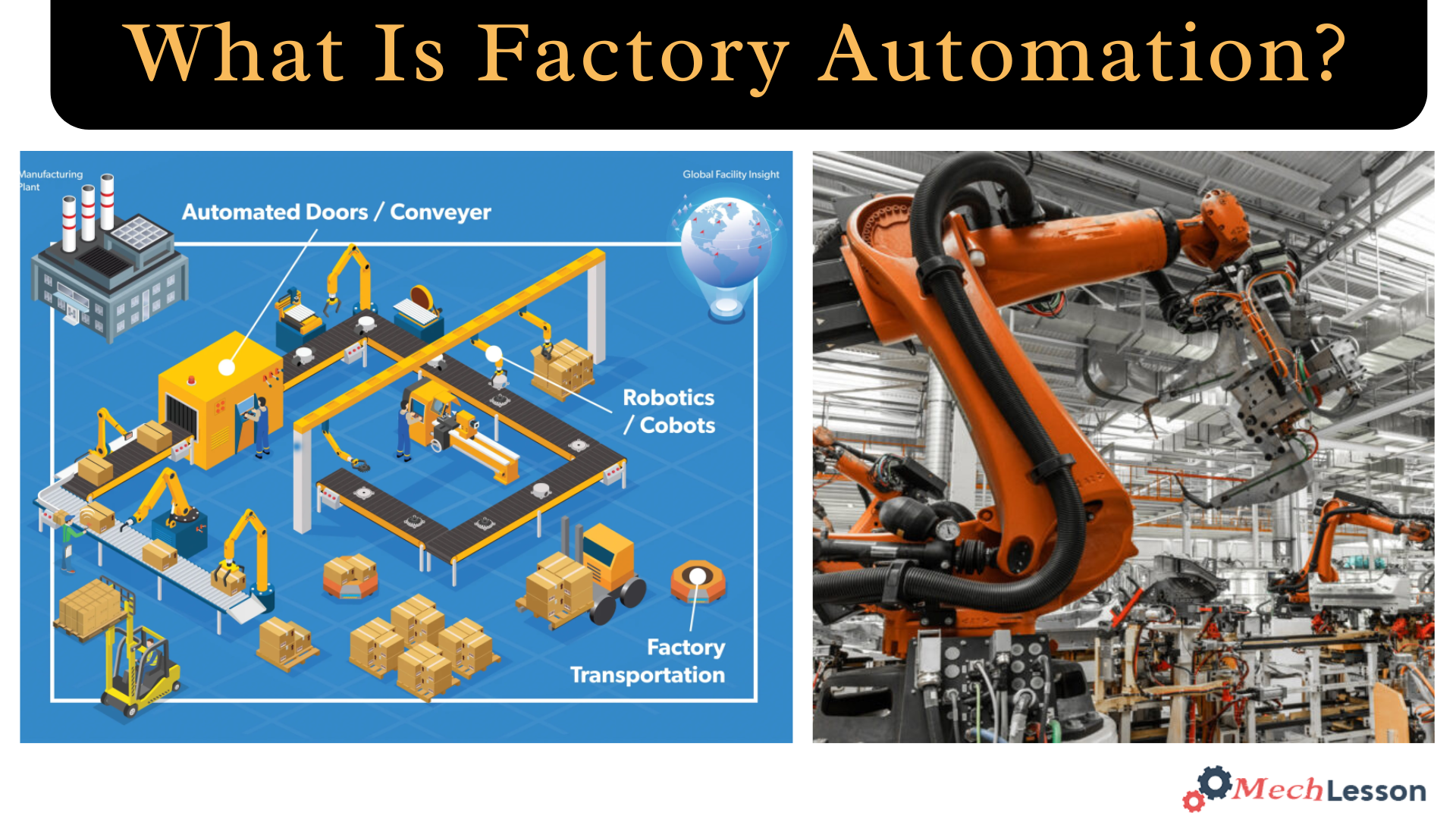
Learn about Digital Manufacturing with this detailed guide!
Benefits Of Factory Automation
Factory automation offers countless benefits in the industry in which it is being used. Some of its major benefits include:
Better Quality
Human error is minimized through the continuous monitoring and adjustment of repetitious activities.
Enhanced Efficiency
Increased productivity must be one of the main goals of manufacturing automation. The benefits of possible round-the-clock production and simplified processes are substantial.
Reduced Waste
Waste is reduced by better planning, automated production, and increased repeatability.
Improved Safety in the Workplace
An automated system with built-in shutdown and reduced human interaction can greatly reduce risks and make the workplace safer.
More Reliability
Automated processes have a number of advantages, including higher quality and better predictability in outputs due to their repeatability, which in turn lowers differences caused by human error.
Reduced Expenses
This is the primary motivation for factory automation, combining all the other elements. After the initial investment in automating the system, the profitability is greatly increased due to increased production, less downtime, decreased training costs, and the elimination of accidents.
Implementation Cost Of Factory Automation
Automation of a production line typically requires a large initial investment due to the specialized nature of the equipment and the fact that it is often custom-built for each line. The design could also be expensive because it is crucial to create a design that can grow with the throughput when achievements are made.
When designing a system, it is helpful to work with an experienced automation engineer who can identify current technologies and incorporate them whenever possible. This will help keep costs down.
Additionally, there will be expenses associated with either recruiting and hiring individuals to oversee and manage the manufacturing line or with enhancing the skills of current operators to better keep an eye on the operation.
Learn about Difference Between Fabrication And Manufacturing with this detailed guide!
FAQs
What is meant by factory automation?
The term “factory automation” refers to the integration of robotics into all stages of production. Automation in manufacturing typically makes use of more complex systems that incorporate technologies like hydraulic systems, pneumatic systems, and robotic arms.
How do you automate a factory?
These include equipment software, factory floor robots, and technologies that streamline, data-driven production processes. Moreover, the main objectives of manufacturing automation are to boost production capacity, cut expenses, and promote efficiency.
What’s the difference between factory automation and process automation?
Factory automation maintains the machinery that produces items, whereas process automation supervises the wider systems that handle these products. While these automation methods may appear to be similar, it is crucial to comprehend their core distinctions prior to implementing any automation system.
What are the 5 levels of automation in factory operations?
Manual Control, Basic Automation, Advanced Automation, Integrated Automation, and Intelligent Automation are the five levels of factory automation that manufacturers can follow to improve their systems.
What is PLC in automation?
In industrial automation, a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a kind of ruggedized computer. These controllers have the capability to automate a wide range of processes and machine functions, including entire production lines.

