In the fabrication process of welding, two or more parts are fused by applying pressure, heat, or both, and when the parts cool, a join is created.
Metals and thermoplastics are the common materials for welding, although wood is also an option. A weldment is the term used to describe the finished welded junction.
Well, in this reading, we’ll explore what welding is, its applications, its diagram, its types, and how it works. We’ll also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of welding.
Let’s Get Started!
Related: Welding Terms And Meaning You Should Know
What is Welding?
Welding is a crucial fabrication process that uses high temperatures to join metals, forming a strong link between the base metal and filler material. This process originated from the search for developing iron into useful shapes, with the first result being welded blades.
The filler material, a pool of molten material, aids in the formation of a strong link between the base metal.
After welding, the shielding process protects both the base and filler components from oxidation. Welding uses various energies, including electron beams, electric arcs, lasers, and friction, to ensure the successful completion of the process.
Homogenous welds are formed when consumables are similar in composition to the base material, while heterogeneous welds are formed when filler with different properties is used. The completed welded joint is referred to as a weldment.
Applications of Welding
Welding is a crucial process in the fabrication of metal structures and components for various applications, from construction projects to automotive repair. Welding is essential for joining two pieces of metal together, creating solid structures like bridges and buildings.
It is also used in automotive repair and maintenance, where welders repair car body panels and exhaust systems.
Welders are also employed in industrial manufacturing, where they fabricate parts from raw materials like steel or aluminum alloys and assemble them into functioning machines.
Welding creates structures like bridges and buildings, as well as objects like cars and ships. It can also be used to repair damaged metal objects, such as cracked pipes or bent structures.
Welding can also be used to create art, such as statues or functional objects like furniture or jewelry. Welding is also used to build cars, as it creates strong, lightweight structures that can withstand high speeds and forces.
In manufacturing, welding is used to assemble products like bicycles, motorcycles, and appliances, often joining together small components that make up larger products.
With the right training and experience, anyone can become a skilled welder, providing quality workmanship in any industry they specialize in. With the right training and experience, anyone can become a skilled welder who can provide quality workmanship in any industry.
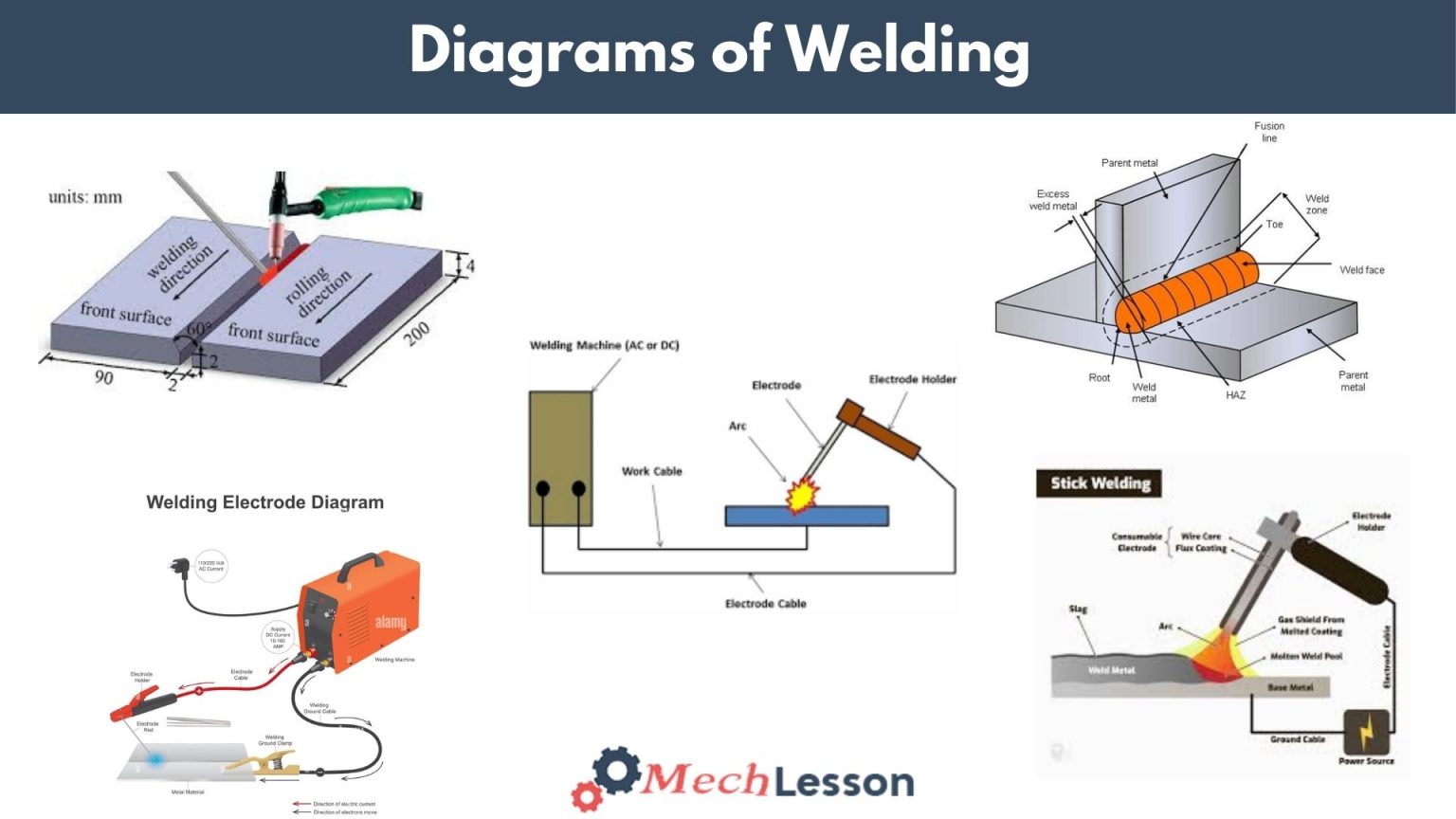
Diagram

Related: What is Fricton Stir Welding? Its Diagram & How it works
What are the Types of Welding?
The list below are the types of welding:
- Gas-tungsten arc welding (GTAW/TIG)
- Gas-metal arc welding (MIG/GMAW)
- Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW)
- Plasma arc welding (PAW)
- Stick welding
- Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW)
- Gas welding
- Submerged arc welding (SAW)
- Electron-beam welding (EBW)
- Laser beam welding (LBW)
How Does Welding Work?
Welding is a process that connects two materials without a separate binder material, unlike brazing and soldering. There are two main types of welding: arc welding and torch welding.
Welding is a fabrication process that uses heat, pressure, or both to fuse two or more parts together, forming a joint as the parts cool. This process is commonly used on metals, thermoplastics, and wood.
The process joins base materials, then adds filler or consumable materials to form the joint.
Arc welding uses an electrical arc to melt work materials and filler material, while torch welding uses an oxyacetylene torch to melt the working material and welding rod.
The welder must feed the filler into the welding joint using small, steady, back-and-forth motions to create a distinctive appearance.
Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), metal inert gas welding (MIG welding), and gas tungsten arc welding (TIG welding) are all examples of arc welding. Stick welding is inexpensive and easy to learn but slower and less versatile.
TIG welding is difficult to learn and requires an elaborate welding rig but produces high-quality welds and can weld materials that other methods cannot. On the other hand, torch welding is less common in industrial settings but still finds use in maintenance, repair work, and sculptures.
Related: What is Tack Welding? Its Diagram and Benefits
Advantages
Below are the benefits of welding in their various applications:
- Welding creates a stable, long-lasting, and permanent joint.
- It’s an easy process with a great result.
- By adding filler materials, the method produces a stronger weld than the base material.
- You can perform it anywhere.
- It’s a cheap and simple procedure.
- Many different industries, including the building and automotive sectors, use it.
- Strong welds have the potential to surpass the strength of base metal.
- The ability to join a variety of materials is impressive.
- It offers a simple design and an attractive look.
- You can carry them out in any direction or shape.
- Automation is a possibility.
- The company offers a rigid joint service.
Disadvantages
Below are the negative aspects of welding:
- When carried out in accordance with safety and security regulations, it is dangerous.
- The joined material is tough to disassemble using welding.
- Need an electric supply and requires a skilled labor
- Uneven heating and cooling during the welding process might cause members to become distorted.
- Since welds are permanent joints, we must cut them to separate them.
- High expense for initial investment
Related: What is Undercut in welding? Causes, Effects & Prevention