A car chassis supports the loads of the engine and transmission as well as other components and occupants. Maintaining the car’s shape helps keep it rigid and prevents deformation when it is in operation.
The chassis is one of the most important parts of a vehicle that needs to be examined, It is a sturdy metal frame that is capable of carrying a whole load of a car in a static or dynamic condition.
In manufacturing industries, a chassis is labeled as the backbone of the vehicle and describes the frame rod as members, making some part to be mounted on it.
The chassis consists of one main rigid part that allows other components like the engine, transmission, shock absorber, wheel and steering, and other parts of the car.
The chassis is designed to offer appropriate strength, strong enough to bear loads. In this reading, we’ll explore what a car chassis is, its diagram, functions, parts, and its types.
Let’s get started!
Related: What is Engine Mount? Its Causes & Replacement Cost
What is a Car Chassis?
A car chassis is a load-bearing structure that supports the load of a vehicle. In other words, the term “chassis” should be used to describe the portion of a car’s structure that carries weight.
The vehicle’s horizontal segment is what joins the other parts of the construction together. The chassis is a group of mechanical parts that enable the drive unit to transmit power to the wheels.
Additionally, the materials utilized in this area of the vehicle’s architecture have a significant influence on how the car drives.
Braking, steering, drive, and suspension systems are just a few of the systems that are part of the chassis and are crucial to how the car works.
All types of vehicles have chassis, including a two-wheeler, car, truck, or even some other designed mechanism.
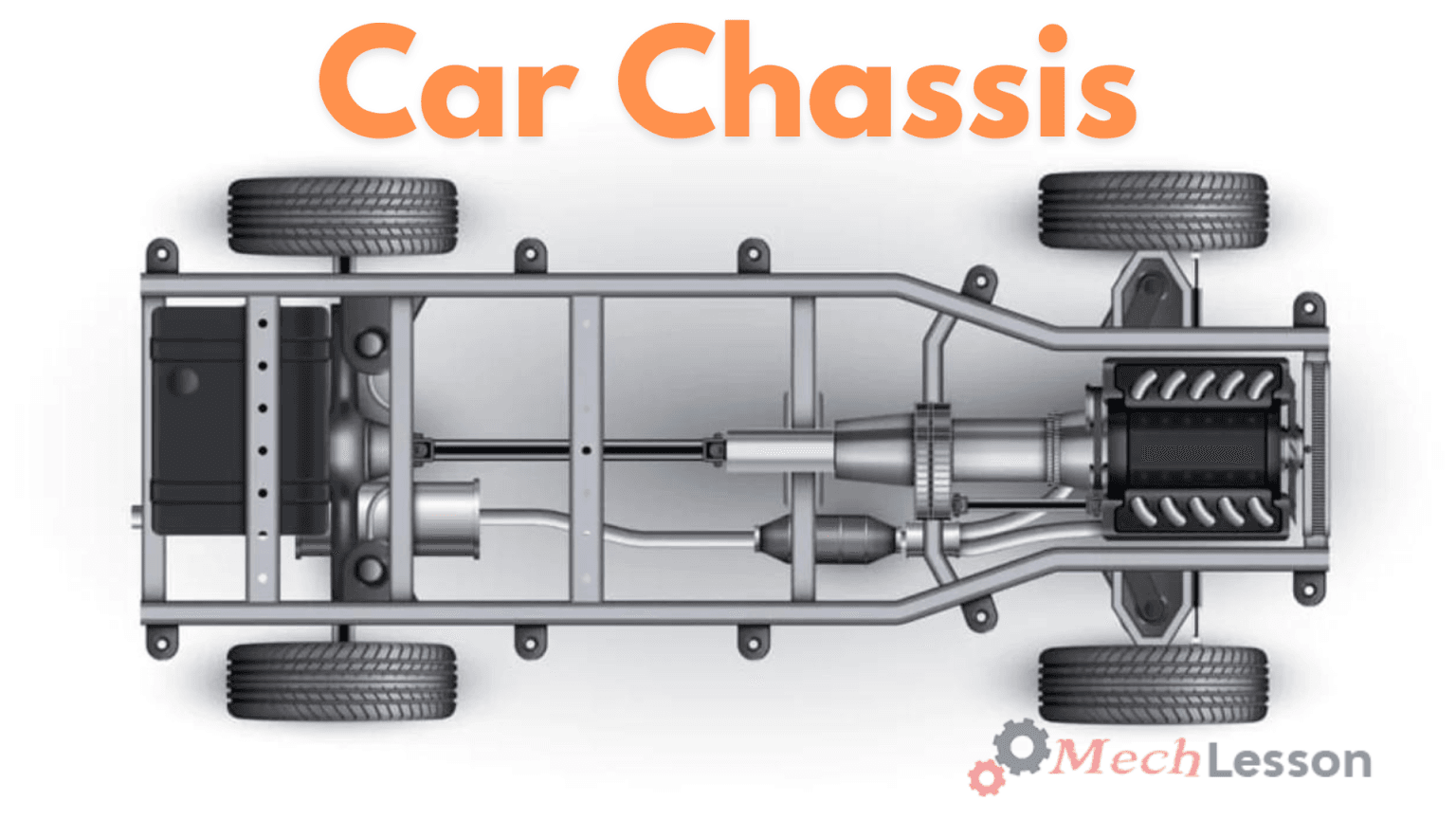
Diagram Of A Car Chassis

Related: What Is Car Suspension System? Its Diagram, Types, And How It Works
Functions Of a Chassis
The functions of a car chassis are as follows:
- It provides space for mounting other necessities like the engine, brake, etc. to the vehicle.
- It supports and bears the load of the vehicle.
- The chassis withstands the stresses arising due to bad road conditions.
- It also withstands stresses during braking and acceleration of the vehicle.
Commercial vehicles manufactured as of 2015 till date are made of light metal materials, especially sports cars for fast speed. The chassis on them are still made sturdy for proper balance.
A rolling chassis is a frame with complete parts attached to it to get it ready in working condition. When an engine transmission system, axles, tires, etc. are fitted to a chassis, it is known to be a running chassis or running gears.
Parts of a Car Chassis
The following are the common car parts associated with a car chassis:
Transmission
The purpose of the transmission, a part of the car’s chassis, is to control engine output. This portion is highly helpful when the car is in a situation that calls for a lot of torque or when the car needs to accelerate quickly.
By altering the ratio of the displacement between the gears, the gearbox of the car can assist in carrying out these tasks.
Universal Joint
Because the axle is under the suspension and the transmission is on the car body, the components between the transmission and the rear axle of the vehicle must have different heights.
As a result, the car requires more parts in order for the propeller to operate without interference.
A universal joint is a part of the car’s chassis that connects torsional moments coming from any angle or direction.
This typically consists of two pieces, one each behind the front axle and transmission.
Garden
The axle is a part of a car’s chassis that separates the rotations of the left and right wheels.
Recognizing this will allow you to adjust how far the left and right wheels travel when the car turns to the left. One of the wheels may slip and wear if it is not recognized.
Rear Axle
This part, which resembles a shaft and connects the axle to the axle, is necessary. An axle bearing the automobile body will have a wheel bearing attached to it at the other end.
Rigid axles and independent axles are the two types of axles commonly seen in cars.
Related: What is Rack and Pinion? its Diagram and How it Works
Steering System
The steering system not only steers the front wheels, but it also facilitates driving. This technology allows the driver to turn the steering wheel with minimal effort. Power steering comes in two types: hydraulic and electric.
The hydraulic type will use the hydraulic compressive force it gets from the steering pump to push the steering rack.
An electric motor will be used to operate the steering rack directly for the electric types.
Clutch
The clutch, which connects and disconnects the engine speed from the gearbox softly, is one of the parts of the car chassis. When you are driving or stuck in traffic, a clutch is helpful. The clutch can smooth down the gear-shifting procedure.
The clutch lining is located in between the flywheel and pressure plate, two rotating metal elements that make up this component.
Spring
Another component of the suspension system is the spring. The spring’s job is to soften the impact of potholes on the car and to reduce road vibrations.
The typical material for springs is pliable steel with a threaded construction.
Shock Absorber
Springs and shock absorbers work differently. It is incapable of withstanding external pressure.
However, while the spring is in use, this part can absorb any resulting shock. This occurs as the car drives over a pothole and the spring absorbs the pressure that builds up.
Stabilizer Bar
Only the free or independent suspension system contains this one component. To prevent the left and right wheels from being too far apart, a stabilizer is utilized.
This is due to the independent suspension system’s ability to provide a significant rolling effect due to the presence of a non-supporting wheel.
Braking System
The car’s speed can be greatly reduced thanks to the braking mechanism. This system works by converting the rotational energy of the wheels into heat energy through the use of friction.
Two materials made of iron and asbestos will rub against one another in this arrangement.
Wheels and Tires
Wheels and tires are the last items you’ll discover in a car’s chassis. The purpose of this component, which is typically found near the end of the powertrain, is to transform the rotational energy into usable power for the vehicle.
Related: What Is Manual Transmission System? Its Parts and How It Works
Type Of Car Chassis
The following are various types of car chassis:
Tubular Space Frame
A steel pipe-shaped chassis known as a tubular space frame is used to directly shape automobiles in accordance with their construction. The caliber of the welded joints on this particular chassis will determine its strength.
Because of its toughness, this chassis is thought to be the greatest. Due to this advantage, racing cars frequently use this particular chassis.
Ladder Frame
A chassis known as a ladder frame resembles a ladder. This chassis is ideal for use as a foundation for vehicle engine mounts and other components, despite its unusual design.
This chassis is often built of steel that is symmetrical and has a beam shape in some places. Additional joints and cross members have been added to strengthen this section. SUV automobiles typically employ this particular chassis.
Backbone Chassis
The backbone chassis resembles a single primary skeleton in appearance. Its position as it crosses the vehicle’s center will link the front and back of the car.
A single chassis is another name for a backbone chassis. Numerous negative aspects of this chassis exist, including its exorbitant cost.
Monocoque Chassis
A monocoque chassis is one that melds with the vehicle’s body. The outside of the car, which serves to cushion the interior from crashes, is a component of the chassis.
Typically, the chassis is composed of strengthened composite steel so that it may serve as the automobile body’s frame. The primary need for chassis material is that it must be robust in order to withstand the weight of the vehicle.
Aluminum Space Frame
The aluminum space frame looks like a monocoque, but its chassis is made of aluminum instead of steel.
On the other hand, monocoque chassis usually use steel plate sheets. This chassis is lighter than the monocoque when weighed side by side.
Related: What is An Engine? It’s Diagram, And How It Works
Car Chassis Video
Bottom Line
A car chassis serves as the foundational backbone of a vehicle, playing a critical role in managing the forces and stresses encountered during various driving conditions.
When navigating rough roads or accelerating, the suspension system relies on the chassis to endure these challenges, ensuring stability and performance.