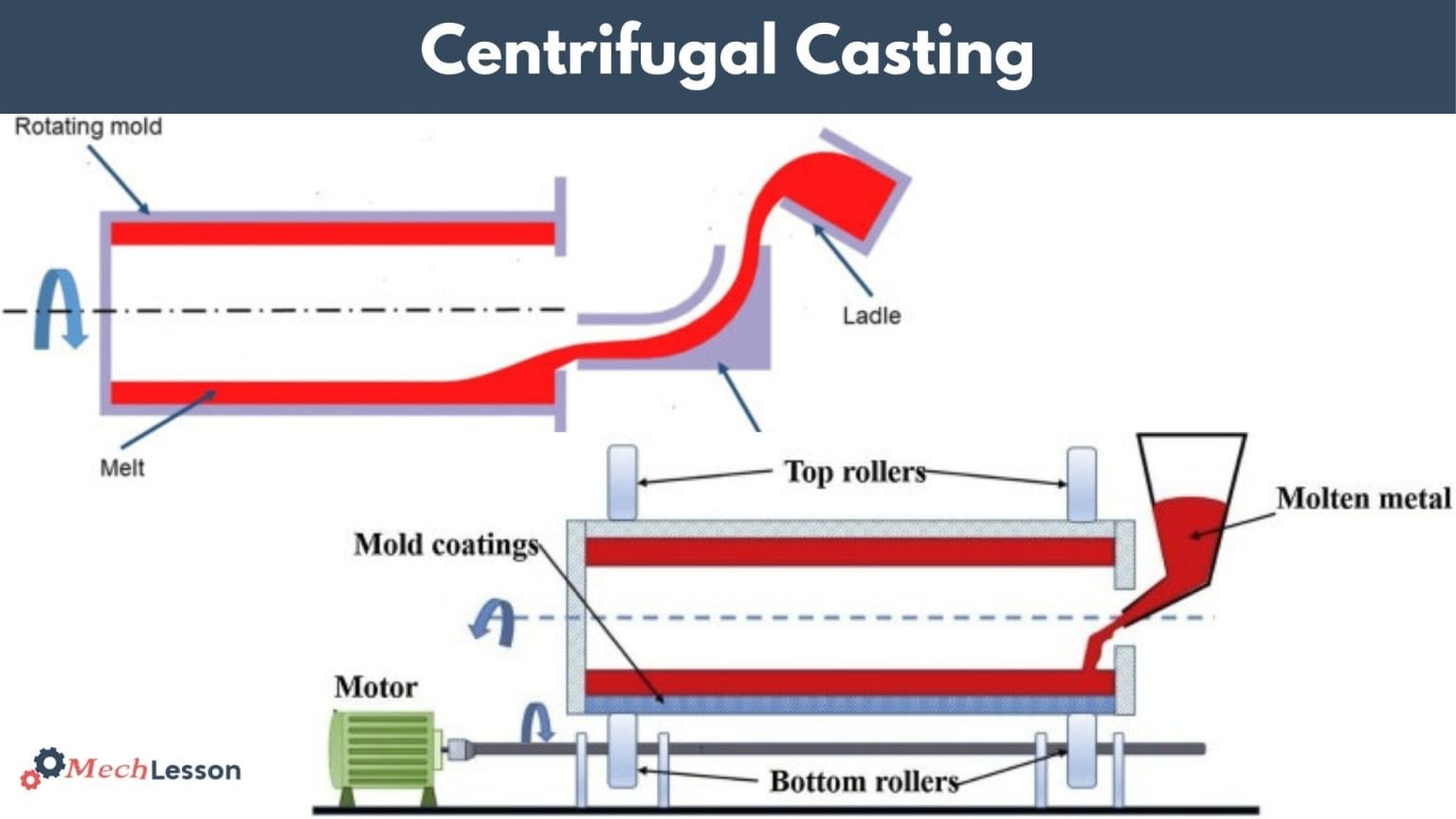
Centrifugal casting is a metal casting process carried out vertically or horizontally in the foundry industry. They are used to produce hollow parts like pipes and other parts with thin-walled cylinders.
Centrifugal casting is used to cast materials like metal, glass, and concrete, although high quality is attainable by control of metallurgy and crystal structure.
The process begins with molten metal being poured into a preheated, spinning die, which is done in either a vertical or horizontal axis depending on the configuration of the desired part.
Centrifugal casting allows mass production of symmetrical products at lower costs. The casting process eliminates defects such as blowholes, shrinkage cavities, and gas pockets. Also, impurities are easily removed because they are all collected at the center of the mold.
Well, in this reading, we’ll explore what centrifugal casting is, its diagram, types, and how it works. We’ll also explore its advantages and disadvantages of centrifugal casting.
Let’s Get Started!
Related: The Four Common Types of Metal Casting
What is Centrifugal Casting?
Centrifugal casting is a metal casting process in which molten metal is poured into a continuously rotating mold and thrown outward from the center with a centrifugal force. It is designed to vertically or horizontally rotate, depending on the type of casting.
The horizontal type of centrifugal casting is implied when producing thin cylinder parts. While the vertically mounted machine is used in producing smaller automotive parts.
In the process, molten metal is poured into a preheated, spinning die, oriented either on a horizontal or vertical axis. The layout is determined by the configuration of the desired part.
We often use centrifugal casting, also known as rotocasting, to cast thin-walled cylinders and materials like metals, glass, and concrete. This kind of casting assures high-quality casting due to controlled metallurgy and crystal structure.
The mold is spun, and the molten metal is poured into it. This centrifugal force acts to distribute the molten metal in the mold at a pressure 100 times the force of gravity. The combination of applied pressure and controlled solidification achieves superior quality.
Applications
Centrifugal casting offers high material soundness and is the metal casting process of choice for jet engine compressor cases, petrochemical furnace tubes, many military and defense components, and other applications requiring high reliability.
Centrifugal casting is a process that delivers components of high material soundness. As a result, it is the technology of choice for applications like jet engine compressor cases, hydro wear rings, many military products, and other high-reliability applications.
It has also proven to be a cost-effective means of providing complex shapes with reduced machining requirements and lower manufacturing costs as compared to forgings and fabrications.
Manufacturers primarily use centrifugal casting to create rotationally symmetric stock materials in their sizes for further machining. Centrifugal casting should be performed when the object requires:
- Symmetrical shapes
- Sand casting material properties are inadequate
- Centerline shrink is an issue using other casting processes
- Limited I.D. features
- Large parts of up to 135,000 lbs. (61,235 kg) or more are needed
- Net-shaping: more precise O.D. detail and lower machining costs are desired
Related: What is Sand Casting, its Applications & How it Works?
Diagram of Centrifugal Casting

Types of Centrifugal Casting
Different kinds of centrifugal casting are true centrifugal casting, semi-centrifugal casting, and centrifuge casting.
True centrifugal casting:
True centrifugal casting is a casting technique employed when producing a part with a symmetrical axis with a uniform diameter. It contains a cylindrical mold that rotates about its axis at a specific speed.
Molten metal is poured through the center, which is thrown to the wall of the mold. Due to the centrifugal force applied to it. The casting solidifies and emerges from the mold. Thickness in this type of casting is determined by the amount of poured liquid metal.
This type of centrifugal casting has a directional solidification as its cooling starts from outside to inside.
The central core is not required, just as in semi-centrifugal casting. It also has a fast production rate because casting can easily be removed when solidified. This type of casting offers very high quality, sometimes 100%.
However, true centrifugal casting required a very large investment, and skilled labor must be employed. True centrifugal casting is used in the manufacturing of bearings for machines, pipes, liners for IC engines, rings, and other annular castings.
Related: What is Evaporative Pattern Casting (EPC)? Diagram & How it Works
Semi-centrifugal casting:
Semi-centrifugal casting is similar to true centrifugal casting, but they have a slight difference. It is used in casting items like wheels, sheaves, blanks, etc. A vertically mounted machine performs semi-centrifugal casting.
Rotating in a vertical or concentric axis at a low spinning speed. The speed ranges between 180 and 200 rpm.
Gateway is needed to have directional solidification. In this type of centrifugal casting, more than one item can be produced at a time. Due to the stacking of multiple numbers of molds.
Centrifuge casting
Centrifuge casting is another type of casting method used in casting unsymmetrical castings in groups. It is carried out in a group in order to produce an equal part in the whole casting. The rotation axes of the mold doesn’t coincide with each other in centrifugal casting.
It helps to induce pressure in the mold as casting rotates at the center. Centrifugal forces feed molten metal into the mold cavities.
Centrifuge casting provides superior quality, achieves high production rates quickly, and is cost-effective due to its reduced cleaning and fettling expenses.
How Does Centrifugal Casting Work?
The working principle of centrifugal casting is carried out by pouring molten metal into a spinning mold preheated to some certain temperature. Mold types can either be vertical or horizontal, depending on the type of item to be produced.
The mold rotates at a certain speed. An electric motor controls the rotation of the mold, causing the molten metal to revolve around its central axis.
The centrifugal casting process involves shaping and feeding molten metal into a fast-rotating mold, utilizing process parameters such as rotational speed, feed speed, mold preheat, and coating.
A rotating plate receives the molten fuel alloy, and the melt flow rotates in a horizontal direction. Centrifugal force aligns and rotates the molds on the distributor’s edge, injecting the melt into them.
At this stage, the molten metal pours into the walls of the mold. Molten metal spread uniformly to the walls, creating cylindrical shapes. There is no such thing as a pouring defect in centrifugal casting. We pour more molten metal until we achieve the required size and shape.
Related: What is Centrifugal Casting? Its Diagram & How it Works
Advantages of Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting has several advantages over other metal casting processes. it allows mass production of symmetrical products at lower costs.
It offers high production rates because it does not rely on gates and risers. Unlike sand casting, where gates and risers must be employed for proper flow of the molten metal.
One of the biggest advantages of centrifugal casting is that it helps to get rid of defects such as blowholes, shrinkage cavities, and gas pockets. Due to the collection of impurities at the center of the mold.
Centrifugal casting removes impurities more easily than any other manufacturing process. it also helps economically in terms of low capital, which allows enough flexibility to produce various sizes and shapes of a part.
It offers good advantages as it saves time and energy. It requires a lower temperature of molten metal. finally, It also provides less dense metal with mechanical soundness.
Disadvantages
Below are the applications of centrifugal casting:
- Incorrect diameter in the inner part of the casting
- High investment is a need in tools and machinery
- More skilled laborers are needed for the process
- Not all type of metal or alloys are compatible with the process
- The process can produce few shapes.
Related: What is Investment Casting? Diagram, & How it Works