The term friction welding is quite straightforward: using friction to obtain a weld. Asperities are an important phrase, as it is a smooth surface containing many microscopic projections.
When we move these smooth surfaces relative to one another, they interact. We use this basic principle to create friction welds.
Friction welding is a solid-state metal joining process that produces high-integrity, full-contact joints. This effect is achieved by rotating one workpiece relative to another under a compressive axial force.
The friction generated between the two surfaces produces intense heat, resulting in the plasticity of the material.
Well, in this reading, we’ll explore what friction welding is, its applications, diagrams, techniques, and how it works. We’ll also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of friction welding.
Let’s Get Started!
Related: What is Arc Stud Welding? Diagram & How it Works
What is Friction Welding?
Similar to forge welding, friction welding is a solid-state welding process that generates heat through mechanical friction between the workpieces in relative motion with one another. The addition of literal forces helps obtain the weld.
Friction welding is used with metals and thermoplastics in a wide variety of aviation and automotive applications.
The friction welding process is different from fusion welding but more like forge welding because no melting occurs. The thermomechanical treatment at the contact surface produces the weld.
As earlier mentioned, in the work of friction welding, heat is generated at the melting part of the workpiece so that it can fuse (weld) when external pressure is applied. The friction takes place between the parts until it turns plastic, normally at 900–1300 degrees centigrade of steel.
At this point, the workpiece receives a uniformly increasing pressure force, resulting in the formation of a permanent joint. Generating friction is the force-resisting motion between two or more interacting surfaces.
The interaction of these asperities through elastic and plastic yielding generates heat. Friction welding utilizes this event for joining applications.
Applications of Friction Welding
The applications of friction welding are vast in today’s world of manufacturing. This is because friction is used in welding tubes and shafts. The aerospace, marine, oil, and automobile industries also widely use friction to weld machine parts.
It is also applicable to components like gears, axle tubes, drivelines, valves, etc.
Applications of friction welding are also used to join hydraulic piston rods, truck roller bushes, etc. It is used to weld drill bits, connecting rods, gear levers, etc. Finally, friction welding processes are widely used in the electrical industry for welding copper and aluminum equipment.
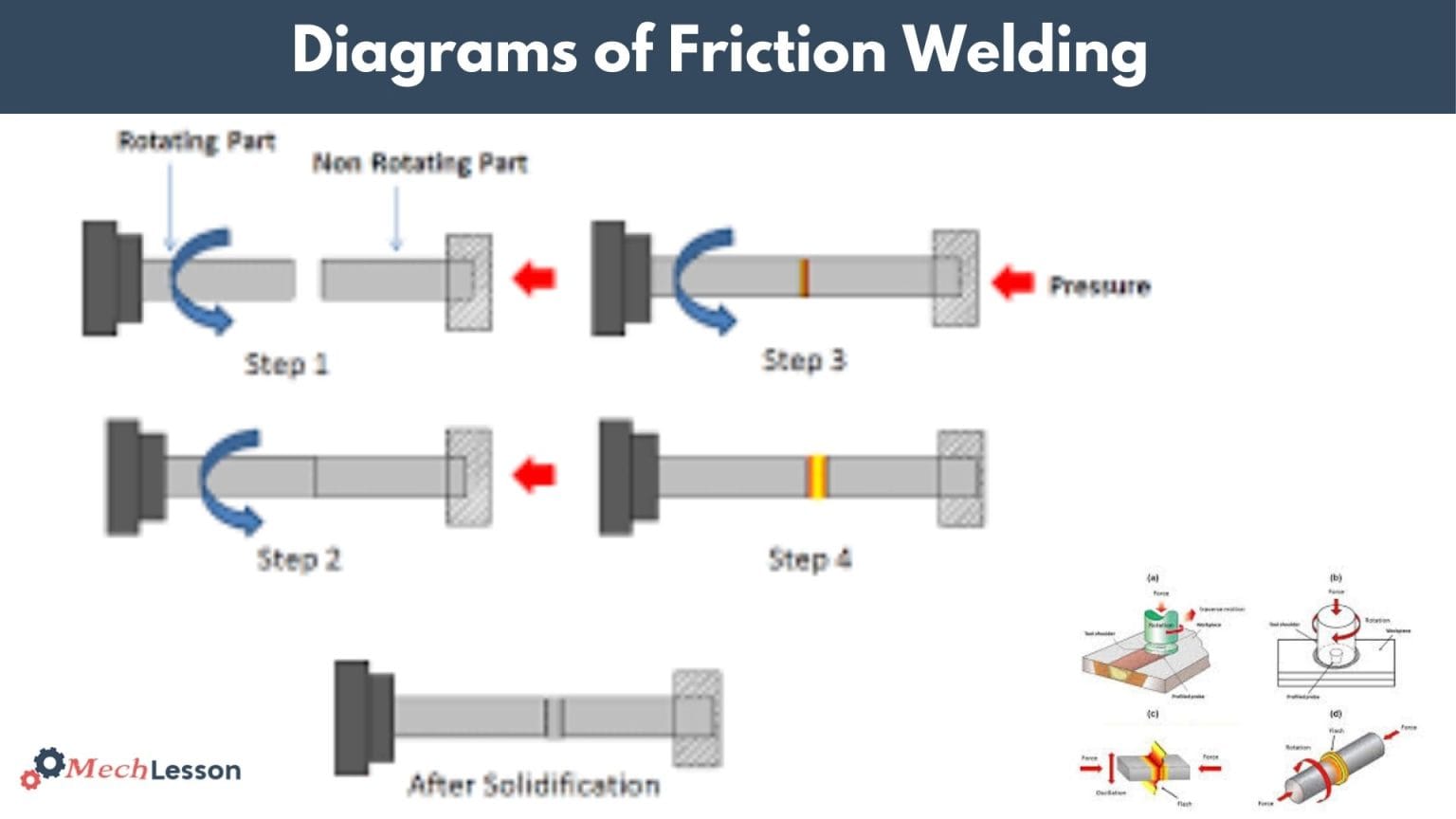
Diagram

Related: MIG vs Stick Welding: Choosing the Best Method for Your Needs
What are the Techniques of Friction Welding?
The techniques of friction welding include rotary, linear, friction stir, and friction surfacing.
Rotary friction welding
Rotary friction welding (RFW) is one of the most common methods of friction welding. The process rotates one part of the material and presses it down.
Friction work causes the material to heat up, creating a permanent weld. The video below illustrates this welding method.
Linear friction welding
Linear friction welding (LFW) is achieved by moving one of the parts to be welded in a linear reciprocating motion across the face of a stationary part.
Friction stir welding
In this method of friction welding, a non-consumable tool is used to join the two facing workpieces. This process is solid-state welding and does not melt the workpiece material. The friction between the rotating tool and the material generates heat.
Friction surfacing
Friction surfacing is a method derived from friction welding where a coating material is applied to a substrate. Mechtrode is the name of the rod that contains the coating material. The rod rotates under pressure, creating a plasticized layer at the interface with the substrate.
How Does Friction Welding Work?
Prepare the workpieces’ surfaces before performing any friction welding operations. One of the workpieces is mounted on a driven rotor and the other remains in a stationary position.
The rotor rotates the workpiece against the other to create friction between them. It rotates at a high speed and a little pressure force is applied toward the stationary workpiece, which is done to remove dirt from the workpiece surface.
The rotor stopped when the temperature reached its limit.
At this point, the stationary workpiece, already in plastic form, undergoes a very high pressure force. We continuously apply pressure until we form the entire weld. Now, let’s explain the working of friction welding in stages:
In the first stage, heat is generated between the workpiece surface by sliding friction and the torque reaches its maximum value. In the second stage, mechanical dissipation in the plasticized material generates heat, causing the softened material to flow radially outwards.
In the third stage, a steady-state situation is attained and the torque, rate of axial shortening and temperature distribution are constant. The fourth stage terminates the rotation between the workpieces. And stage five is where upsets occur.
In friction welding, before joining or forming an item into a usable product, there must be an industrial standard for various applications.
We must consider other parameters in the friction welding method, such as rotational speed, friction time, friction pressure, forging time, and forging pressure.
Related: What Is Orbital Welding? Its Diagram, Types, And Application
Advantages of Friction Welding
Now you can see that this type of welding applies to different fields and can be used to weld different items. This is because it helps in reducing grain growth in engineering materials such as high-strength heat-treatment steel. Additionally, it eliminates the need for melting.
Dissimilar materials can be joined In this type of welding. This type of welding finds its application in aerospace, particularly in the joining of lightweight materials like aluminum with high strength.
Another advantage is that the weld surface is cleaned due to the motion between the materials that are joined and full strength is obtained in the joint with no additional weight on the workpiece.
Thermoplastic materials also undergo friction welding. It uses very low heat and pressure on the materials. Friction welding enables the joining of metals to plastics by machining the metal interface. The following are some additional advantages of friction welding:
- It is an environmentally friendly process. That is, the welding operation can be performed anywhere as it generates no smoke, flame, light, etc.
- No filler material is required.
- The welding process is fast.
- It is easily automated.
Disadvantages
The following are the limitations of friction welding:
- Friction welding equipment is of high cost.
- Unforgeable materials will not weld. finally,
- One of the greatest disadvantages of friction welding is that it has limitations to workpiece dimensions. Friction welding restricts round bars with similar cross-sections, limits joint designs, and necessitates the fixing of workpieces.