Arc welding is a popular joining technique that uses an electric arc to create heat of high temperatures to melt and weld metals.
The metal manufacturing industry widely uses it because of its versatility and reliability, which results in strong bonds between different metal parts.
An electrode conducts current through a workpiece during the working process to fuse two pieces together. The electrode used may be consumable or non-consumable depending on the process; it can use a shielding gas.
Arc welding produces an electric arc that is used to melt base metal and filler wires, which create a pool of molten metal that solidifies and fuses the parts together. Electricity is passed from the power source through an electrode to the workpiece.
Well, in this reading, we’ll explore what arc welding is, its applications, parts, diagrams, tools, machines, and how it works. We’ll also explore the safety precautions, advantages, and disadvantages of arc welding.
Let’s begin!
Related: What is Welding Ventilation? Its Types & Their Examples
What is Arc Welding?
Arc welding is a welding process that uses an electric arc to create enough heat to melt metal; it cools and results in bonding. This fusion welding uses an AC or DC power supply as its source of heat.
The power supply creates an arc between a consumable or non-consumable electrode, passing either AC or DC current to the base material.
In other words, it is a type of welding process that uses a welding power supply to generate an electric arc between a metal stick (electrode) and the base metal. It melts the metals at the point of contact.
There are choices and stability for welders to use direct or alternating current and consumable or non-consumable electrodes, depending on the factors considered.
Arc welding was first developed in the late part of the 19th century and used in shipbuilding during the second world war. This process today becomes one of the fastest and most common welding processes in fabrication companies.
Applications of Electric Arc Welding
Arc welding is widely used in many areas today as it comes in different types. Arc welding is used in various applications, including:
- Shipbuilding
- Construction industries
- Automotive industries
- Mechanical industries.
Here are some other applications of arc welding
- Aerospace industries use gas tungsten arc welding in many joining areas, most especially sheet metals
- Most fabrication industries use GTAW for welding thin workpiece, especially nonferrous metals
- Arc welding is used extensively in manufacturing space vehicles
- It is used for welding parts of small diameter, thin wall tubing, making it applicable in bicycle industries
- The GTAW types of arc welding are used to make nut or first-pass welds for piping of various sizes
- It is used to repair tools or dies, mostly on parts made with aluminum and magnesium
- GTAW welds are highly resistant to corrosion and cracking over a long period of time; they are used where these qualities are needed.
Related: Welding Terms And Meaning You Should Know
Arc Welding Tools & Equipment
The arc welding tools and equipment mainly includes AC machine, or DC machine, Electrode, Electrode Holder, Cables, Connectors for cable, Earthing clamps, Chipping hammer, Helmet, Wire brush, Hand gloves, Safety goggles, sleeves, Aprons, etc.
Arc welding power source:
Power sources for arc welding come in two types: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). These machines have their own advantages; AC power supply is used where electricity supply is available.
Well, the advancement of arc welding has brought about a reduction of supply voltage from 200-400 volts to 50-90 volts. Here are some factors to be considered when selecting an arc welding power supply.
- Available power source
- Electrode type
- Require output
- Efficiency
- Initial and running cost
- Duty cycle
- The available floor space area
- Operation type
- Versatility of equipment
Welding cables
welding cables are made of aluminum or copper cables insulated with either red, black, or blue color. It is used for connecting or transferring current from the power source to the electrode holder and produces an arc from the workpiece back to the power source.
Electrode holder
The electrode holder’s design allows for manual electrode clipping to receive current and generate an arc. It is available in sizes that range from 150 to 500 amps
Welding electrode: an electrode is a piece of wire or rod of metal. We classify the arc welding electrode into consumable and non-consumable electrodes.
The consumable electrode is a bare and coated electrode, while the non-consumable electrode is a carbon or graphite electrode and tungsten electrodes. All these electrodes are used for specific arc welding jobs.
Chipping hammer
We use this arc welding equipment to reduce slag that occurs during welding. The equipment consists of a wooden or rubber handle and a metal flat punch head. To use it, strike off the slags on the flat head of the hammer.
Wire brush
These types of arc welding tools are used to clean dirt and to wipe away rust from the metal before welding. it is made of a wooden handle and wires on its surface.
Hand screen
A hand screen is used for supervising weld beads and for protection of the eye.
Protective clothing
These types of arc welding equipment are used to protect the body of the operator; protecting clothing includes an apron, booth, goggles, etc.
Related: What is Under-Water Welding? Why is Its Dangerous
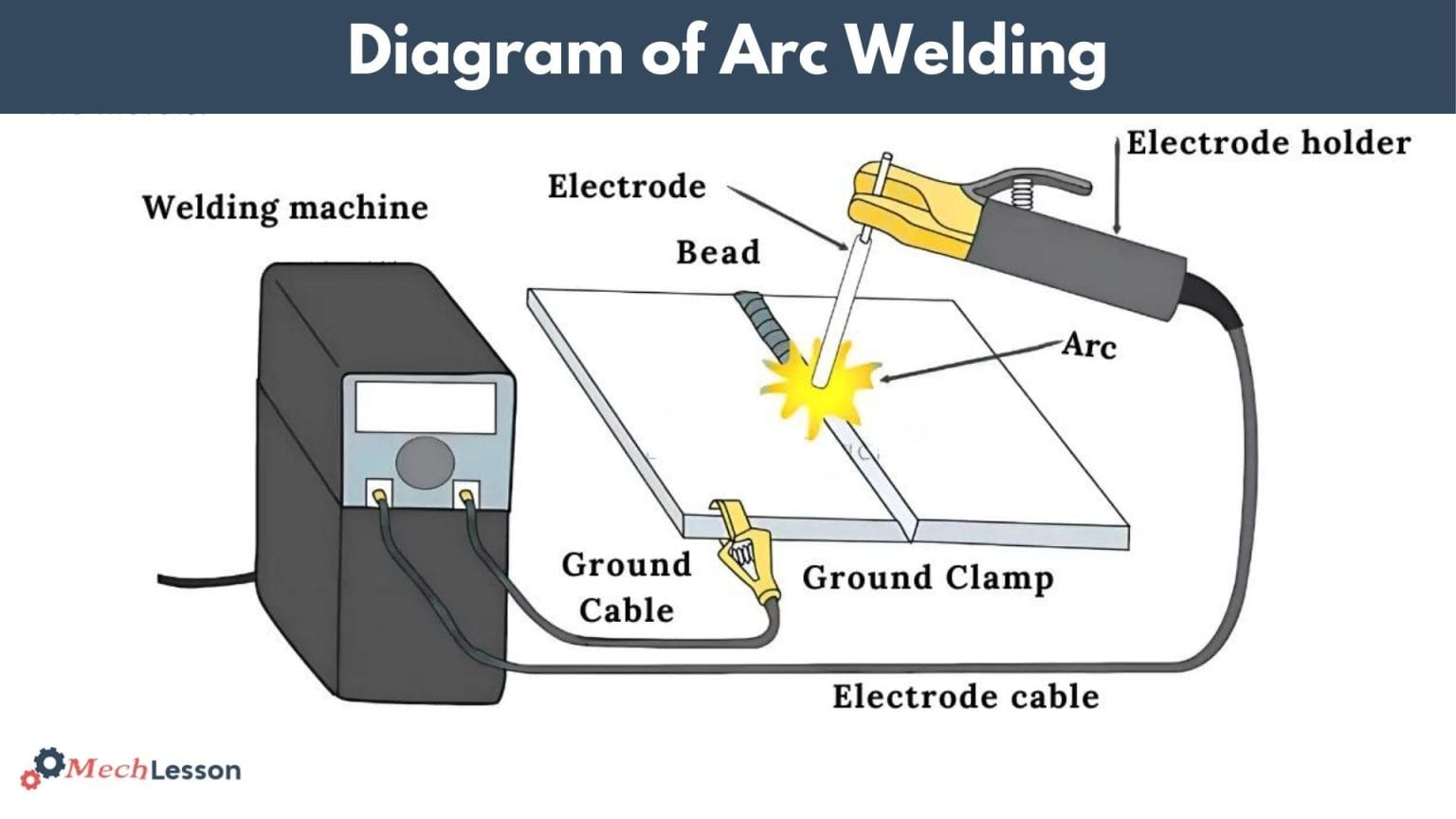
Parts and Diagram of Arc Welding

Types of Arc Welding
The various types of arc welding include Plasma Arc Welding, Metal Arc Welding, Carbon Arc Welding, Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, Gas Metal Arc Welding, Submerged Arc Welding, SMAW (shielded metal arc welding), FCAW (Flux Cored Arc Welding), ESW (Electro-Slag Welding), and Arc Stud Welding
1. Metal Inert Gas Welding (MIG)
These types of arc welding are also known as gas metal arc welding (GMAW). It uses a shielding gas to protect the base metals from defilement.
2. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
These types are also known as manual metal arc welding (MMA or MMAW), flux shielded arc, or stick welding. it is achieved by striking the arc between the metal rod (electrode flux coated) and the workpiece.
The metal rod and workpiece joint surface melt and form a pool. These two contact forms, gas and slag, help to protect the weld pool from the surrounding atmosphere.
That is why this perfect for joining ferrous and nonferrous metals with a range of material thickness in all positions
3. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
This arc welding serves the alternative purpose of SMAW, FCAM, using a continuous feed of consumable flux core electrode and a constant voltage power supply. This method ensures a consistent arc length. These types of arc welding can use a shielding gas or gas created by the flux to provide protection from contamination.
4. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
This process also uses continuous-fed consumable electrodes and a blanket of fusible flux. When molten, it becomes conductive and provides a current path between the parts, the current, and the electrode.
Flux also prevents spatter and sparks while suppressing fumes and ultraviolet radiation.
5. Electro-slag Welding (ESW)
We use these types of arc welding to vertically weld a thick plate above 25mm in a single pass. It works on an electric arc before flux helps to extinguish the arc.
This flux melts immediately after the wire consumable is fed into the molten pool. It creates a molten slag on top of the pool.
6. Stud Arc Welding (SW)
This arc welding process is similar to flash welding; it is used to join nuts or fasteners with a flange and nubs that melt in order to produce the joint to another metal piece.
7. Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG)
This consumable arc welding is known as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). It uses a tungsten electrode to create the arc and inert shielding gas to protect the weld and molten pool against atmospheric contamination.
8. Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)
Plasma arc welding is similar to TIG welding. it uses an electric arc of a non-consumable electrode and an anode, they are placed within the body of the torch. The electric arc produces the plasma.
This arc is also used to ionize the gas in the torch, which is pushed through a fine borehole in the anode to reach the base metal. This separates the plasma from the shielding gas.
Arc Welding Electrode
Arc welding can be categorized into two types: non-consumable (non-fusible) electrode type (TIG welding) and consumable (fusible) electrode type (shielded metal arc welding). The type of electrode used depends on the specific welding method.
Arc welding involves the use of consumable and non-consumable electrodes. Consumable electrodes conduct current, supply filler metal to joints, and melt the metals under welding.
This type is commonly used in steel product manufacturing. Non-consumable electrodes, on the other hand, are made of material that is not melted during the weld, such as tungsten.
Related: What is Under-Water Welding? Why is Its Dangerous
How Does Arc Welding Work?
Electric arc welding needs to be set up and prepared before you know how it works. The welder should be well dressed and the equipment should be arranged. Two cables are from an AC or DC power source; one of them is fixed to the electrode holder.
The other cable serves as earth, which transfers current back to the welding machine. The type of welding determines whether the electrodes are consumable or non-consumable.
The thickness of the case metal will determine the adjustment of the power supply to the arc.
The arc from the AC or DC power supply creates an intense heat of around 6500 degrees Fahrenheit, melting the metals between their joining spot. Remember the earth cable is placed in any part of the base metal but in such a way that it touches both metals.
The electrode carrying current sparks to the base metal at first, before it is placed close to the workpiece. The above process is done at a close distance to produce the arc. At this point, the arc obtained produces intense heat, which melts the work below the arc and forms a weld pool.
Filler material may be required in certain cases to achieve greater joint strength or to fill a workpiece. If necessary, we add it to the weld pool.
The metal reacts chemically with oxygen and nitrogen in the air when exposed to the arc heat at high temperatures. It produces a protective shielding gas or slag, helping to minimize the contact of molten metal with air. The weld forms when it cools, producing a metallurgical bond.
Related: 15 Different Types of Welding and Their Uses
Advantages of Arc Welding
Below are the benefits of arc welding:
- The welding equipment is portable, making it easy to transport for outside jobs
- It has the ability to weld on porous and dirty metals
- Its equipment is inexpensive
- It is a fast welding process when compared to others
- Its operation can be performed during wind or rain
- It offers strong joint
- Arc welding beads can be used to create designs on fine metals
- Its power supply can be used where there is electricity and the alternative can be used if there is no electricity but a generator.
Disadvantages of Arc Welding
The following are the limitations of arc welding:
- An increase in project costs as wastage is inevitable during the process
- The well trained and skillful operator is needed for the task
- Not all thin metals can weld on arc welding
Related: MIG vs Stick Welding: Choosing the Best Method for Your Needs
Safety Precaution in Arc Welding
Arc welding is a hazardous process that uses an electric arc to create high temperatures, heat, and melt metal workpieces. Safety precautions are crucial in arc welding, including personal protective clothing, environmental safety, and operation and equipment safety.
Operators should wear protective clothing such as long-sleeve jackets, heavy leather gloves, helmets with dark faceplates, and safety boots to protect their bodies from heat, flames, and sparks.
Modern welders are protected from ultraviolet light due to auto-darkening elements and a thick safety booth.
Environmental safety is crucial in arc welding, as it produces dangerous gases that can cause the surrounding air to break down. Proper ventilation is necessary to protect welders from these gases.
The environment should be well-ventilated, with ample natural air entering the workplace. Tools and equipment should be kept in the right place, and jobs should be kept away from walkways.
Operation and equipment safety is essential in arc welding, with the welding power source kept away from sun, water, grease, and oil, and the welding machine not being a bridge.
Related: What is Gas Welding? Its Diagram, Types & How it Works