Hey gearheads, do you know that cooling systems and radiators are the secret behind your engine’s controlled temperature? Think of it this way, your car is always firing up due to the tiny explosion in the combustion chamber, and the truth is, too much uncontrolled heat could lead to a complete breakdown.
As an automotive technician, student, or a curious driver, with over a decade of experience, i have replaced and repaired more than 600 radiators. So, in this reading, we’ll explore what a car radiator is, its functions, parts, diagram, and how it works. We’ll also explore the symptoms, replacement cost, and maintenance of bad ones.
Let’s begin!
You should learn about Cooling System with this detailed guide!
What is a Radiator?
Radiators are essential in cooling internal combustion engines, such as piston-engined aircraft and railway locomotives. These radiators circulate engine coolant through the engine block and cylinder head, where it is heated and then lost to the atmosphere before returning to the engine.
A radiator is a component of the engine’s cooling system that disperses a mix of antifreeze and water. It releases some of the heat while taking in cool air before returning to the engine
The engine’s cooling system, including the radiator, plays a crucial role in keeping the engine cool. It disperses a mixture of antifreeze and water, releasing some heat while absorbing cool air before returning to the engine.
The radiator, along with the spur line, water pump, and fan clutch, plays different roles in assisting the radiator in keeping the engine cool. The spur line sends warm coolant to the heater core, while the water pump circulates the coolant throughout the engine.
The fan clutch brings more air into the radiator, lowering the temperature of the antifreeze and water mixture. The radiator is located under the hood and in front of the engine. The coolant reservoir is located next to it.
Functions
The primary purpose of a radiator is to radiate the engine’s coolant before returning back to the engine. It also serves as a reservoir that stores the coolant for the purpose of cooling.
Learn about Radiator Hose with this detailed guide!
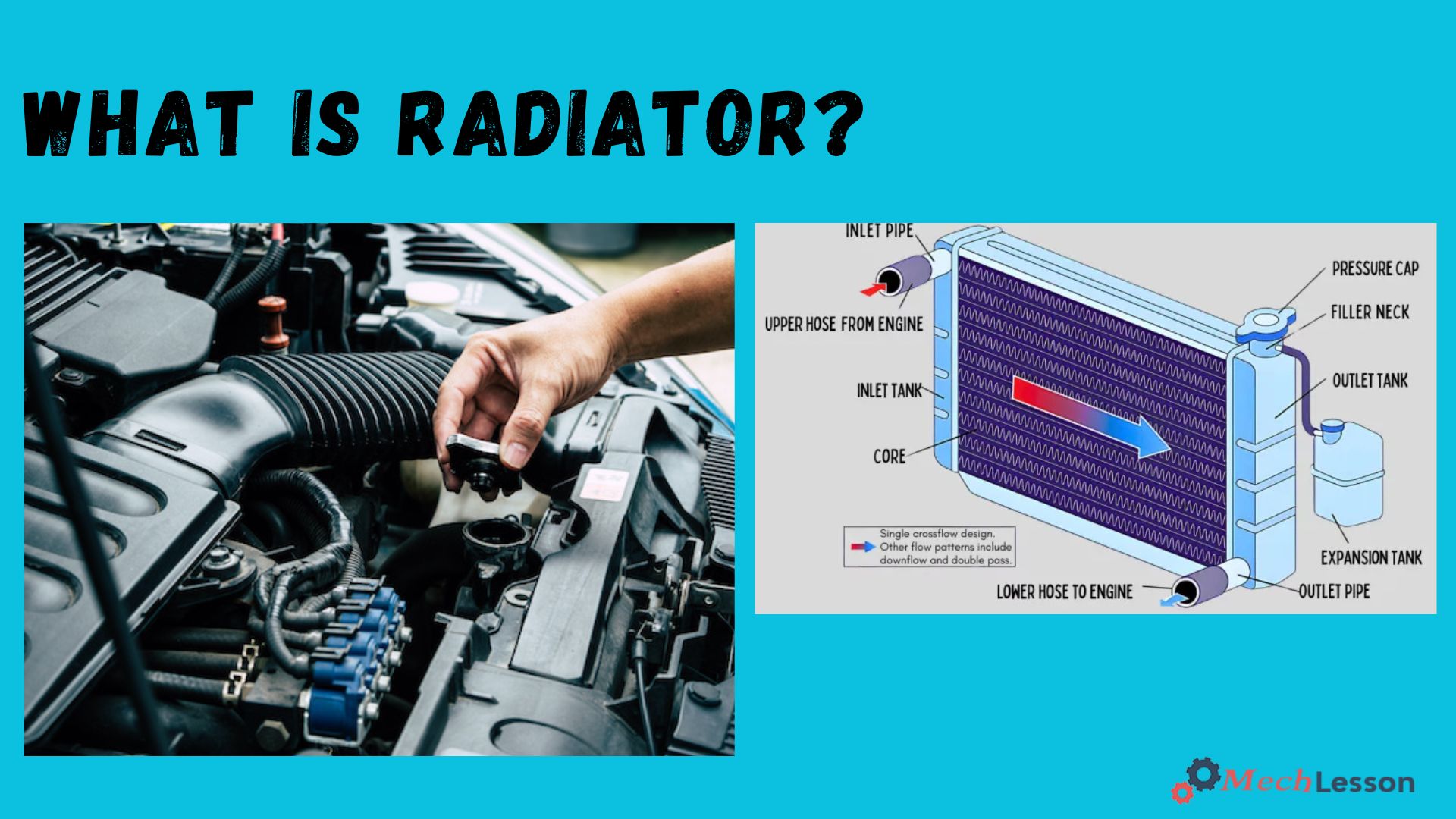
Radiator Parts and Diagram
The major parts of a car radiator are of 3 main parts, known as the outlet and inlet tanks, the core, and the pressure cap. Each of these 3 parts plays its own role within the radiator.
The radiator contains the core, pressure cap, inlet and outlet tanks, and radiator hoses. The core is the largest part of the radiator, containing the core where hot liquid releases heat and cools before being sent through the cooling process again.
The pressure cap seals the cooling system, preventing the coolant from boiling and making it more efficient.
The inlet and outlet tanks are located in the radiator head, where hot liquid flows from the engine through the inlet tank and cools before going out through the outlet tank and back into the engine.
Radiator hoses are essential for connecting the inlet and outlet tanks to the radiator and the engine. Other important cooling system parts include the water pump and thermostat, which regulate the engine’s temperature and push coolant through the system.
The water pump is operated by the engine drive belt, and gaskets and seals keep the coolant contained. Finally, coolant is crucial in preventing the engine from overheating and lubricating the various parts it contacts.
Diagram
You should learn the Step-by-Step Guide on How to Bleed A Radiator with this detailed guide!
How Does a Radiator Work?
In the working of a radiator, the radiator hose connects the engine to the radiator, allowing coolant to circulate through the tank. The inlet tank guides hot coolant from the engine to the radiator, cooling it down before returning it to the engine through the outlet tank.
The core cools the incoming coolant, and it circulates through a metal plate. The pressure cap, or radiator cap, secures and seals the cooling system, ensuring it stays pressurized until a certain point.
Without it, the coolant may overheat, causing an overspill, causing the radiator to work inefficiently. The pressure cap ensures the coolant stays pressurized and prevents overheating, ensuring the engine’s efficiency.
In automobiles and motorcycles with a liquid-cooled internal combustion engine, a radiator is connected to channels running through the engine and cylinder head, through which a liquid (coolant) is pumped by a coolant pump.
The liquid may be water but is more commonly a mixture of water and antifreeze in proportions appropriate to the climate. A typical automotive cooling system comprises galleries surrounding the combustion chambers.
A radiator with small tubes equipped with a honeycomb of fins, a centrifugal water pump to circulate the coolant, a thermostat to control temperature by varying the amount of coolant going to the radiator, and a fan to draw cool air through the radiator.
The combustion process produces a large amount of heat, which can cause detonation and failure of components outside the engine. To combat this effect, coolant is circulated through the engine, absorbing heat and transferring it to the radiator. You should watch the video below learn more about car radiator and cooling system:
You should also learn How to Flush a Car Radiator in Few Steps with this detailed giude!
Symptoms of Bad Radiator
The common symptoms of a car radiator include overheated engine, coolant leakage, discolored or sludgy coolant, lack of coolant, and damaged or clogged radiator fins
1. Overheated Engine
An overheated engine is a common sign of radiator failure. Your engine’s moving parts generate significant heat during operation that the radiator is designed to dissipate.
Insufficient cooling can lead to heat buildup, increasing friction, and potentially causing internal components to melt. If severe enough, this may necessitate a complete engine replacement.
2. Coolant Leaks
A leaking radiator often results in coolant pooling under your vehicle. This fluid may appear green, orange, or pink. While leaks might start small, they tend to worsen over time as the radiator deteriorates.
In some vehicles, underbody panels might conceal the leaks, making them harder to spot.
3. Discolored or Sludgy Coolant
Coolant that appears rusty or sludgy indicates contamination in the cooling system, often caused by a failing radiator. Contaminants like rust, oil, or transmission fluid can mix with clean coolant, altering its color and reducing its effectiveness.
4. Low Coolant Levels
If the radiator leaks, coolant levels will drop, impairing its ability to cool the engine. Insufficient coolant can lead to overheating and, if ignored, severe engine damage.
5. Damaged or Clogged Radiator Fins
Radiator fins, the thin metal blades on the sides and back of the radiator, help dissipate heat by increasing the surface area for airflow. These fins can become damaged over time from road debris or regular wear, reducing cooling efficiency and causing the engine to overheat.
Learn about Radiator Pressure Cap with this detailed guide!
Radiator Replacement Cost
The cost and complexity of replacing a radiator can vary significantly depending on factors such as the make and model of your vehicle, its age, the cost of replacement parts (including antifreeze), and whether the work is done by a professional or as a DIY project.
If you decide to tackle the job yourself, an invaluable resource is YouTube. The platform offers a wealth of instructional videos covering a wide range of repairs for vehicles, appliances, and more.
I replaced the radiator on my 2001 Dodge Dakota. Thanks to online discounts from retailers like Advance Auto Parts, I was able to purchase the radiator and the required antifreeze for under $200.
By doing the work myself, I avoided the $500–$600 expense of having it done at a shop or dealership.
Repair shops often charge $300–$400 or more for parts, plus labor costs at around $100 per hour, with a typical repair time of 2–4 hours. After researching dealer costs, I was motivated to take on the repair myself, guided by YouTube tutorials.
Fortunately, I had the necessary tools, a driveway to work in, and an alternate vehicle to make trips to the parts store. While DIY repairs can take considerably longer than those performed by trained mechanics, the experience offers a sense of accomplishment and self-reliance.
However, DIY projects can come with challenges. YouTube videos often condense the process, omitting details about small issues that can turn into significant hurdles. For me, the main challenge was a hose clamp located in a nearly inaccessible spot, which added frustration to the repair.
Despite such obstacles, completing the repair myself not only saved money but also provided the satisfaction of knowing I could handle such tasks independently.
How to Maintain Your Car Radiator
Maintaining your vehicle’s radiator requires regular checks and care. It’s crucial to avoid opening the radiator cap or heater hose connector cap when the engine is running to prevent burns and injuries.
Turn off the engine, wait for it to cool, and then slowly open the cap with a thick cloth. When refilling the coolant during winter, add antifreeze at a 5:5 ratio to prevent freezing and corrosion of the radiator grille or related parts.
Clear the radiator at least once every 30,000 km or 12 months to prevent harmful particles or rust erosion. Check the radiator hoses for cracks or leaks during oil changes.
If electrical work was done on your vehicle, check for stray currents to prevent corrosion and radiator failure. These tips can help ensure your vehicle’s radiator is in good working order.
You should also learn about Transmission Cooler with this detailed guide!
Conclusion
The car radiator is a vital part of the engine’s cooling system, preventing the engine from overheating by dissipating excess heat. It works by circulating coolant through the engine and back to the radiator, where heat is transferred to the air.
Regular maintenance, such as checking coolant levels, cleaning debris, and flushing the system, is essential for keeping the radiator—and your engine—running efficiently. A well-functioning radiator ensures better engine performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does a car radiator do?
A radiator removes heat from the engine coolant and releases it into the air, helping to regulate engine temperature and prevent overheating.
What are the signs of a bad radiator?
Common signs include
- Engine overheating
- Coolant leaks under the car
- Low coolant levels
- Sludge or discoloration in the coolant
- Steam from the hood
How often should I flush my radiator?
Most manufacturers recommend a radiator flush every 30,000 to 60,000 miles, or every 2-3 years, depending on driving conditions.
Can I drive with a leaking radiator?
It’s not advisable. A leaking radiator can lead to coolant loss and engine overheating, causing severe damage if not addressed promptly.
What causes radiator failure?
Common causes include
- Corrosion or rust inside the radiator
- Cracks or physical damage
- Clogged coolant passages
- Faulty radiator cap
- Poor coolant maintenance
How much does it cost to replace a car radiator?
The cost varies by vehicle but typically ranges between $300 and $900, including parts and labor.
What type of coolant should I use?
Always use the coolant type specified in your vehicle’s owner’s manual—either green, orange, pink, or blue coolant, depending on manufacturer requirements.
Can a radiator cap cause overheating?
Yes. A faulty cap can’t maintain proper pressure, leading to coolant boil-over and engine overheating.
Can you drive a car with a bad radiator?
Driving a car with a busted radiator is not advisable. The radiator plays a crucial role in the vehicle’s cooling system, helping to regulate the engine’s temperature.
If the radiator is damaged or leaking, the engine can overheat, which can lead to severe damage, including warped cylinder heads or a blown head gasket.
How do I know my radiator is bad?
The common symptoms of a car radiator include overheated engine, coolant leakage, discolored or sludgy coolant, lack of coolant, and damaged or clogged radiator fins
How much does a radiator cost for a car?
If you need to replace your radiator, you can expect to spend between $700 and $1,000. You can save on labor costs (about $300) by replacing the radiator yourself if you’re experienced with auto DIY jobs. Keep in mind this is a big undertaking that will likely take all day.
Is a car radiator repairable?
If you think you have a problematic radiator, you’re left with two options. You could either replace it or repair it. Many automotive shops may try to push you for a replacement, but the decision isn’t always that simple.
Why is my car overheating?
The source of the issue could include a cooling system leak, bad radiator fan, faulty water pump, low engine oil level, or thermostat failure.
Regardless of the problem’s source, an overheating engine isn’t something you want to let linger. Your engine could sustain serious, if not permanent, damage.

