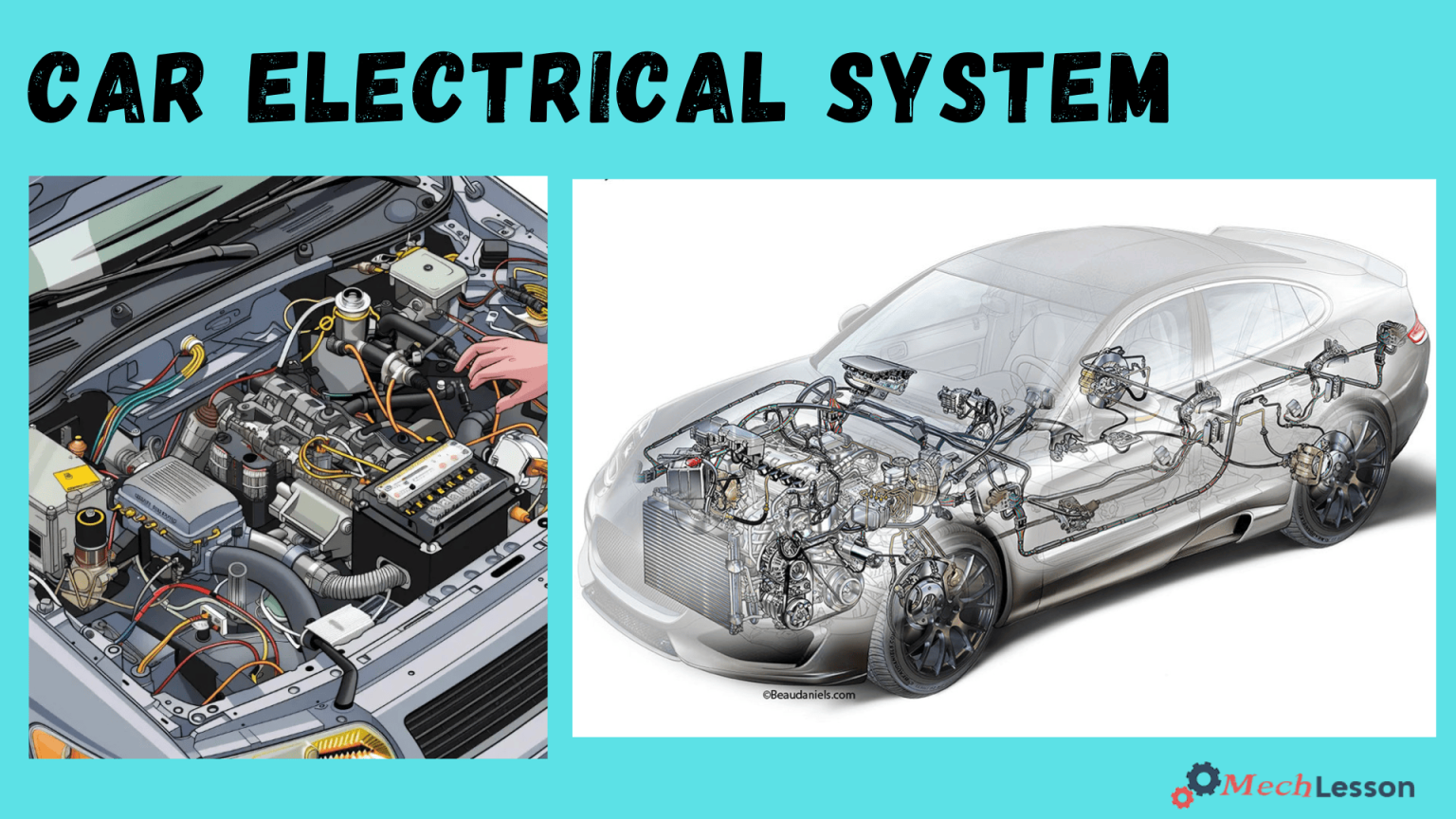
The primary function of a vehicle’s electrical system is to generate, store, and supply electrical current to the various electrical devices in a car. In automobiles, especially the modern ones, a variety of parts are electronic and operate electrically.
Well, charging systems are the basic electrical systems in a vehicle, which include an alternator, battery, and voltage regulator. These components are a source of power for other electrical components in the vehicle.
In this reading, we’ll explore what a car’s electrical system is, its application, function, diagram, parts, and how it works.
Let’s get started!
You should learn about Ignition System with this detailed guide!
What Is A Car Electrical System?
Car electrical systems are electrically controlled devices in a vehicle; they receive energy from the battery and return it to the battery through the earth.
The charging system comprises an alternator and battery. This battery is used to power the starter motor and helps the engine to start running while the alternator is used to charge the battery and other electrical components in the vehicle.
Apart from this charging, some vehicles are designed with magneto ignition, which generates power that powers a spark plug in the combustion chambers. It’s also used to power some electrical components, which helps to save battery power.
Although some ignition systems depend on the battery’s power. All electrical circuits in vehicles are opened and closed either by switches or relays, and fuses are used to prevent overloads.
Applications
The primary use of the electrical system is to power all electrical and electronic devices in a vehicle. Starting from the electrical motor, sensors, gauges, heating element, headlights, brake and trafficator lights, radio, television, air conditioning system, blowers, interior lights, refrigerator system, ignition system, etc.
All these components receive power from a battery and the battery is charged by the alternator. Note that when the engine is running, all electrical devices are powered with the alternator regulator’s power. This is because the alternator output is greater than the battery current when the engine is running.
Functions
- The primary function of a vehicle’s electrical system is to generate, store, and supply electrical current to the various electrical devices in a car.
- It operates all electrical parts and components of a vehicle.
- Again, the vehicle’s electrical systems help to keep devices in good working condition as they can achieve some features.
You should learn about Spark Plug with this detailed guide!
Diagram
Parts of Car Electrical System
The common parts that make up the electrical system in a car include
Battery
Your car’s electrical current comes primarily from the battery until you start the engine. This includes the current flowing to the fuel and ignition systems, which are in charge of producing the combustion required for your engine to run.
Starter
The battery is responsible for supplying the necessary energy to start your vehicle, but it is the starter’s job to turn the engine over. The starter motor receives just enough electricity from the battery.
After that, the starter turns the flywheel, which is responsible for turning the crankshaft and starting the pistons to move in the engine. It is critical to ensure the starter is functional because of this complex operation.
Alternator
The alternator keeps your battery charged and your electrical system operational while your engine is running. A malfunctioning alternator can start your car, but it will not be able to operate for very long. If you need to replace the alternator, your car’s electrical system will operate strangely, the battery will drain, and finally, your engine will not start.
You should also learn about car voltage regulator with this guide!
How A Car Electrical System Works
All electrical devices in a vehicle are designed with switches or relay systems, with the major source of energy (battery) all receiving power. So, immediately the engine starts the starter motor, which is an electrical device that receives power from the battery.
The combustion process keeps the engine running, and the alternator is used to charge the battery. This alternator’s voltage is less than the battery voltage when the engine is not running. This is because the current from the battery is used to power the vehicle loads and not the alternator.
Alternators are designed with diodes that prevent current from flowing into them. In a situation where the engine is running, the alternator’s current output is greater than the battery voltage. The current flows from the alternator to the electrical load in the vehicle and the battery to charge it up.
Conventionally, an alternator’s output voltage is above the battery voltage when the engine is working. Today, the vehicle’s electrical load is powered even though the engine is not running, as long as the battery is charged enough. A large amount of energy is needed to power the various electrical systems contained in a vehicle.
Car Electrical System Video
Learn about fuse with this detailed guide!
Conclusion
The car electrical system is the backbone of modern vehicle operation. From starting the engine to powering infotainment, lighting, sensors, and safety systems, the electrical system ensures every function runs smoothly.
Key components like the battery, alternator, and starter motor work in harmony with a complex wiring network and control modules. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to warning signs—such as dim lights or starting issues—can prevent bigger electrical failures and keep your vehicle running efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main parts of a car’s electrical system?
- Battery
- Alternator
- Starter motor
- Wiring and fuses
- ECU (Engine Control Unit)
- Sensors and switches
- Relays and control modules
What causes electrical problems in cars?
- Dead or weak battery
- Faulty alternator
- Blown fuses or relays
- Corroded or loose wiring connections
- Malfunctioning sensors or ECU
How do I know if my car has electrical issues?
- Dim or flickering headlights
- Clicking sound when starting
- Dashboard warning lights
- Power windows, radio, or AC not working
- Car won’t start or randomly stalls
Can a bad battery affect the entire electrical system?
Yes. A weak battery can cause voltage drops, leading to malfunctioning electronics, difficult starts, and alternator overload.
What does the alternator do in a car?
The alternator charges the battery and supplies power to the electrical system while the engine is running.
What is a blown fuse and how do I fix it?
A fuse protects electrical circuits by breaking the connection if there’s too much current. Replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage after identifying and fixing the root cause.
How often should I check my car’s electrical system?
It’s a good practice to inspect the electrical system every 6-12 months or during routine maintenance checks.
Can I fix car electrical issues myself?
Minor issues like replacing fuses or a dead battery can be DIY. However, for complex issues like ECU faults or wiring problems, professional diagnosis is recommended.